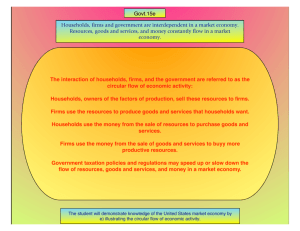
Three Basic Economic Questions
advertisement

1. 2. 3. 4. Define economic system. List and describe the Three Key Economic Questions. List and describe the four types of economic systems. Using the Chart Below, describe each of the Economic Goals and Societal Values. Then provide a real-life example of each. Economic Goal and Societal Values 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Economic Efficiency Economic Freedom Economic Security and Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth and Innovation Additional Goals Summary Example Economic System Economic System – method used by society to produce goods and services Four Economic Questions What and how much should be produced? Who should produce it? How should it be produced? Who should share in its use? Four Economic Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. Traditional economy – relies on habit, custom, or ritual to decided the 3 economic questions Market economy – economic decisions are made by individuals and are based on exchange, or trade. Command Economies – in a centrally planned economy, the central government alone decides how to answer the three economic questions. Mixed Economies – market-based economic systems in which government plays a limited role. Economic Goal and Societal Values 1. Economic Efficiency 2. Economic Freedom 3. Economic Security and Predictability 4. Economic Equity 5. Economic Growth and Innovation 6. Additional Goals Summary Making the most of scarce resources Freedom from government intervention in the production and distribution of goods/services Knowing that goods and services will be available, payments made on time, government will provide a safety net in times of economic downturns Fairness, being paid according to your skill level, not being discriminated against Example Manufacturer knowing the best way to use resources wisely (Assembly Line) Working where you want, spending money the way that you want, owning a business, etc. Security – Unemployment Checks, Social Security Predictability – gas at gas pumps, food at store Lawyers earn more than nurses, computer programmers more than truck drivers Economic growth refers to improving standard of living and GDP. Innovation, improving existing technology. Agricultural age to industrial age to information age. Innovations in computers, communication. Future goal for society. Environmental protection, full employment, universal medical care. Statements 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Last week I willingly enrolled in college courses at Coastal. I am so happy that I make my decisions about my future. My uncle lost his job, but thankfully he is able to receive unemployment checks. Wal-Mart recently upgraded all of their registers to touch screen monitors. General Motors replaced all of their human workers with robots in order to increase productivity. As a result of the internet and technology, our economy has experienced significant expansion over the past 30 years. I can always expect Publix to have the food I like! Hopefully in the future we will have full employment. With every degree/skill I earn, I improve my ability to make money. Economic Goal 1. Economic Freedom 2. Economic Security 3. Economic Innovation (Efficiency) 4. Economic Efficiency (Innovation) 5. Economic Growth (Innovation) 6. Economic Predictability 7. Additional (Future) Goals (Equity) 8. Economic Equity (Growth) Poster Requirements: 1. Title - Economic Goals and Societal Values 2. Summary Statement – “The Economic Goals and Societal Values provide a basic framework for each society and their attempts to provide for their people.” 3. 8 pictures to represent each of the economic and social goals. 4. Label, describe and summarize each picture 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Economic Efficiency Economic Freedom Economic Security Economic Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Additional Goals Economic Efficiency Description: Using the factors of production in the most productive way possible, as to maximize profit Picture Summary: This picture represents assembly line production at an automobile manufacturing plant. This shows how the division of labor and specialization can increase efficiency. Economic Goals and Societal Values Summary Statement: The Economic Goals and Societal Values provide a basic framework for each society and their attempts to provide for their people. Economic Efficiency Definition: societies try to maximize the factors of production Picture:This picture represents an efficient use of resources through assembly line production Economic Predictability Economic Innovation Economic Freedom Economic Security Economic Growth Economic Equity Additional Goals Poster Requirements: 1. Title - Economic Goals and Societal Values 2. Summary Statement – Purpose of economic and Societal Values 3. At least 8 pictures to represent each of the Economic Goals and Social Values 4. Label, definition and picture description for each of the 8 Economic Goals and Societal Values Bead Game Simulation Chapter 2 Section 1 – Daily Assignment Questions pgs. 26 -27 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. How does a traditional economy answer the three economic questions? Describe traditional economies and their communities. What is a disadvantage to a traditional economy? How are the three economic questions answered in a market economy? What are other names for market economies? How are the three economic questions answered in a command economy? Why are they referred to as command economies? Why are most modern