Economic Systems: Fundamental Questions & Goals
advertisement
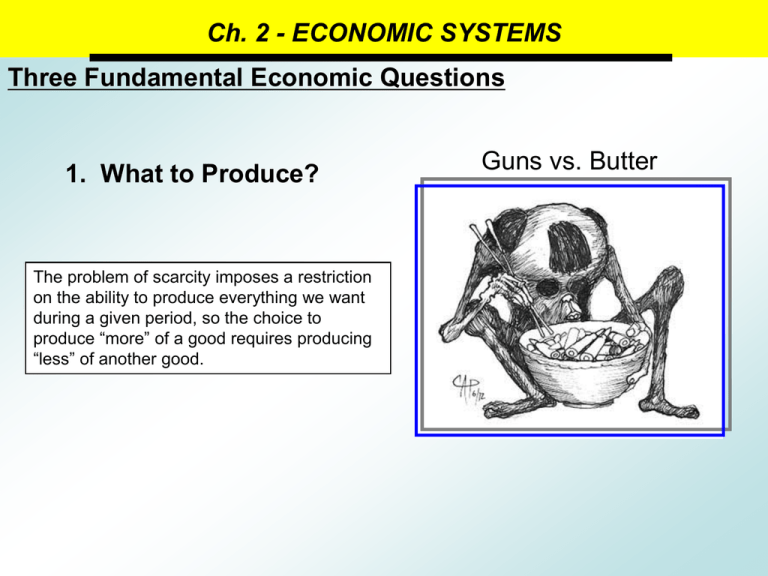
Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Three Fundamental Economic Questions 1. What to Produce? The problem of scarcity imposes a restriction on the ability to produce everything we want during a given period, so the choice to produce “more” of a good requires producing “less” of another good. Guns vs. Butter Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Three Fundamental Economic Questions 2. How to Produce? Vs. How do we mix technology and scarce resources in order to produce goods and services? Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Three Fundamental Economic Questions 3. For Whom to Produce? Society must have a method to decide who will be “rich” and who will be “poor”. Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS 5 Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Making the most of resources Economic Freedom Freedom from government intervention in the Economic Freedom production of goods and services Economic Efficiency Assurance that goods and services will be available , Economic Security payments will be made time, and a safety net will Economic Security andon Predictability and Predictability protect individuals in times of economic disaster Fair distribution of wealth Economic Equity Economic Equity Economic Growth Innovation leads to economic growth, and economic Economic Growth andstandard Innovation growth leads to a higher of living and Innovation Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Traditional Economies Relies on habit, or ritual to decide how to answer the 3 economic questions. • Revolves around the family • Work divided along gender lines • Agricultural and hunting practices usually dominate the economy • Slow to adopt new technology or ideas Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Centrally Planned (Command) Economies The government owns both the land and capital and decides on behalf of the people how to answer the 3 economic questions • Government controls all aspects of production • Socialism – government owns some FOP • Karl Marx – The Communist Manifesto Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Free Market Economies Individuals and privately owned businesses own the factors of production and decide how to answer the 3 economic questions • Specialization of tasks makes the economy more efficient • Everyone acts in their own self-interest • There is no government intervention • Laissez Faire Adam Smith’s Invisible Hand Self-interest and competition work together to regulate the marketplace Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Circular Flow of Money $ Factor Market $ $ $ $ Households Businesses Product Market $ $ $ $ $ Ch. 2 - ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Mixed Economies The people answer the 3 economic questions with some intervention from the government to account for market failures • Economic decisions are made by individuals with government oversight • Government is a key component of economic activity • All nations exist in the “mixed economy continuum” Centrally Planned Free Market Iran N. Korea Cuba France Russia Peru United Kingdom Canada United States Singapore