GL ORIENTATION
advertisement

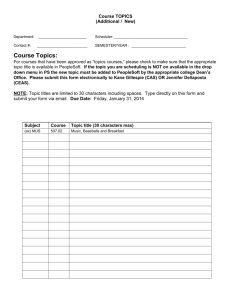
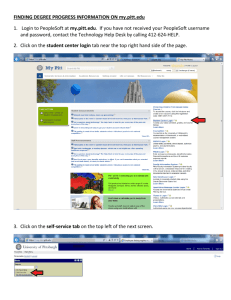
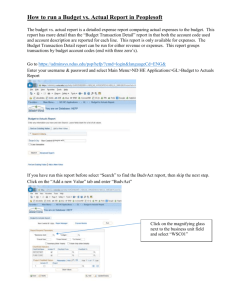
WELCOME! To the Orientation Class for PeopleSoft General Ledger UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON SYSTEM-WIDE PeopleSoft Concepts & Environment • • • • Toolbars Menus Menu groups Panels • • • • Panel Groups Control Tables Transaction tables Effective dating Toolbars • Toolbars contain buttons which are used to invoke common tasks. • If a button is grayed out on the toolbar, the associated function is unavailable. • Toolbar functions can also be accessed from a menu. Toolbar Example Menus • Menus are the traditional method of navigation in Windows applications. • Destinations in PeopleSoft are achieved through selecting commands on the menu bar. • The available menu items vary depending on the security class to which your Operator ID is assigned. Menu Groups Menus with similar functionality are grouped together for ease of access. Menu Group Panels • Panels are commonly called forms or screens in other databases. • Panels present information from the database in a user-friendly display. • Panels provide the means to update the database. Panel Groups • Panels grouped by a common topic are referred to as panel groups. • Panel groups are created to organize data entry procedures by subject or business process. • The individual panels in a panel group share a common topic, they are processed together. Control Tables • Most control tables are loaded with values by analysts during setup and implementation and cannot be updated by users. • The values are used to define accounting parameters and to verify fields entered by users from panels. • Also called lookup tables as most drop-down list boxes reference a control table. Sample Control Tables • ChartFields, such as – Fund – Department • Calendars Transaction Tables • Used in PeopleSoft to store transaction data. • Directly related to the panels used to enter data. Sample Transaction Tables • • • • Journal Header Journal Line Ledger Budget Ledger Effective Dating • A key feature of PeopleSoft. • Effective dating maintains a complete chronological history of all of your data. • 3 categories of effective dates: History, Current and Future. • Allows for future dating of transactions. Example of Effective Dating Row No. 1 2 3 4 Department H0166 H0167 H0166 H0166 Manager Effective Date 555-55-5555 444-44-4444 666-66-6666 777-77-7777 Sep-01-1999 Sep-01-1999 Nov-01-1999 Dec-01-1999 Row numbers that are… Calendar Date History Current Future Sep-05-1999 Nov-02-1999 Jan-01-2000 -1 1, 3 1, 2 2, 3 2, 4 3, 4 4 -- Overview of Elements of the PeopleSoft General Ledger • TableSet, SetID and TableSet Sharing • Ledgers • Trees TableSet, SetID and TableSet Sharing • TableSet refers to the series of tables that control the general ledger. • SetID is the label that identifies the TableSet used for a Business Unit. • TableSet Sharing allows multiple Business Units to share a common table, such as Account or Fund. Ledgers • Ledgers store the posted net activity for a set of ChartField values by accounting period and fiscal year. • A ledger is a set of posted balances that represent a set of books for a Business Unit. • Can store actuals, budgets, statistical or other types of data. • They are primarily maintained through journal entries. Ledgers • The various ledger types include: – Actuals – Budget – Statistical • Detailed transactions are stored in the actuals ledger. Trees • PeopleSoft uses Trees to organize data. • A Tree is a summarization of rules, reporting hierarchies and roll-up structures. Trees provide a graphical organization of fields. Chartfield Definition • PeopleSoft General Ledger uses chartfields to identify journal entries. • Each chartfield contains information that defines a transaction in terms of responsible party, fund source and function of entity. PeopleSoft E&G ChartFields • • • • • Business Unit Fund Code Department Account Program • • • • Project ID Class Budget Period Statistics Code Fund Related Values • Fund Code • Grant Related Values – – – – Sponsor Type Funding Agency CFDA Code Sponsor ID Organizational Related Values • Business Unit • Department Code Activity Related Values • Program Code • Project ID Cost Center Definition • A combination of Chartfields constitutes a cost center. It defines whose money it is, what type of money it is, and what type of activity it is being spent to support. Cost Center Composition • A Cost Center will include: – – – – Business Unit Department Fund Code Program • And, for projects: – Project ID Non-Project/Grant Cost Center Example 00730-H0066-2063-A0838-NA where…. 00730 = Business Unit H0066 = Department 2063 = Fund Code A0838 = Program NA=Non project/grant Project/Grant Cost Center Example 00730-H0124-1026-B0001-G000052 where…. 