DNA replication
advertisement

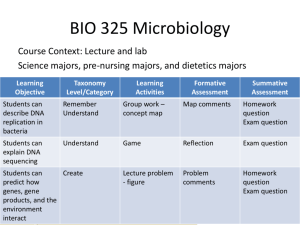
DNA Structure, Function and Replication B5 – Describe DNA replication: • Review DNA structure and function • Describe the purpose of DNA replication • Identify the site of DNA replication in a cell • Describe the three steps in DNA replication • Explain why DNA replication in called “semiconservative” Comic by Kate Beaton, http://harkavagrant.com/ Double helix Backbone is sugar and phosphate joined by covalent bonds Rungs are complementary base pairs joined by hydrogen bonds (purine-pyrimidine: A-T, G-C) Note that the nucleotides in the two strands are laid out in opposite directions (antiparallel) • • • • DNA carries the genetic code Replicates to pass on genetic information Instructions for synthesis of proteins Proteins are required to build an organism and catalyze all of its biochemical reactions (therefore controlling all of the functions of the cell and organism) Questions for discussion: • What is meant by the term DNA replication? • Why is DNA replication necessary? • Where does it take place? • When does it take place? • What is the function of the genetic code? • • • DNA must be replicated in every cell before the cell divides This is necessary so that each new cell has a complete copy of the genetic code The method of DNA replication is known as “semi-conservative” (what do you think this means?) The double-stranded DNA molecule “unzips” when the enzyme DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases Each strand acts as a template to make new double helix New complementary nucleotides attach to the exposed bases Catalyzed by the enzyme DNA polymerase Adjacent phosphate and sugar groups are attached by another DNA polymerase We now have two DNA molecules, each identical to the original This is called semi-conservative replication because half of each DNA strand is “old” and the other half is “new”