Nerve - Mahidol University
advertisement

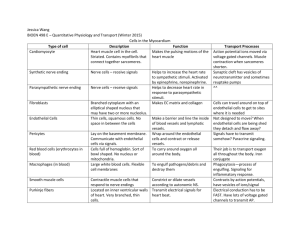
The Upper Limb Viroj Mitranonda Department of Anatomy Faculty of Science Mahidol University Parts of the upper limb •Shoulder or Scapular region •Arm •Forearm •Hand Bones • Shoulder : Scapula, Clavicle • Arm : Humerus • Forearm : Radius, Ulna • Hand : 8 carpal bones, : 5 metacarpal bones, : 14 phalanges • carpal bones : trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate : scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform Superficial structures of the upper limb •Cutaneous nerves •Superficial veins •Lymph vessels Cutaneous nerves of the upper limb •Shoulder : Lateral branches of the supraclavicular n.(c.3,4) •Arm : Upper lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (axillary n.) : Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (radial n.) : Medial cutaneous nerve of arm (medial cord) : Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (radial n.) : Intercosto-brachial nerve (T.2) Cutaneous nerves of the upper limb (continued) Forearm •Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm (from musculocutaneous n.) •Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (from medial cord) •Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm (from radial n.) Cutaneous nerves of the upper limb (continued) Hand •Lateral 3 1/2 •of the palm : Cutaneous branches of the median n. •of the dorsum : Cutaneous branches of the radial n •Medial 1 1/2 •of the palm : Cutaneous branches of the ulnar n. •of the dorsum : Cutaneous branches of the ulnar n. •Distal part of the dorsum of the lateral 3 1/2 fingers : •Cut. br. of the median n. Superficial veins of the upper limb •Digital veins •Dorsal venous arch •Cephalic vein •Basilic vein •Median cubital vein •Median veins of forearm •(Median cephalic vein) •(Median basilic vein) The lymph vessels •Accompanied the superficial veins •The medial side •drains to the lateral group of the axillary node •The lateral side •drains to the delto-pectoral node Muscles found in the shoulder (scapular) region •Deltoideus muscle •Supraspinatus muscle •Infraspinatus muscle •Teres minor muscle •Subscapularis muscle •Teres major muscle •Axillary nerve •Suprascapular nerve •Suprascapular nerve •Axillary nerve •Upper and Lower subscapular nerves •Lower subscapular nerve The rotator cuff muscles Consists of : •Supraspinatus m. •Infraspinatus m. •Teres minor m. •Subscapularis m. Deltoideus muscle •Origin : Lateral 1/3 of clavicle, : Acromion, Spine of scapula •insertion : Humerus, deltoid tuberosity •Action : Arm Flexion, medial rotation, Abduction, extension, lateral rotation •nerve : Axillary nerve Supraspinatus muscle •Origin : Scapula, supraspinous fossa •Insertion : Upper facet of greater tuberosity of Humerus •Action : Abduction •Nerve : Suprascapular nerve Infraspinatus muscle Origin : Scapula, infraspinous fossa Insertion : Middle facet of greater tuberosity of the Humerus Action : Lateral rotation Nerve : Suprascapular nerve Teres minor muscle Origin : Scapula, superior 2/3 Lateral margin Insertion : Lower facet of greater tuberosity of the Humerus Action : Lateral rotate nerve : Axillary nerve Subscapularis muscle •Origin : Scapula, subscapular fossa •Insertion : Lesser tuberosity of the Humerus •Action : Medial rotation •Nerve : Upper and lower subscapular nerve Teres major muscle •Origin : Inf. 1/3 lat. margin of scapula •Insertion : Humerus, crest of lesser tubercle •Action : Adduction,medial rotate, extension •Nerve : Lower subscapular nerve The arm Flexor muscles of the arm •Coracobrachialis m. •Biceps brachii m. •Brachialis m. •Musculocutaneous n. •Musculocutaneous n. Extensor muscle of •Musculocutaneous & radial the armnn. •Triceps brachii m. •Radial n. Biceps brachii muscle •Origin : Short head; Coracoid process : Long head; Supraglenoid tubercle •Insertion : Radial tuberosity, bicipital aponeurosis •Action : Supination, flexes elbow •Nerve : Musculocutaneous nerve Coracobrachialis muscle •Origin : Coracoid process •Insertion : Humerus, middle of body,medial •Action : Flexion (flexes shoulder) •Nerve : Musculocutaneous nerve Brachialis muscle •Origin : Humerus, ant. surface distal 1/2 •Insertion : Ulna, coronoid process, ulnar tuberosity •Action : Flexes elbow •Nerve : Musculocutaneuos n. & radial n. Cubital fossa Boundaries •Base •Laterally •Medially •Apex •Roof •Floor •Contents : Imaginary line between the condyles of the humerus : Brachioradialis muscle : Pronator teres muscle : Brachioradialis m. overlapped Pronator teres m. : Skin, superficial fascia & veins, bicipital aponeurosis : Brachialis m.,Supinator m. : Tendon of Biceps brachii m. Brachial a. and its’ terminal branches(radial a. and ulnar a.) Median n., fat Triceps brachii muscle •Origin : Long head;Scapula, infraglenoid tubercle : Lateral head; Humerus, post. surface above groove for radial nerve : Medial