Monopolistic Competition
advertisement

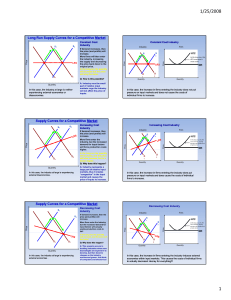
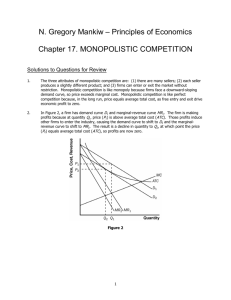
*Monopolistic Competition 1 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Pure Monopoly Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition: • Relatively Large Number of Sellers • Differentiated Products • Some control over price • Easy Entry and Exit (Low Barriers) • A lot of non-price competition (Advertising) 2 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Examples: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Fast Food Restaurants Furniture companies Jewelry stores Hair Salons Clothing Manufacturers 3 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 “Monopoly” + ”Competition” Monopolistic Qualities • Control over price of own good due to differentiated product • D greater than MR • Plenty of Advertising • Not efficient Perfect Competition Qualities • Large number of smaller firms • Relatively easy entry and exit • Zero Economic Profit in Long-Run since firms can enter/exit 4 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Differentiated Products Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 5 Differentiated Products • Goods are NOT identical. • Firms seek to capture a piece of the market by making unique goods. • Since these products have substitutes, firms use NON-PRICE Competition. 6 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Examples of NON-PRICE Competition •Brand Names and Packaging •Example? •Product Attributes •Example? •Service •Example? •Location •Example? •Advertising •Example? •Two Goals 1. Increase Demand 2. Make demand more INELASTIC Monopolistic Competition *Firm’s demand curve *How does it compare to previous models? *Down-sloping and highly elastic (Why?) *Elasticity depends on number of rivals and degree of product differentiation *Short run profit or loss *How is profit maximized? *Produce where MR=MC *Long run profit/loss? *Normal profit *Easy entry and exit *Inefficient 11-8 *Drawing Monopolistic Competition 9 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Monopolistic Competition is made up of prices makers so MR is less than Demand In the short-run, it is the same graph as a monopoly making profit P MC ATC P1 In the long-run, new firms will Denter, driving down the DEMAND for firms already in the market. MR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Q1 Q 10 *Why does DEMAND shift? When short-run profits are made… *New firms enter. *New firms mean more close substitutes and less market shares for each existing firm. *Demand for each firm falls. When short-run losses are made… *Firms exit. *Result is less substitutes and more market shares for remaining firms. *Demand for each firm rises. 11 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Firms enter so demand falls until there is no economic profit P MC ATC P1 D MR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Q1 Q 12 Firms enter so demand falls until there is no economic profit Price and quantity falls and TR=TC P MC ATC PLR D MR QLR Q 13 LONG-RUN EQUILIBRIUM Quantity where MR =MC up to Price = ATC P MC ATC PLR D MR QLR Q 14 What happens when there is a loss? In the short-run, the graph is the same as a monopoly making a loss ATC P MC P1 In the long-run, firms will leave, D driving up the DEMAND for firms already in the market. MR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Q1 Q 15 Firms leave so demand increases until there is no economic profit ATC P MC P1 D MR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Q1 Q 16 Firms leave so demand increases until there is no economic profit Price and quantity increase and TR=TC ATC P MC PLR D MR QLR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Q 17 * *A normal profit is the result in the theoretical model, but in the real world, variables can create variation from the model. *Stronger product differentiation may produce more monopolistic power and long-term economic profits *Air Jordan, anyone? *Barriers to entry may differ from industry to industry *Ex: Large scale shoe manufacturer vs. local cobbler * *What three options can a monopolistically competitive firm undertake to gain/sustain an economic profit? *1. Reduce costs *2. Increase demand (and costs?) for their product through differentiation *3. Increase demand (and costs) through advertising *Are Monopolistically Competitive Firms Efficient? 20 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Long- Run Equilibrium Not Allocatively Efficient because P MC Not Productively Efficient because not producing at Minimum ATC P MC ATC PLR D MR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 QLR QProd Efficient QSocially Optimal Q 21 Long- Run Equilibrium This firm also has EXCESS CAPACITY P MC ATC PLR D MR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 QLR QProd Efficient Q 22 Excess Capacity • Given current resources, the firm can produce at the lowest costs (minimum ATC) but they decide not to. • The gap between the minimum ATC output and the profit maximizing output. • Not the amount underproduced 23 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Long- Run Equilibrium The firm can produce at a lower cost but it holds back production to maximize profit P MC ATC PLR D Excess Capacity Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 MR QLR QProd Efficient Q 24 Monopolistic Competition is inefficient, but other benefits accrue to society… • Product Variety – More Choices! – #AMERICA! • Innovation – Better Stuff! Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 25 Practice Question Assume there is a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. 26 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 2008 Audit Exam