Perfect Competition
advertisement

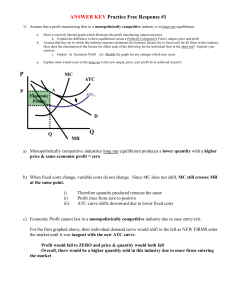
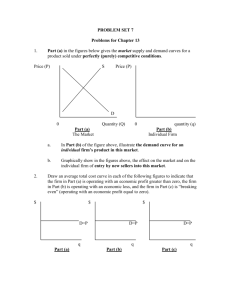
Perfect Competition in the Long-Run You are a wheat farmer. You learn that there is a more profit in making corn. What do you do in the long run? Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 1 In the Long-run… •Firms will enter if there is profit •Firms will leave if there is loss •So, ALL firms break even, they make NO economic profit (No Economic Profit = Normal Profit) •In long run equilibrium a perfectly competitive firm is EXTREMELY efficient. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 2 Side-by-side graph for perfectly completive industry and firm in the LONG RUN Is the firm making a profit or a loss? Why? P S P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D 5000 Industry Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Q 8 Q Firm (price taker) 3 Firm in Long-Run Equilibrium ***Price = MC = Minimum ATC*** Firm is making NO economic profit Firm is making positive accounting profit P MC ATC $15 MR=D There is no incentive to enter or leave the industry TC = TR Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 8 Q 4 4 Going from Short-Run to Long-Run Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 5 1. 2. 3. 4. Is this the short or the long run? Why? What will firms do in the long run? What happens to P and Q in the industry? What happens to P and Q in the firm? P S P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D 5000 6000 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry 8 Firm Q 6 Firms enter to earn profit so supply increases in the industry Price decreases and quantity increases P S P MC S1 ATC $15 MR=D $15 $10 D 5000 6000 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry 8 Firm Q 7 Price falls for the firm because they are price takers. Price decreases and quantity decreases P S P MC S1 ATC $15 $15 MR=D $10 $10 MR1=D1 D 5000 6000 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry 5 8 Firm Q 8 New Long Run Equilibrium at $10 Price Zero Economic Profit P P MC S1 ATC $10 MR1=D1 $10 D 5000 6000 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry 5 Firm Q 9 1. 2. 3. 4. Is this the short or the long run? Why? What will firms do in the long run? What happens to P and Q in the industry? What happens to P and Q in the firm? P S P $15 MC ATC MR=D $15 D 4000 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 8 Firm Q 10 Firms leave to avoid losses so supply decreases in the industry Price increases and quantity decreases S1 P S P MC ATC $20 $15 MR=D $15 D 4000 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 8 Firm Q 11 Price increase for the firm because they are price takers. Price increases and quantity increases S1 P S P $20 MC $20 $15 $15 ATC MR1=D1 MR=D D 4000 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 89 Firm Q 12 New Long Run Equilibrium at $20 Price Zero Economic Profit S1 P P $20 MC $20 ATC MR1=D1 D 4000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 9 Firm Q 13 Going from Long-Run to Long-Run Constant Cost Industry- New firms entering the market does not increase the costs for the firms already in the market. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 14 Currently in Long-Run Equilibrium If demand increases, what happens in the short-run and how does it return to the long run? P S P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 8 Firm Q 15 Demand Increases The price increases and quantity increases Profit is made in the short-run P S P MC ATC $20 $20 $15 $15 MR1=D1 MR=D D1 D 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 8 9 Firm Q 16 Firms enter to earn profit so supply increases in the industry Price Returns to $15 P S S1 P MC ATC $20 $20 $15 $15 MR1=D1 MR=D D1 D 5000 7000 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry 8 9 Firm Q 17 Back to Long-Run Equilibrium The only thing that changed from long-run to long-run is quantity in the industry S1 P P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D1 D 7000 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry 8 Firm Q 18 What if demand falls? If demand decreases, what happens in the shortrun and how does it return to the long run? P S P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 8 Firm Q 19 Demand Decreases The price decreases and quantity decreases Loss is taken in the short-run P S P MC ATC $15 $10 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 MR=D $15 $10 D1 D Q Industry MR1=D1 7 8 Firm Q 20 Firms exit to avoid losses so supply decreases in the industry Price Returns to $15 S1 P S P MC ATC $15 $10 MR=D $15 $10 3000 5000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 D1 D Q Industry MR1=D1 7 8 Firm Q 21 Back to Long-Run Equilibrium The only thing that changed from long-run to long-run is quantity in the industry S1 P P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D1 3000 Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q 8 Firm Q 22 Practice 23 2012 Multiple Choice #23 24 2012 Multiple Choice #38 25 2010 FRQ #1 27 28 Going from Long-Run to Long-Run Increasing Cost Industry- New firms entering the market increase the costs for the firms already in the market. (Only asked once on a FRQ- 2011 Form B) Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 29 Currently in Long-Run Equilibrium If demand increases, what happens in the short-run and how does it return to the long run? P S P MC ATC $15 MR=D $15 D Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q Firm 30 INCREASING COST Industry The price increases and quantity increases Profit is made in the short-run P S P MC $25 $25 ATC $15 $15 MR=D D1 D Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q Firm 31 Firms enter to earn profit but fight for resources causing costs to increase Price Falls to $20 $25 $25 MC1 MC ATC1 ATC $20 $15 $15 MR=D P S P S1 D1 D Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q Firm 32 Firms enter to earn profit but fight for resources causing costs to increase Price Falls to $20 P S1 MC1 P ATC1 MR1 $20 D1 Q Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 Industry Q Firm 33 2008 Audit Exam Efficiency Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 35 In general, efficiency is the optimal use of societies scarce resources •Perfect Competition forces producers to use limited resources to their fullest. •Inefficient firms have higher costs and are the first to leave the industry. •Perfectly competitive industries are extremely efficient There are two kinds of efficiency: 1. Productive Efficiency 2. Allocative Efficiency Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 36 Productive Efficiency- Producing at the lowest possible cost (minimum amount of resources are being used) Graphically it is where price equals the minimum ATC Allocative Efficiency- Producing at the amount most desired by society (allocating resources towards the products society wants) Graphically it is where price equals marginal cost Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 37 Long-Run Equilibrium Single Firm P=MC=Minimum ATC (Normal Profit) Market MC S Price Price ATC MR P P D 0 Qf Quantity 0 Qe Quantity Productive Efficiency: Price = minimum ATC Allocative Efficiency: Price = MC Pure competition has both in its long-run equilibrium What about in the short run? 9-38 Summary Perfectly competitive firms are allocatively and productively efficient in the long-run In the short-run, they are always allocatively efficient, but they are not productively efficient. Copyright ACDC Leadership 2015 40