economies referred to as mixed economies? Imagine that you are walking into Walmart. List 3 items that you could purchase and the departments that you would find them in. Chapter 2 Section 2 – The Free Market Market – buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services Market Economy – economic decisions(what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce) are made by consumers and businesses based on exchange of goods and services Capitalism (free market) – Individuals and businesses own the factors of production and can profit on them Voluntary Exchange - is the act of buyers and sellers freely and willingly engaging in market transactions Specialization – the separation of tasks within a system; people focus on a specific purpose/task Division of Labor – Workers perform fewer tasks in order to operate more efficiently Households and Firms Household – Person or group of people living in a residence Consumers - use the goods and services (outputs) to satisfy wants and needs Firm – business, organization that uses resources to produce a product, which it then sells Suppliers – transform “inputs” (F.O.P.) into “outputs” (products) Product Markets Product Markets – Houses and firms interact; producers sell their goods and services to consumers Households are buyers of goods and services Firms are sellers of goods and services (outputs) Factor Markets Factor Markets – the markets where productive resources (F.O.P)/Inputs are bought and sold Labor - Firms (businesses) hire workers and pay them salaries Land - Purchased/rented land Capital - Use money from households, purchase capital goods Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity – shows the flow of money and goods/services from and to businesses and households Consumer Spending Product Product Market Market Business Income/Revenue •Market for Goods and Services •Firms sell Households Buy Consumer Goods and Services Final Goods and Services Sold Households Households Firms Firms (Business) • Buy and Consume Goods and Services •Own and sell the F.O.P • Produce and sell Goods and Services •Hire and use F.O.P. Land, Labor, Capital - provided by household Inputs for Production (F.O.P.) Factor Market Income to Households/Individuals Market for F.O.P •Households sell •Firms buy Payment for F.O.P. – Rent (Land) Wages (Labor), Interest (Capital), Profit (Entrepreneurs) Application Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. In the factor market, what do businesses provide households? Income/payment the F.O.P The flow of goods and services in the product market is represented by which firm and products on the model below? Starbucks/Coffee When you apply for a job at the local Starbucks which market are you in? Factor Which color arrows represent the flow of money; what color arrows represent the flow of inputs and outputs. Blue/Tan Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity Consumer Spending/Investing Business Income/Revenue Product Market Goods and Services Purchased: Caramel Frappuccino Goods and Services Sold Firms Households Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurs Inputs for Production (F.O.P.) Factor Market Income to Households/Individuals Payment for F.O.P. – Wages, rent, capital goods Daily Assignment - Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity Consumer Spending Business Income 1. _________________________ 1. _________________________ Product Market Goods Purchased Goods Offered 1. ___________________________ 1. ______________________________ 2. ___________________________ 2. _______________________________ Firm Household 1. ________________________ Firm 1. _____________________________ Firm 2. _____________________________ Input for Production Factor of Production Offered 1. ___________________________ 1. ___________________________ Weekly Income 1. __________________ Factor Market Payments for F.O.P 1. _________________ Vince Lombardi “What it Takes To Be Number 1” "Winning is not a sometime thing; it's an all the time thing. You don't win once in a while; you don't do things right once in a while; you do them right all the time. Winning is a habit. Unfortunately, so is losing. There is no room for second place. There is only one place in my game, and that's first place. I have finished second twice in my time at Green Bay, and I don't ever want to finish second again. There is a second place bowl game, but it is a game for losers played by losers. It is and always has been an American zeal to be first in anything we do, and to win, and to win, and to win. Every time a football player goes to play his trade he's got to play from the ground up-from the soles of his feet right up to his head. Every inch of him has to play. Some guys play with their heads. That's O.K. You've got to be smart to be number one in any business. But more importantly, you've got to play with your heart, with every fiber of your body. If you're lucky enough to find a guy with a lot of head and a lot of heart, he's never going to come off the field second. Vince Lombardi “What it Takes To Be Number 1” Running a football team is no different than running any other kind of organization-an army, a political party or a business. The principles are the same. The object is to win-to beat the other guy. Maybe that sounds hard or cruel. I don't think it is. It is a reality of life that men are competitive and the most competitive games draw the most competitive men. That's why they are there-to compete. To know the rules and objectives when they get in the game. The object is to win fairly, squarely, by the rules-but to win. And in truth, I've never known a man worth his salt who in the long run, deep down in his heart, didn't appreciate the grind, the discipline. There is something in good men that really yearns for discipline and the harsh reality of head to head combat. I don't say these things because I believe in the "brute" nature of man or that men must be brutalized to be combative. I believe in God, and I believe in human decency. But I firmly believe that any man's finest hour, the greatest fulfillment of all that he holds dear, is that moment when he has worked his heart out in a good cause and lies exhausted on the field of battle - victorious." ...Vince Lombardi 1. 