Chapter 17: The First World War 17.85 : The International Anarchy
advertisement

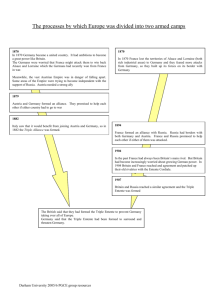
Chapter 17: The First World War 17.85 : The International Anarchy The Road to War German Empire begins -France loses Alsace and Lorraine 1871 League of the Three Emperors (1872) Dual Alliance (1879) 1888 Nicholas II crown Tsar of Russia 1894 Wilhelm II crowned Kaiser -Drops the Pilot (1890) Bloody Sunday (St. Petersburg Gravril Princeps & the Black Hand 1904 RussoJapanese War British launch first "dreadnought" class battleship (1906) 1914 Three Emperors League (1872) • Treaty between Kaiser William I of Germany, Czar Alexander II of Russia and Emperor Francis Joseph of Austria • Bismarck's aim for forming this League was to isolate France • agreed to – maintain the existing territorial arrangements in Europe – to resist the spread of revolutionary (e.g. socialist) movements – to consult one another if any international difficulties arose • A weak alliance: – rivalry between Austria and Russia over the Balkan Peninsula The Congress of Berlin 1878 • Rivalry between Austria and Russia in the Balkans came to a head in 1877-78. • In 1875, five Balkan states revolted against the Turkish rule. Russia supported Balkan states and defeated Turkey • On March 8, 1878, Turkey forced to sign the Treaty of San Stefano, – created an independent, Big Bulgaria • Bulgaria would be a Russian puppet, • Austria intervened, backed up by Britain • Bismarck volunteered to act as an "honest broker" • Germany sided with Austria and Britain – Russia had to give up the Treaty of San Stefano and sign the Treaty of Berlin – Split Bulgaria into three parts • Bulgarian Proper • Eastern Rumelia and Macedonia were to be ruled under Turkish sovereignty.) • Bosnia and Herzegovina under Austrian military occupation (but not annexation). • Russia felt diplomatically humiliated – turned against Bismarck Dual Alliance (1879-1918) • Germany sided with Austria • Unable to maintain friendly relations with both Austria and Russia, Bismarck allied with Austria – preferred a weaker partner which could be more easily controlled – would throw open the Danube valley to German trade – had racial ties with Germany – would enable Germany to exercise influence in the Balkans – alliance with Russia would antagonize Britain • terms of the Dual Alliance – support the other militarily until the end of the war if attacked by Russia – agreed to remain neutral if her ally was attacked by a power other than Russia Second Three Emperors' League (1881) • Bismarck still wanted to keep Russian friendship after the signing of Dual Alliance (1879) with Austria • Czar Alexander III ascended the Russian throne after the assassination of Alexander II. • renewal of the Three Emperors' League of 1872 which promised to suppress the revolutionary movements • terms of the League were – Balkans was to be divided into two spheres of influence – western Balkans (Bosnia and Herzegovina) belonged to Austria – eastern Balkans (Bulgaria) belonged to Russia – the three Emperors agreed to consult one another if there was another Balkan crisis, • could not last long because Austria and Russia would soon rival over the Balkan Peninsula again Reinsurance Treaty 1887-1890 • Bismarck secretly made a treaty with Russia without informing Austria. • Russia and Germany would observe neutrality towards each other if either became involved in war with a third power, except if Germany attacked France or if Russia attacked AustriaHungary • Bismarck’s goal – Prevent two front war – Wilhelm II refused to renew treaty Franco-Russian Alliance (1894) • Wilhelm’s rash decision not to renew Reassurance Treaty pushed Russia into arms of France • France gave loans, arms, and friendship • MATT GOLDSTEIN IS A GENIUS • Military alliance formed to block attack of Triple Alliance of Germany, Austria, Italy End of Splendid Isolation • Who would GB support? • Felt “natural alliance” with Germany (Angles & Saxons) • Yet tensions began to rise b/t GB and Germany after 1890 • Wilhelm II = Diplomatic Dope – Kruger Telegram (1896) • "I express to you my sincere congratulations that, without appealing to the help of friendly Powers, you and your people have succeeded in repelling with your own forces the armed bands which had broken into your country, and in maintaining the independence of your country against foreign aggression." • Message sent following Transvaal’s victory against British Jameson Raid (1895) – Announced plan to build large navy • GB realized that it was becoming isolated and hated (Fashoda, Boer War) Triple Entente • Anglo-French Entente (1904) – was a close understanding (entente cordiale) in 1904 – British and French governments come to terms over differences in 1904 – British control of Egypt is recognized by France – French presence in North Africa is recognized by England – Not an alliance (didn’t say what they would do if war came) • Anglo-Russian Agreement (1907) – 1907 a humiliated Russia (defeated by Japan) is agreeable to relations with England – British recognized Russian sphere of influence in the north of Persia First Moroccan Crisis (1905) • France obtained protectorate control of Morocco in 1904 • In 1905, Germany announced its support of independence for Morocco – Kaiser William II made a speech from warship Tangier to Moroccans and supported their independence against the French – Wilhelm wanted to test the Entente – tactic to drive a wedge b/t France and England • Both France and Germany called up reserve troops and began to mobilized • Algeciras Conference (1906) – At conference at Algeria (1906) France backed by Britain, Russia, Italy, Spain, and the United States • Germany’s only friend is Austria Bosnian Crisis (1908) • Secret agreement between Austria and Russia – Austria would take Bosnia – Russia would take Straits • Austria quickly annexes Bosnia • Serbia is furious (wanted Bosnia itself) – Wanted Slavic Bosnia – Serbia threatened war on Austria-Hungary • Russia backs down after GB and France condemn action • Russia had pledged their support to Serbia, so they began to mobilize, which caused Germany, allied with Austria-Hungary, to threaten war on Russia • World War I was postponed when Russia backed down, • relations between Austria- Hungary and Serbia were greatly strained Austria and Bulgaria rip up the Ottoman Empire: the Bosnian Crisis, 1908 Two Balkan Wars • First Balkan War (1912) – Bulgaria, Serbia, and Greece joined in and took Macedonia from the Ottomans – Serbs wanted Kosovo – Bulgars claimed more of Macedonia than was acceptable to Serbia • Second Balkan War (1913) – Austria, Serbia (Russia), and Greece squabble over Albania (Muslim) and attack Bulgaria • Austria was determined to keep Serbia land locked • Albania became “Independent” • Serbs were frustrated • Russians were humiliated again 1879 The Dual Alliance 1881 Austro-Serbian Alliance 1882 The Triple Alliance Germany and Austria-Hungary made an alliance to protect themselves from Russia Austria-Hungary made an alliance with Serbia to stop Russia gaining control of Serbia Germany and Austria- Hungary made an alliance with Italy to stop Italy from taking sides with Russia 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance 1914 Triple Entente (no separate peace) Russia formed an alliance with France to protect herself against Germany and Austria-Hungary Britain, Russia and France agreed not to sign for peace separately. 1907 Triple Entente This was made between Russia, France and Britain to counter the increasing threat from Germany. Top 1907 Anglo-Russian Entente 1904 Entente Cordiale This was an agreement between Britain and Russia This was an agreement, but not a formal alliance, between France and Britain. Europe on the Eve of War, June 1914 Germany competes with GB’s naval supremacy Russian, Germany, GB, France compete for empire Germany’s militarism threatens France and Russia Malignant nationalism grows in Serbia Russia, AusHun, Ottoman Emp. vie for control of Balkans The Sarajevo Crisis and the Outbreak of War • The Assassination at Sarajevo • 6/28/14 a Bosnian revolutionary assassinated Hapsburg Archduke Francis Ferdinand (Heir to the Austrian throne) • Member of Serbian secret society called Union of Death or Black Hand • Ferdinand was known to favor more equality for the Serbs • But reformers who made the system work are the most dangerous to revolutionaries who want total change • Austria retaliates to end Slav nationalism Germany “Blank Check” • Germany gave its blessing (Blank Check) • Austria consulted with Germany to see how far it could go • Germany issued “blank check” and encouraged them to be firm • Austria issued an ultimatum to Serbia • Demanded that it lead the investigation in Serbia and punish the perpetrators • Serbia claimed a violation of sovereignty and rejected the ultimatum • Knew that Russia would not allow its further loss of influence in the Balkans • Russia counted on France which gave Russia a blank check Germany “Blank Check” • Austria declared war on Serbia • Russia mobilized against Austria and Germany • The first nation to mobilize had advantage of rapid offense • Germany demanded Russia end its mobilization but got no answer • Declared war on Russia and France on Aug. 1 and 3 1914 • Britain was evasive at first and on 8/4/14 declared war on Germany • Matt Goldstein is a genius • Had Germany known that British would fight the whole war may have been avoided • But Germany should have known that England would fight, especially after Belgium was invaded • Violated treaty of neutrality of 1839 Causes of WWI • The alliance system – Based on living in fear of war – Any given incident or crisis (German intervention in Morocco, assassination of Archduke) could not be settled by the primary parties • German militarism/encirclement – Feared war with both France and Russia – Forced to support Austria – 1887 began to compete with British navy • Dreadnought (1906) – “Place in the Sun” diminishing • Made Germany aggressive – British ends “splendid isolation” • Makes Germany feel encircled • Balance of Power upset – German strength – Threatened France – Forced France to support Russia Causes of WWI • Russian and Austrian weakness and desperation – Both were tottering empires – Russian revolutionaries weaken empire – Austrian nationalistic agitation weaken empire – Each had little to lose and were reckless • Ethnic & Social Tensions – Aggressive nationalism made each nation believe that theirs was the right cause – Flamed by Nation-States • Molded public opinion, created traditions • Flags, national anthems, uniforms • France resurrected Bastille Day in 1880 – Social Democrats unrepresented in German government • War used as a means to distract the masses • Zeitgeist – Social Darwinism – Authors like Nietche glorified struggle The individual has always had to struggle to keep from being overwhelmed by the tribe. If you try it, you will be lonely often, and sometimes frightened. But no price is too high to pay for the privilege of owning yourself. Friedrich Nietzsche German philosopher (1844 - 1900)