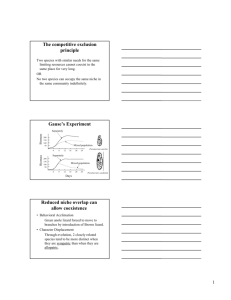
Communities
advertisement

Ecology Part 3 Communities In: pg 30 What is a community? Answer in blue, black or Pencil. What is a community? Do it Now Pg. 30 • What is your niche or what do you think niche means in biological terms? • Answer in blue, black or Pencil. Lap top Day • • • • • • • • • Get your computer – Laptop Plug in to the ether net cable Log on Use Google Chrome and go on line to my.ccsd.net Search Vincent Ossana Biology Resources Ecology 3 power point load power point Unplug from ether net and take your computer back to your table. 31 Title Page 31 1. Write the topic for the unit in the middle of the paper and box it in. 2. Divide the paper into 3 equal sections. 3. Put a subtopic/key word in each section. 4. Add an appropriate picture to each section(no stick figures). 5. Each section must have 3 different colors(black and white don’t count). Don’t use the same 3 colors for 2 different sections. Biodiversity Unit 2:Ecosystem Dynamics: Biodiversity Niche Extinction Communities PG. 33 Cornell Notes found on my.ccsd.net Vincent Ossana Biology Resources Ecology Power Point 3 Why are certain populations found in a community? • Limiting factors-any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts organisms in the environment. What are Community Interactions • Predation(+-) – One organism kills and eats another organism. • Competition(--) – 2 organisms are competing for the same resource. – May be interspecific (between members of different species) or intraspecific (between members of the same species). • Habitat-place where an organism lives. • Niche-role and position a species has in its environment. – Organisms with the same niche compete if they are in the same habitat. What is Stability • Disturbance-events that change a community by removing organisms or changing resource availability. • Stability is the ability to resist disturbance and not change. What is Biodiversity • The variety of life in an area. • Extinction is when the last individual of a species disappears. – Endangered species=species that are likely to become extinct. – Threatened species=species that are close to becoming endangered. • Biodiversity increases the stability of a community Vocabulary :pg 32 3 Column Vocab 1. Biodiversity 2. Habitat 3. Niche 4. Interspecific Competition* 5. Intraspecific Competition* 6. Predation* 7. Limiting factors 8. Succession 9. Disturbance* 10. Stability* 11. Extinction 12. Threatened species 13. Endangered species 14. Exotic species *In notes, not in textbook Do it again Pg. 30 • Why is niche an important concept to understand? • Answer in blue, black or Pencil. Out Pg. 30 • It is often said that a habitat is the organisms “address” and its niche is like its “job”. Please explain this in 3+ sentences. • Answer in blue, black or Pencil. In Pg. 34 Define – from notes yes you were supposed to do them on your own. 1. Paramecium 2. Intraspecific competition 3. Interspecific competition 4. Competitive exclusion principle Do it Now Pg. 34 • What is your niche at home? • Answer in Blue, Black or Pencil. Pg. 35 - Niche worksheet 100pts • Answer the Questions on the worksheet called Climate and Life about Niche. • Staple tape or Glue this into page 35. • Paramecium are microscopic, unicellular protists that live in water. • The 2 species we are looking at do not eat each other, it isn’t a predator prey relationship. • They compete for the same food. Paramecium are predators that feed on algae and bacteria https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a4aZE5FQ284 Lab Pg. 36 & 37Virtual Lab: Competing Paramecium Pg. 36 Analysis Questions 1. What is exponential growth? 2. What is carrying capacity? 3. What is competition? • Pg. 37 – Staple tape or glue the lab sheet into your notebook. • Lab sheet must be glued so you can see it when it opens. Do it again Pg. 34 • Which axis do the independent and dependent variables go on? Out pg. 34 In the virtual lab, 1. What were the paramecium competing for? 2. Was this inter or intraspecific competition? In: pg 38 1. When the number of rabbits is high, the lynx (increase/decrease). 2. When the number of lynx is high, the rabbits (increase/decrease). 3. What negative effect would the removal of the lynx have on the rabbit population? Do it now Pg. 38 • So how do niche and carrying capacity work with each other? Deer of the Kaibab pg. 39 • Staple tape or glue Deer of the Kaibab into your notebook after you finish the Sea otter project. • You will be working on the hand out first then you will write the otter questions after that appear on the next slide. Sea Otter - Enhydra lutris Pg. 39 Article: Ocean Keepers write out questions: 1. What is kelp? 2. Why are scientists keeping a close eye on the sea otter? 3. What is an ecosystem? 4. Why was the sea otter population almost wiped out in the 1700-early 1900’s? 5. What is causing the sea otters to die out now? 6. What parasites are infecting sea otters? 7. How do the parasites get inside the sea otter? 8. What is a keystone species? 9. Why are otters considered a keystone species? 10. How do sea otters keep kelp populations healthy? In: pg 40 – 100pts Watch the movie clip ”Khan Academy: Disturbance” and explain the following terms(9 minutes) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Primary succession Pioneer species Secondary succession Climax community Intermediate disturbance hypothesis https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/crash-course-bioecology/crash-course-ecology-2/v/crash-course-ecology-06 Do it now Pg. 40 • What would happen to Las Vegas if all of the people left one night and never came back? (You need word your answer using the succession terms learned in the video) Mt. St Helens Project pg. 41 Mount St. Helens: A Story of Succession Questions • Read Mount St. Helens: A Story of Succession and answer the questions • Tape the completed question sheet on this page. • Succession is a change in the species that make up a community over time. • If a community is disturbed it has to “start over” – Primary succession-development of a community in an area that has not supported life before—no soil. – Secondary succession-sequential replacement of an existing community following a disturbance (fire , flood, landslide,etc.) Wed 10/14 and Thurs 10/15 In: pg 42 • Species can be native or endemic to their habitat, that means they occur naturally. Exotic species or Introduced species are not native to an area. Sometimes an exotic species will overwhelm native species and cause harm, when this happens the exotic species is called an invasive species. • Do you think the following species are Endemic, Exotic or Invasive in Southern Nevada? 