Stoichiometry
advertisement

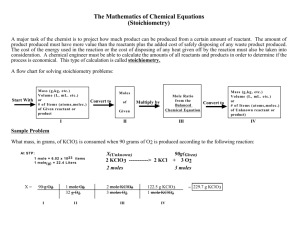
Stoichiometry Devon Bateman Essential Question • Why is a foot…a foot? –King Henry I had a foot 12 inches long. Unit Questions • What are measurements? • What do we measure? • How do we measure? • Why do we measure? • How do chemists measure molecules? Overview • Measurement – List examples of measurement – Define purpose of measurement – Explain chemist’s use of the mole • Stoichiometry – Relate stoichiometry to a recipe – Demonstrate mole ratios in balanced equations WHAT DO WE MEASURE AND HOW? • Measurements allow us compare or analyze data. • Therefore, measurements must be reasonable. • How do chemists count molecules? • Can chemists count by measuring? Chemists count using the mole. • Mole: the unit used to measure the amount of a substance • 1 mole = 6.02x1023 particles • Stoichiometry- the study of mole and mass relationships in a chemical reaction http://www.lsua.us/chem1001/stoichiometry/stoichiometry.html • The mass of the reactants must equal the mass of the products. H2 + Cl2 2 HCl • A balanced chemical equation is very similar to a recipe. • Coefficients represent the mole ratio between substances. 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O Example 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 • It takes 4 moles iron & 3 moles oxygen to produce 2 moles iron (III) oxide. Conclusion • The mole allows chemists to analyze chemical reactions. • Balanced equations can be treated like recipes. • Amount of ingredients determines the amount of product