00730 = Business Unit H0124 = Department 1026 = Fund Code B0001 = Program G000052 = Project ID Review of ChartFields • • • • • Business Unit Fund Code Department Account Program • • • • Project ID Class Budget Period Statistics Code Understanding the Business Unit • Organizations are divided into entities for operational or reporting purposes. • PeopleSoft defines these entities as Business Units. • Each UHS component is defined as a Business Unit. UHS Business Units • • • • • • 00730 - University of Houston 00759 - UH Clear Lake 00784 - UH Downtown 00765 - UH Victoria 00783 - UH System Administration 00797 - UH System Consolidated Fund Code • Each fund is a balanced ledger. • Funds are coded by source or type of monies they represent. • Defined through a four digit Fund Code. UHS Fund Codes • • • • 1XXX = State 2XXX = Designated 3XXX = Auxiliary 4XXX = Restricted • • • • 5XXX = Grants 6XXX = Endow. & Loans 7XXX = Plant 9XXX = Agency Department Code • Each UHS department is assigned a unique five digit code. – Leading alpha character for campus. – Four numeric characters assigned sequentially. • Hierarchy is assigned through department trees. UHS Department Codes • • • • • HXXXX = UH departments CXXXX = UHCL departments DXXXX = UHD departments VXXXX = UHV departments SXXXX = UHSA departments Program Code • Five digits are used to uniquely identify a nonproject cost center either within or across departments • First digit tells the purpose of the program by expenditure function – Expenditure function is related to required NACUBO reporting UHS Program Codes • • • • • • • • • AXXXX = Instructional programs BXXXX = Research programs CXXXX = Public Service DXXXX = Academic Support EXXXX = Student Services FXXXX = Institutional Support GXXXX = Plant HXXXX = Scholarship IXXXX = Auxiliary Project ID • Project cost centers use a common Program. • Uniqueness of Cost Center provided by Project ID. • Can be used for Grants, Capital and other projects. • Project ID is a seven digit code. UHS Project ID • • • • GXXXXXX = Grant or sponsored project. PXXXXXX = Capital or building project. AXXXXXX=Administrative project. IXXXXXX=Internal Award project. Account • Account describes the nature of the transaction. • Account uses a five digit code. • There are five Account types. • The first digit of the code describes the type of account. UHS Account Codes Balance Sheet Items Income Statement Items • 1XXXX = Asset • 2XXXX = Liability • 3XXXX = Fund Equity • 4XXXX = Revenue • 5XXXX = Expense PeopleSoft Journal for Non-Proj/Grnt Cost Center • Identified as: 00730-H0066-2063-A0838-NA-53905 PeopleSoft Journal for Proj/Grnt Cost Center • Identified as: 00730-H0124-1026-B0001-G000052-53905 Budget Period • Budget Period is the period of time for which expenditures are planned and authorized. • UHS has designed six digit budget period coding. – BPXXXX • UHS Budget Period is equivalent to the Fiscal Year. Budgetary Control Elements that must be part of the Budgetary Control design include: • Budget Types • Budget Keys and Budget Key Translation • Budget Checking Budget Types • Revenue (REVEST) Budgets – Represents authorization to generate revenue • Organization (ORG) Budgets – Expenditure budget for Non-Proj/Grt cost centers • Project/Grant (PROJ_GRT) Budgets – Expenditure budget for Proj/Grt cost centers Budget Keys Budget Keys • The fields on which budget control will be decided. Budget Checking Budgets can be: • Controlled – Lack of sufficient budget will cause a journal to fail. • Tracked – A journal will pass regardless of adequacy of budget, but will be tracked as an exception. Overview of Reporting • PeopleSoft provides Inquiry capabilities--drill down, panels, etc. • Critical reports and screens have been identified in FRS and similar functionality will be provided in PeopleSoft. – Reports may be hard copy or delivered to directories. – Screens will be replaced by Public Queries. Tools for Getting Information Out of PeopleSoft • PS Query • nVision • Crystal • SQR PS Query • Queries allow users to extract information from the database. • Queries can be used to analyze data, identify errors and create ad-hoc reports. • Query results can be viewed several ways: – on-line. – exported to an MS Excel spreadsheet. – sent to Crystal Reports for inclusion in a report. Crystal • A 3rd party reporting tool bundled with PeopleSoft. • Crystal is used with PS Query to develop custom hard-copy reports for distribution to users. • Can be formatted and highly customized. nVision • • • • Reporting tool provided by PeopleSoft. nVision interacts with and uses MS Excel. Accessed through PeopleSoft menu options. Allows development of reports with superior drilldown capability. SQR (Structured Query Reporting) • SQR stands for Structured Query Reporting. • Normally used only by programmers and developers to provide standard reporting capability. • Also used to provide programs and other functionality within the application. Application Access and Security • Users sign on to a specific PeopleSoft database. • Access to PeopleSoft is controlled by OPERID and password. • OPERIDs are assigned to Security Classes. • OPERIDs will be issued and Security Classes designed according to campus policies and procedures. Questions and Answers