head; below groove for radial n. •Insertion : Ulna,olecranon process •Action : Extends elbow •Nerve : Radial nerve The forearm Flexor muscles of forearm Superficial layer •Pronator teres muscle •Flexor carpi radialis muscle •Palmaris longus muscle •Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle Median nerve Median nerve Median nerve Ulnar nerve Flexor muscles of forearm (continued) Intermediate layer •Flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis) muscle Median nerve Deep layer •Flexor pollicis longus muscle •Flexor digitorum profundus muscle •Pronator quadratus muscle Median nerve Median&Ulnar nn. Median nerve Pronator teres muscle •Origin : Medial epicondyle of humerus, : Coronoid process of ulna •Insertion : Midlateral surface of radius •Action : Pronation •Nerve : Median nerve Flexor carpi radialis muscle •Origin : Medial epicondyle of humerus •Insertion : Base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones •Action : Flexes and abducts wrist (hand) •Nerve : Median nerve Palmaris longus muscle •Origin •Insertion •Action •Nerve : Medial epicondyle of humerus : Palmar aponeurosis : Flexes wrist : Median nerve Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle •Origin : Medial epicondyle of humerus, Upper dorsal border of ulna •Insertion : Pisiform bone (& base of 5th metacarpal bone) •Action : Flexes wrist, adduct wrist (hand) •Nerve : Ulnar nerve Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle •Origin : Medial epicondyle of humerus, Coronoid process of ulna, Oblique line of radius •Insertion : Middle phalanges of medial four fingers •Action : Flexes middle phalanges of each finger, Flexion of MP & PIP joints •Nerve : Median nerve Flexor pollicis longus muscle •Origin •Insertion •Action •Nerve : Radius, ant. surface middle 1/2 : Distal phalanx of thumb : Flexes thumb : median nerve Flexor digitorum profundus muscle •Origin : Ulna, prox. 2/3 ant. and medial surfaces •Insertion : Bases of distal phalanges of medial four fingers •Action : Flexes distal phalanges of each finger (DIP joints) Flexes MP & IP joints (PIP joints) •Nerve : Median and ulnar nerves (lateral 1/2 : median nerve, medial 1/2 : ulnar nerve) Pronator quadratus muscle •Origin •Insertion •Action •Nerve : Ulna, ant. surface distal 1/4 : Radius, ant. surface distal 1/4 : Pronation. Holds radius to ulna : Median nerve THE HAND Viroj Mitranonda Department of Anatomy Faculty of Science Mahidol University Muscles of the hand 3 Thenar muscles : •Abductor pollicis brevis m. •Median n. •Flexor pollicis brevis m. •Median n. •Opponens pollicis m. •Adductor pollicis m. •Median n. •Ulnar n. Muscles of the hand (continued) 3 Hypothenar muscles : •Abductor digiti minimi m. •Flexor digiti minimi m. •Opponens digiti minimi m. •Ulnar n. •Ulnar n. •Ulnar n. •3 Palmar interossei mm. •Ulnar n. •4 Dorsal interossei mm. •Ulnar n. •4 Lumbricales mm. •1st and 2nd Median n. Palmaris brevis m. •3rd and 4th Ulnar n. Ulnar n. Extensor muscles of forearm Superficial group Laterally •Brachioradialis m.* •Extensor carpi radialis longus m. * •Extensor carpi radialis brevis m.** Posteriorly •Extensor digitorum m.** •Extensor digiti minimi m.** •Extensor carpi ulnaris m.** •Anconeus m.* * = Radial nerve ** = deep branch of radial nerve Extensor muscles of forearm (continued) Deep group •Supinator m. •Abductor pollicis longus m. •Extensor pollicis brevis m. •Extensor pollicis longus m. •Extensor indicis m. Nerve supply : Deep branch of radial nerve or posterior interosseous nerve Brachioradialis muscle •Origin : Humerus, lateral supracondylar line •Insertion : Radius, base of styloid process •Action : Flexes elbow •Nerve : Radial nerve Extensor carpi radialis longus muscle •Origin : Humerus, lateral supracondylar line •Insertion : Base of second metacarpal bone •Action : Extends wrist, abduct hand •Nerve : Radial nerve Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle •Origin •Insertion •Action •Nerve : Humerus, lateral epicondyle : Base of third metacarpal bone : Extends wrist, abduct hand : Deep branch of the radial nerve Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle •Origin : Lateral epicondyle of humerus, posterior border of ulna •Insertion : Base of fifth metacarpal bone •Action : Extends wrist, adduct hand •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve Extensor digitorum muscle •Origin : Humerus, lateral epicondyle •Insertion : Middle and distal phalanges, extensor expansion •Action : Extends phalanges •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve Extensor digiti minimi muscle •Origin : Humerus, lateral epicondyle •Insertion : Extensor expansion of fifth digit •Action : Extends fifth digit •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve Anconeus muscle •Origin : Lateral epicondyle of humerus •Insertion : Proximal 1/3 lat. surface of ulna •Action : Holds ulna to radius, extends elbow •Nerve : Radial nerve Supinator muscle •Origin : Humerus, lateral epicondyle : Ulna, supinator crest •Insertion : Proximal 1/3 of radius •Action : Supination •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve Abductor pollicis longus muscle •Origin : Radius and ulna distal to supinator m. •Insertion : Base of first metacarpal bone •Action : Abducts thumb •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve (Posterior interosseous nerve) Extensor pollicis brevis muscle •Origin : Radius, posterior surface •Insertion : Base of proximal phalanx of thumb •Action : Extends thumb •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve (Posterior interosseous nerve) Extensor pollicis longus muscle •Origin : Middle 1/3 post. surface of ulna •Insertion : Distal phalanx of thumb •Action : Extends thumb •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve (Posterior interosseous nerve) Extensor indicis muscle •Origin : Ulna, posterior surface •Insertion : Extensor expansion •Action : Extends index •Nerve : Deep branch of radial nerve (Posterior interosseous nerve) Out cropping muscles •Abductor pollicis longus m. •Extensor pollicis brevis m. •Extensor pollicis longus m. : Bounded the anatomical snuff box Tendon of the muscles in the fascial tunnels •2 = Abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis •3 = Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis •1 = Extensor pollicis longus •5 = Extensor digitorum and extensor indicis •6 = Extensor digiti minimi •4 = Extensor carpi ulnaris Arthrology (Study of joint) 1. According to the movement 1.1 Immovable or synarthrosis eg. suture 1.2 Slightly movable or amphi(ar)throsis • Fibrous tissue lies between the bones (syndesmosis) eg. Intermediate radio-ulnar jt. • Cartilage joins the bones (synchondrosis) eg. Pubic symphysis, intervertebral disc, sterno-costal joint 1.3 Freely movable (diarthrosis) • have joint cavity, joint capsule eg. Shoulder joint, elbow joint 2.According to the structures found in the joint 2.1. Fibrous joint •there are fibrous tissue in the joint eg. Suture, radio-ulnar joint, tibio-fibular joint 2.2. Cartilagenous joint •there are cartilage in the joint eg. Pubic symphysis, sterno-costal joint 2.3. Synovial joint General patterns of synovial joint •There are at least 2 bones •It’s articular surfaces lied with hyaline cartilage (articular cartilage) •It has articular or joint capsule •It has joint cavity •Inner surface of the joint capsule lied with synovial membrane which secrete the synovial fluid or synovia Classification of the synovial joint Classified into 7 types 1. The ball and socket type • For example : shoulder joint • Bones : humerus and scapula • Ball : the head of the humerus • Socket : primary socket is the glenoid cavity of the scapula : secondary socket is the coraco-acromial ligament The ball and socket type (continue) • Movement : multiaxial - flex, extend, adduct,abduct and circumduct •Joint capsule : thin fibrous membrane •Ligaments : coraco-humeral, superior, middle and inferior gleno-humeral ligaments 2. Hinge type •For example : the elbow joint •Bones : humerus, ulna and radius •Movement : around horizontal axis; flex and extend •Joint capsule : thin at the anterior and posterior sides : thicken at medial and lateral sides •Ligaments : medial or ulnar collateral ligament : lateral or radial collateral ligament 3. Pivot type •For example : proximal radio-ulnar joint •Bones : radius and ulna •Movement : around the vertical axis ; medial and lateral rotation •Ligament : annular ligament 4. Ellipsoidal type •For example : wrist or radio-carpal joint •Bones : distal end of radius, scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum •Movement : modified hinge type; flex, extend, adduct and abduct •Ligaments : medial or ulnar collateral ligament : lateral or radial collateral ligament 5. Plane or gliding type •For example : intercarpal joints •Bones : carpal bones •Movement : gliding •Ligaments : interosseous ligaments 6. Saddle type •For example :1st carpometacarpal joint •Bones : 1st metacarpal bone and trapezium •Movement : flex, extend, adduct, abduct and circumduct 7. Condyloid type •For example : metacarpophalangeal joint (MP) interphalangeal joint (IP) •Bones : metacarpal bone, phalanges •Movement : flex and extend, (adduct, abduct) •Ligaments : medial and lateral collateral ligaments Joints of the upper limb • Sternno-clavicular joint • Coraco-acromial joint • Coraco-clavicular joint • Acromio-clavicular joint • Shoulder joint • Elbow joint Joints of the upper limb (continue) • Radio-ulnar joints (prox.,middle and distal) • Wrist or radio-carpal joint • Intercarpal joints • Carpometacarpal joints • Intermetacarpal joints • Metacarpophalangeal joints (MP joint) • Interphalangeal joints (IP joint) NERVE LESIONS OF UPPER LIMBS BY VIROJ MITRANONDA Department of Anatomy Faculty of Science, Mahidol University