Air pressure Notes and assignment
advertisement

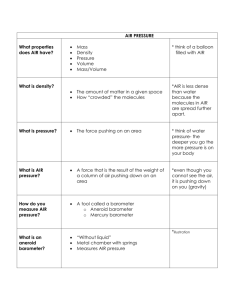
https://vimeo.com/50050728 Bill Nye on Atmosphere Air Pressure Air pressure What is air pressure? Air Pressure is Differences in air pressure cause Earth’s winds and weather to change. Air has pressure b/c air has mass. Is defined as force per unit area. The less mass a volume of air has the less dense the parcel. The weight of the atmosphere per unit area. At the surface , 1 kg per square centimeter is the average air pressure. Measuring Air pressure Mercury Barometer At sea level the height of the column normally is 76 cm. The instrument used to measure air pressure is the BAROMETER There are two types of barometers—mercury and aneroid. The Aneroid Barometer Barograph Uses a thin metal can and by pumping most of the air out of the can, the can is made sensitive to air pressure, A spring or similar device keeps the can from collapsing inward. As the shape of the can changes with the changes in air pressure, a pointer attached to the can moves over a scale. Is a recording aneroid barometer. Its pointer is a pen that writes on a chart. Altimeter Since air pressure is the weight of the air overhead, what happens to air pressure as you go up in altitude?? The air pressure drops with an increase in altitude. Is a aneroid barometer that reads height above sea level. Air Pressure Units Air pressure is reported in two different ways. The first way gives the height of the mercury column in the barometer. It may be given in centimeters or in inches. The second way uses a metric unit called a millibar . 1000 millibar of air pressure is roughly equivalent to the average air pressure at sea level. F. Understanding Pressure Maps 1. Isobars- areas with equal air pressure Sea- level = 1013.3 mb Denver, CO = 835 mb Meridian, ID = 975 mb 2. Isobar map rules: a. If # is 499 or less, place 10 in front b. if # is 500 or more, place 9 in front c. decimal is moved before last digit. + Isobars always make a circle! Ex. 950 = 995.0 ISOLINE ACTIVITY: 1. In PEN, uncode each pressure: 103= 1010.3 2. In PENCIL, label the highest pressure H and the lowest pressure L. 3. For the H draw the following isobars: 1016, 1012, 1008 mb (each in a different color) 4. For the L draw the following isobars: mb (each in a different color) 996, 1000, 1004 5. For each wind indicator- show wind movement. 1016 mb H L 1016 mb H 1012 mb L 1016 mb H 1012 mb 1008 mb L 1016 mb H 1012 mb 1008 mb L 996 mb 1016 mb H 1012 mb 1008 mb L 996 mb 1000 mb 1016 mb H L 1012 mb 996 mb 1000 mb 1008 mb 1004 mb 1016 mb H L 996 mb 1012 mb 1000 mb 1008 mb 1004 mb Why does air pressure change? Changing Temps. Warm air is lighter than cold air because the molecules are farther apart. When cold air replaces a warm air mass then the air pressure at the ground goes up. Changing humidity. The more water vapor the air contains the lighter it is. How? When water vapor enters the atmosphere it pushes out and equal volume of dry air. Dry air has more nitrogen and oxygen and both of these elements in their gaseous state weigh more than does water vapor. In General scientist have found that a falling barometer means warmer weather, rain or snow. Changing Pressure A rising barometer = increasing air pressure. This usually means: Clear Cool Dry. 20 Changing Pressure A falling barometer = decreasing air pressure. This usually means: warm, wet, cloudy Tut tut it looks like rain 21 Air is forever trying to find… Equilibrium Air travels from high to low pressure. This affects wind direction and speed. Low & High Comparison Table Atmospheric condition Pressure Temp. Humidity Gasses Result Low warmer Greater Water vapor (low mass) Cloudy & precipitation, unsettled High Cooler Lesser Oxygen & nitrogen (high mass) Clear & stable Follow up questions: 1. Describe the wind motion in the H. 2. Describe the wind motion in the L. 3. In what area is the wind speeds the greatest? 4. Winds go from ___ to ____ for pressure. 5. What type of weather is associated with high pressure systems? 6. What type of weather is associated with low pressure systems? * Answer questions 17-23 pg 433 blu text.