Meat, Poultry, Seafood, Legumes
advertisement

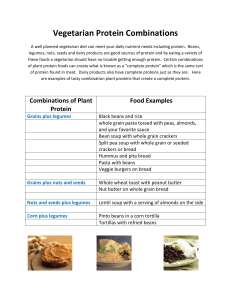
Meat, Poultry, Seafood, Legumes Beef Meat is the edible portion of mammals. Beef comes from mature cattle over 12 months of age. After animal carcasses have been halved and quartered, they are cut into smaller pieces called Wholesale cuts for easier handling. Steak= Less than 2” thick Roast=More than 2” thick Rib Short Loin Chuck Exercise Support= Dry Heat Exercise= Moist Heat Support Sirloin Support Round Support Exercise Exercise Brisket and Foreshank Exercise Exercise Short Plate Flank Meat cutters divide the wholesale cuts into smaller pieces, called Retail Cuts, at the grocery store. Reading a Meat label Other Types of Meat Veal is very young beef that comes from cattle less than three months of age. The meat from swine is called Pork and it has a grayish-pink to light rose color. Pork is not graded because it comes from very young animals. The meat of sheep less than one year old is called lamb. The edible parts of animals other than muscles, such as liver, kidney, heart and tongue are called variety meats. Flecks of fat throughout the lean portion of the meat is called marbling. There are three grades of beef: Methods of Dry Heat Cooking Broiling Roasting Panfrying/Stir-frying Panbroiling Methods of Moist-Heat Cooking Braising Cooking in Liquid Internal Temperatures Ground meats should be cooked to an internal temperature of 155°. Roasts and steaks should be cooked to an internal temperature of at least 145°. Poultry Types of Poultry The most common types of poultry eaten in the United States are chicken, turkey, goose, and duck. Ducks and geese have all dark meat. Dark meat has more fat than white meat. Giblets- edible poultry organs, such as the heart and liver. Poultry Grades Most poultry sold is US Grade A. Full-fleshed and meaty with well distributed fat. Grade B and C birds are usually used in processed products. Methods of Cooking Poultry Roasting Broiling Grilling Frying Braising Stewing Fish and Shellfish Choosing Fish A fresh fish should have a stiff body, tight scales, and firm flesh. The gills should be red, and the eyes bright and bulging. A finger pressed into the flesh should leave no indentation. The outside should have little or no slime and the fish should smell fresh. Cooking Fish To check for doneness, look to see if the flesh is firm and it flakes easily with a fork. You should cook fish about 10 minutes for every inch of thickness. Legumes Nutrition Legumes fit into two of the food groups: Vegetables Proteins Legumes are good sources of vitamins and minerals such as Iron Calcium and phosphorus (cell growth, utilize vitamins, and covert food into energy) B vitamins---helps with cell metabolism Kinds of Legumes Split Peas Yellow or green. Mild flavor. Used mainly in soups. Black Eyed Peas Small, oval, white with black spots. Mild flavor. Many uses. Kinds of Legumes Lima Beans Small or large in size. Mild, buttery flavor. Many uses. Kidney Beans Large beans. Light or dark red. Hearty flavor. Uses include chili, red beans and rice, and salads. Kinds of Legumes Navy Beans Small, white beans. Mild flavor. Many uses, including baked beans and soup. Garbanzo Beans Also known as chickpeas. Round with rough texture. Nut-like flavor. Many uses, especially in Middle Eastern Foods. Types of Legumes Pinto Beans Small, oval beans with pink dots. Mild flavor. Used for chili, refried beans, and other Mexican foods. Forms of Legumes Uncooked legumes are sold in plastic bags. You can also buy canned beans that are already cooked. Store uncooked legumes in a tightly covered container in a cool, dry place. Preparing Dried Legumes Sort the Beans Remove any foreign materials Rinse beans several times to wash off dirt and dust. Preparing Dried Legumes Soak the Beans Soak the beans overnight Soaking reduces cooking time and helps prevent the beans from forming gas in the digestive system. To soak, place beans in a large pot. Add water to cover the beans. Preparing Dried Legumes Simmer the Beans Beans should be simmered until they are tender. This will take 1-3 hours, depending on the type of bean. Tofu Soybeans are used to make tofu. Tofu is a custard-like product that is very high in protein and low in calories and sodium. Many vegetarians use tofu as a meat substitute.