Chapter 5 Lesson 4 Congressional Committees Committees do the
advertisement

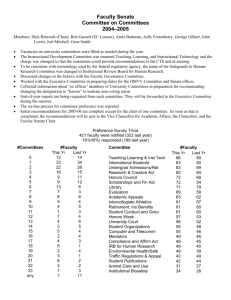
Chapter 5 Lesson 4 Congressional Committees Committees do the majority of the work in Congress Divide the work Allow for specialists Alert the public to important issues Types of Committees 1. Standing- permanent committees that oversee certain types of issues. Chairpersons picked by the majority party. Most members are also from the majority party. Sometime form subcommittees- a smaller group from a standing committee that specialized in a topic or issue. 2. Select- a temporary committee formed to study an issue and then report back to the House or Senate 3. Joint- a committee formed from members of the House and Senate to study an issue and report back to both Houses 4. Conference- temporary committee set up when the House and Senate have passed different versions of the same bill. Choosing committee members Each party assigns members to standing committees Representatives can request certain assignments Increase reelections chances Influence national policy Influence other members of congress Committee Chairperson- powerful Decides when they meet Decides which bills to consider Controls witnesses and hearings Controls budgets Longest serving member is usually the chair (seniority system)