2. 3. 4. Do you agree with Vincent Lombardi’s assertion that people are born with the desire to compete why or why not? What areas do you see competition in the economy of the United States ? How is competition beneficial to our economy/society? How is it harmful to our economy/society? Competition – efforts among sellers/producers to attract consumers at various prices At the heart of market economic philosophy Incentive – an expectation that encourages people to behave in a certain way (positive and negative) Businesses respond to profits Consumers respond to price change (high/low) Chapter 2 Section 2 – Daily Assignment Economic Profile Adam Smith pgs. 33 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What was Adam Smith’s ethnic and professional background? What was the name of the book that he published; when was it published? What did Smith identify in the book? What did he assert about specialization and division of labor? What did he believe about the role of government in the economy? Define the French term Laissez Faire; why did Smith believe in LaissezFaire economics? What is meant by his metaphor of the Invisible Hand? How do both consumers and businesses benefit from this philosophy? Economics Daily Ten #2 - Fill in the blanks for each of the following: 1. QB Peyton Manning’s high salary, vs. a cashier’s low equity _________. salary, represents economic 2. Moving from the personal computer to handheld innovation_________. devices represents an economic 3. “Today, I know Chevron will have gas” represents economic ___________. predictability 4. GM receiving a government bailout represents economic security ____________. 5. Increasing the production of goods, services and jobs growth ________. would represent economic Word Bank: innovation, predictability, growth, security, equity. Chapter 2 Section 3 – Centrally Planned Economies Command – central authority owns and operates the Factors of Production Centrally Planned Economy – central government answers the three economic questions; WHAT to produce, HOW to produce, and FOR WHOM to produce Oppose private property, free market pricing, economic freedom Socialism and Communism Karl Marx – German social philosopher that studied economic systems in Europe Communist Manifesto – written by Marx and Frederick Engels became basis for modern-day command economies Thought capitalism would fail because it put to much wealth in the hands of few and left everyone else poor Believed in a “no-class” system, where all share in wealth/power Socialism – distribution of wealth and F.O.P. equally amongst society Communism – political and economic system with centralized economic decision-making Authoritarian Government – exact strict obedience from their citizens; do not allow individual freedom 1. Why does a free market economy need some government intervention? a. so that the government has total control over factor resources b. to ensure the government has the freedom to tax as necessary c. to make sure that the government can fulfill its needs for goods and services d. to provide for things that the marketplace does not address (i.e. market failures) Explanation: (d) – most modern economies are mixed, or have some government involvement to regulate, protect and oversee. 2. In what kind of economy does the government make all the decisions? a. socialist b. laissez faire c. centrally planned, or command economy d. free enterprise Explanation: (c) – command economies are controlled by a dictator, or small group of economic policy makers. Chapter 2 Section 3 – Daily Assignment Questions “The Former Soviet Union” pgs. 36-38 How did the Soviet Union arise? 2. Where did Soviet planners allocate the factors of production? 3. How did the Soviet Union control agriculture? 4. What three industries did Soviet Planners favor? 5. How did the Soviet Union view entrepreneurial endeavors? 6. What was the quote used by Soviet consumers as a joke? 7. Why were Soviet Consumers’ left unsatisfied? Page 39 – Russia in Crisis 1. How did many Russians initially respond to the Communist collapse? 2. What happened over the next decade? 3. How did Russia deal with corruption? 4. What were some characteristics of Russia’s financial problems? 5. What evidence can be seen that success is in sight? 1. Scenario 1 You have two cows. You trade one to your neighbour for a bull. You only produce what you need to survive. Scenario 2 You have two cows. The State takes both and gives you just enough milk to live Scenario 3 You have two cows. You sell one and buy a bull. Your herd multiplies, and your wealth grows. You sell your herd and retire on the income. 1. 2. 3. 