1. 8. 1. Dog 2. Desert Tortoise 3. Tumble weed 4. Pigeon 5. Coyote 6. African honeybee 7. Mustang 8. Roadrunner Do it again Pg. 42 • Why do you think invasive species are bad for an area? Notes pg. 43 – not Cornell use the diagram we will make. The number of different ecosystems created by unique interactions between biotic and abiotic factors. Ecosystem Diversity Types of Types of Biodiversity Biodiversity How many different ecosystems do you see? Thru 1:pg Measured by species richness-the number of different species in an ecosystem. Species Diversity Types of Types of Biodiversity Biodiversity Which has more species diversity? Thru 1:pg Types of Types of Biodiversity Biodiversity Genetic Diversity The number of genetic variations (genes) between members of the same species. High Genetic Diversity Thru 1:pg Measured by species richnessthe number of different species in an ecosystem. Species Diversity The number of different ecosystems created by unique interactions between biotic and abiotic factors. Ecosystem Diversity Types of Types of Biodiversity Biodiversity Genetic Diversity The number of genetic variations (genes) between members of the same species. Thru 2 Pg. 44 Top 10 #5 Cartoon • Pick ANY concept we have talked about in this chapter. • Make sure you read the directions on your Top10 sheet. Pg. 65 Invasive Species Web Quest • Answer the 12 questions here. • You do not need to write out the questions. Do it again pg. 42 • Why might an invasive species be released into an area on purpose? Out Read the comic below and then select the response that best matches your response. Pick 1 Which of the following best matches how you would respond to releasing the crawdad (i.e. crayfish) into a non-native environment? • Releasing one crayfish into the creek will have no impact on the organisms that currently live there. • The crayfish will adapt to its environment or die because nature works on the rule of “survival of the fittest.” • Introducing the crayfish to a new environment could have a serious impact on the organisms that currently live there. Why did you select your response? Please explain your logic in more detail. Fri 10/16 and Mon 10/19 • Quiz #6 today-get out paper and your INB • Test and INB check next class. Quiz #6 In: pg 62 6 Facts Endangered Species Act Thru 1: pg. 63 Movie: Extinction • Complete the questions on this page as you watch the movie. Out One of the first mass extinction events was when the dinosaurs were wiped out by a meteor impact. Scientist say we are currently in the Sixth Mass Extinction. What is the primary cause of the Sixth Mass Extinction? A tree left behind in a deforested Amazon rainforest Old stuff Symbiotic relationships Symbiosis-living together • Parasitism (+-) – A parasite lives off of a living host. • Mutualism(++) – Both species benefit from the relationship. • Commensalism(+0) – One organism benefits, the other organism is not affected. Thru 2 Pg 48 Pg 49 Human Population More/ Less Map • Create a More/Less map with your group on the white board. – Start by placing the “More People” card in the center of the board. – Place the remaining cards around the central idea of “More People”. – Draw arrows to represent logical connections between the cards. All cards must be used. – There are 4 blank cards. Write a “more or less” statement on each blank card and incorporate it into your “More/Less” Map. • Copy the More/Less map into your INB—you can use both pages. More/Less Map More More Fossil fuel use Energy use More CO2 emissions More People Out • What are some negative consequences of increasing human population? • What are some of the positive consequences? In: pg 142 1. What is the difference between population size and population density? 2. Where is the greatest human population density on the globe? Human population • Human population is experiencing exponential growth. • As of October 12, 1999, the human population on earth was 6 billion. As of 2006, it was more than 6.5 billion. What do you think our carrying capacity is? •How many people can the earth hold? World population clock In: Pg 146 • Watch the “World Population” clip. What are 5 things you notice about human population growth? Homework • Finish vocab Out • The first species to come in after a disturbance is called a pioneer species—where do you think this name came from? Mon. 5/20 and Tues. 5/21 • Quiz #6 today! • Test and INB check next class! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. INB quiz #6 The number of individuals per area is the population ________. Pg 139. What is the answer to # 4? Pg 139. What is the answer to # 11? Pg. 139 What is the answer to # 23? Pg. 139 What is the answer to #29? Is flooding a density independent or density dependent factor? What are the first species into an area after a disturbance called? What community interaction is (+, +)? A ________is the role or position a species has in the environment. ________ is the ability to resist disturbance. In: pg 150 • What are 3 adaptations that prey species have evolved to escape predators? In: Pg 58 • In order for California sea otters to be taken off the list of threatened species--part of the 1977 Endangered Species Act--the population needs to reach at least 3,090 animals and remain at that level for three consecutive years. 1. How many sea otters were there in 2004? 2. How many more otters does the population need to not be considered threatened? 3. In the future, do you think the sea otters will be taken off the list? Why? Thru 1: pg. 151 • Movie: Baking Deserts Organism 1. Adaptation 15. Organisms 1. 5. Interaction