Water as a Resource Notes Hydrologic Cycle

Water as a Resource
Notes
Hydrologic Cycle
Hydrologic Cycle
Solar-powered movement of water between the sea, air, and land
Follows water as it evaporates from the earth’s surface, forms clouds, and then falls back to the surface as precipitation
Cycle is continuous with no beginning or end
Basic Steps:
Condensation
Precipitation
Infiltration
Runoff
Evapotranspiration
Hydrologic Cycle
Review
Provide examples for the following terms:
Condensation
Precipitation
Infiltration
Runoff
Evapotranspiration
Water as a Resource
Water available for use:
97.2% salt water
2.8% fresh water
2.2% is in glaciers and ice caps
0.6% is groundwater
0.01% in lakes, rivers, and streams
0.001% is water vapor
Water Availability
Salt Water
Glaciers and Ice Caps
Groundwater
Lakes and Rivers
Atmosphere
Water as a Resource
Uses of Fresh Water
Agriculture
69% for irrigation
Industrial
15% for power plants, refineries, manufacturing
Household
15% for drinking, cooking, sanitation, gardening, etc.
Recreational
Environmental
Review
What steps of the water cycle can we get our water from?
For each use of water, identify if you use it directly (D), indirectly (I), or not at all (N/A).
Agriculture
Industrial
Household
Recreational
Environmental
Freshwater Shortage
Estimated only 0.34% of all water on earth is available for human use
Fresh water supply decreasing due to pollution:
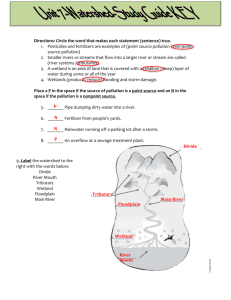
Point Pollution
Landfills
Industrial waste
Power plants
Smoke stacks
Leaking pipelines or storage tanks
Livestock waste
Non-Point Pollution
Sewage/Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO)
Road salt
Fertilizer/pesticide runoff
Litter
Water Pollution
Water Pollution
Any chemical, biological, or physical change in water quality that has a harmful effect on living organisms or makes water unsuitable for desired uses
Major Pollutants
Fecal Coliform
Disease causing bacteria
Non-point toxic chemicals
Discharges of untreated sewage
Discharges of industrial wastes
Non-degrable Waste
Non-degradable wastes
Toxic lead, arsenic, fluoride are permanent pollutants
Slowly degradable wastes
Ex. DDT
May be there for decades, centuries, or longer
Review
Compare and contrast point and non-point pollution.
Consider runoff. Is this a bigger concern for point or non-point pollution?
Explain why slowly degradable and nondegradable water pollution is such a concern.