4. What economic system matches each scenario? Which scenario do you think is the most ideal and why? Which scenario do you think sounds the most like the United States? Why? What countries do you know of that could fall into scenario 2. Chapter 2 Section 4 – Modern Economies Free Enterprise – competition in the marketplace is allowed to flourish with no interference from government Modified Free Enterprise (mixed economy) – businesses are free to compete with some government regulation/intervention Centrally Planned Free Market Mexico North Korea France Hong Kong Iran South Africa Cuba United Kingdom Canada China Poland Japan United States Singapore Laissez Faire in a Modern Economy Laissez Faire – no government intervention in the economy Some government intervention is necessary in the economy; some needs are difficult to answer in the marketplace National defense, roads and highways, education, etc… Government acts a protector, regulator and overseer of economy Government Money Taxes from both households and businesses Income, state, social security, Medicare/Medicaid, unemployment insurance, etc. Government in the Factor Market Government purchases land, labor, and capital from households United States gov’t pays 2.8 million employees $9.7 billion for labor Government in the Product Market Government purchases goods and services from firms (businesses) Buildings, office supplies, telephones, computers, etc. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Economic Freedom Economic Security Economic Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Market Yes - High levels of economic freedom Command No - Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Tradition No - Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Market Economy Economic Freedom Yes - High levels of economic freedom Economic Efficiency Economic Security Economic Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Command Economy Traditional Economy No - Many aspects of economic No - Extremely limited, a person’s activity are tightly controlled and role in society is based on custom, state-dominated heritage and tradition Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Market Highly stressed because of scarcity and competition Economic Freedom High levels of economic freedom Economic Security Economic Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Command Tradition Lack of profit motive can lead to a lack of efficiency Slow to adapt to new ideas/technology. Inefficient by standards of modern societies Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Market Highly stressed because of scarcity and competition Command Tradition Lack of profit motive can lead to a lack of efficiency Slow to adapt to new ideas/technology. Inefficient by standards of modern societies Economic Freedom High levels of economic Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Economic Security Economic security is assured based on full employment and government sponsored programs Economic security is assured based on traditional means of production freedom Economic Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Safeguards In society, but general employment is not assured Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Market Highly stressed because of scarcity and competition Command Tradition Lack of profit motive can lead to a lack of efficiency Slow to adapt to new ideas/technology. Inefficient by standards of modern societies Economic Freedom High levels of economic Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Economic Security Safeguards In society, but general employment is not assured Economic security is assured based on full employment and government sponsored programs Economic security is assured based on traditional means of production Economic Predictability High predictability Lack predictability because government controls F.O.P. Predictable in most cases. Can be unpredictable, because F.O.P. are controlled through traditional means freedom Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Market Highly stressed because of scarcity and competition Command Tradition Lack of profit motive can lead to a lack of efficiency Slow to adapt to new ideas/technology. Inefficient by standards of modern societies Economic Freedom High levels of economic Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Economic Security Safeguards In society, but general employment is not assured Economic security is assured based on full employment and government sponsored programs Economic security is assured based on traditional means of production Economic Predictability High predictability Lack predictability because government controls F.O.P. Predictable in most cases. Can be unpredictable, because F.O.P. are controlled through traditional means Economic Equity Fairness (hiring and payment) is a primary goal of a market economy Lack of equitable payments based on the production of goods and services Equity is based on customary means of production, women have assigned roles, men have assigned roles freedom Economic Growth Economic Innovation Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Market Highly stressed because of scarcity and competition Command Tradition Lack of profit motive can lead to a lack of efficiency Slow to adapt to new ideas/technology. Inefficient by standards of modern societies Economic Freedom High levels of economic Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Economic Security Safeguards In society, but general employment is not assured Economic security is assured based on full employment and government sponsored programs Economic security is assured based on traditional means of production Economic Predictability High predictability Lack predictability because government controls F.O.P. Predictable in most cases. Can be unpredictable, because F.O.P. are controlled through traditional means Economic Equity Fairness (hiring and payment) is a primary goal of a market economy Lack of equitable payments based on the production of goods and services Equity is based on customary means of production, women have assigned roles, men have assigned roles Economic Growth Grow at a fast rate due to competition and profit motive Lack of growth because of a lack of efficiency and profit motive Lack of growth due to a lack of productivity and innovation freedom Economic Innovation Using the Chart Below, identify how each of the economic goals are addressed. Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Market Highly stressed because of scarcity and competition Command Tradition Lack of profit motive can lead to a lack of efficiency Slow to adapt to new ideas/technology. Inefficient by standards of modern societies Economic Freedom High levels of economic Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled and state-dominated Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Economic Security Safeguards In society, but general employment is not assured Economic security is assured based on full employment and government sponsored programs Economic security is assured based on traditional means of production Economic Predictability High predictability Lack predictability because government controls F.O.P. Predictable in most cases. Can be unpredictable, because F.O.P. are controlled through traditional means Economic Equity Fairness (hiring and payment) is a primary goal of a market economy Lack of equitable payments based on the production of goods and services Equity is based on customary means of production, women have assigned roles, men have assigned roles Economic Growth Grow at a fast rate due to competition and profit motive Lack of growth because of a lack of efficiency and profit motive Lack of growth due to a lack of productivity and innovation Economic Innovation Innovation is at a high rate due to changes in the marketplace and competition Less incentive to innovate because profits and credit go to the state Innovation is non-existent by modern standards freedom Disadvantages Advantages Examples Tradition Command Market 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 1. 1. 2. 2. 1. 1. 1. 2. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Chapter 2 – VIS Terms 1. Traditional Economy 15. Socialism 2. Command Economy 16. Communism 3. Market Economy 17. Authoritarian 4. Market 18. Laissez-Faire 5. Free Market 6. Specialization 7. Division of Labor 8. Household 9. Consumer 10. Firm 11. Supplier 12. Product Market 13. Factor Market 14. Centrally Planned Economy Junk!!! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. DAQ's pg. 26-27, Ch. 2 Sec. 1 Video Questions - North Korea Comparing Economic Systems, Advantages + Disadvantages Economic Systems + Reflection Questions D.A. Circular Flow Model Circular Flow (Elisa and Marcella) Online Assignment - Scarcity Ch. 2 Sec. 2 D.A. Adam Smith Ch. 2 Sec. 3 D.A. "The Former Soviet Union" Economic Goals and Am. Free Enterprise Flow Chart Chapter 2/3 Study Guide Ch. 2 CW Puzzle Ch. 3 CW Puzzle Ch. 2 Notes Daily Tens (12) Vocab Terms Junk!!! Circular Flow Model of a Mixed Economy Consumer Spending/Investing Business Income/Revenue Product Market Goods and Services Sold Goods and Services Purchased: Households Expenditures Expenditures Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneur Income to Households/Individuals Firms Inputs for Production (F.O.P.) Factor Market Payment for F.O.P. – Wages, rent, capital goods 26. EF3b: From the principle of voluntary exchange, we conclude that: a. often buyers are made better off at the expense of sellers b. often sellers are made better off at the expense of buyers c. both the buyer and the seller must be better off as a result of a transaction d. neither the buyer nor the seller are necessarily made better off as a result of a transaction 27. EF3b: The concept that people may decide what and when they want to buy and sell a. voluntary exchange b. fraudulent exchange c. competition d. economic integrity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Economic System What to produce, Who to produce them for, How to produce them Economic: efficiency, freedom, security, predictability, equity, growth, innovation, additional goals Tradition, custom, ritual, habit Central planners dictate the what, how, for whom Households and firms through production and consumption Market Market economy Capitalism Households and Firms Input is something used to produce and output, which is a final good or service Product Factor Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations 15. 16. 17. 18. Be limited in its role in the economy, “Let them do as they please”. Invisible Hand See Circular Flow a) Product b) c) d) e) 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. when it changed hands from the household to the firm Factor, labor Grills, hostesses, cashiers Factor Karl Marx, Communist Manifesto That it would fail because it put too much money in the hands of the rich and not in the hands of the poor Communism, Socialism Authoritarian Economic Freedom Property Rights Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange Competition 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. Their purchases signal to producers what to produce (consumer sovereignty) Overseer, protector, regulator, informer Technology Public Good Public Private Free Rider Market Failure Externality Extra Credit 1. Give an example of specialization/division of labor, and explain why it is beneficial. 2. Give an example of a positive and negative externality not mentioned on the test. 3. Explain why the United States is not a true “pure market/free enterprise” system.