SL/AP Biology 9-19-05
advertisement

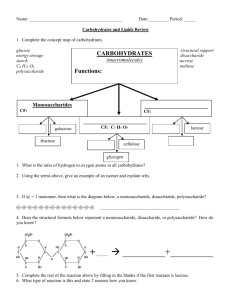
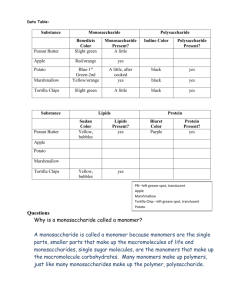
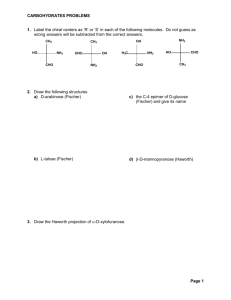
SL/AP Biology 9-19-05 2.2.8 State one function of a monosaccharide and one function of a polysaccharide. List two examples for each of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. 2.2.9 State three functions of lipids. 2.2.10 Discuss the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage. Syllabus Outline for 9-20-05 2.4.1 Outline DNA nucleotide structure in terms of sugar (deoxyribose), base and phosphate. – spatial arrangement is required. 2.4.2 State the names of the four bases in DNA. 2.4.3 Outline how the DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand. Syllabus for 9-21-05 • 2.4.4 Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complementary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. (In other words, which nucleotide bases pair in DNA?) • 2.6.1 Compare the structure of RNA and DNA (In other words, how are they different sugar-wise and nucleotide basewise?) Notes for 9-22-05 • A.2.3 List three sources of lipids in the diet • A.2.6 List four sources of protein in the diet • A.3.1 Discuss the significance of diets which are rich in lipids in relation to obesity and coronary heart disease. • A.3.2 Explain the significance of saturated and unsaturated lipids in relation to a healthy diet. Protein Review 1. Proteins are polypeptides 2. Polypeptides are made with amino acid monomers. Biuret Test • Tests for protein • Solution turns purple when NaOH and CuSO4 are added to the substance tested. How does the Biuret test Work? The Biuret reagent bonds to the peptide bond in a protein and turns purple/violet (very simplistic explanation…) Lipid Review • Lipids are hydrophobic/non-polar – They are non-polar because they have a lot of H-C bonds. (The HYDRO-CARBON bond shares the electrons equally, and this makes it nonpolar/hydrophobic.) • Examples are triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids… Triglycerides are made like this: Sudan Test for Lipid • Put water into a test tube • Put the substance that you are testing into the test tube • Sudan dye is NON-POLAR and will cling to the NON-POLAR lipid and turn it red. • Soap is an emulsifier! Half of the soap molecule is polar, half is non-polar. That is why everything mixes when soap is added! Carbohydrate Review • Carbohydrates are polysaccharides made from long chains of monosaccharides. • Carbohydrates are made from C,H,O. • There is usually one oxygen for every carbon. Specific names for popular carbohydrates Iodine test for Starch/polysaccharide Test for polysaccharide Iodine test: How does it work? • Polysaccharides wrap around iodine. Polysaccharide Polysaccharide wrapped around iodine Benedict’s test for Monosaccharide 1. Add Benedicts to solution and heat. 2. If it turns orange, red, or brown, it has monosaccharide. Bennedict’s test for monosaccharide The more Monosaccharides, the darker the red… Blue (No monosaccharide) green orange red brown (The most monosaccharide) How does the Benedicts test work? (Cu++ ) + (Reducing Sugar) makes (Cu+) So, if there is a monosaccharide in the solution, it will give an electron to the Copper ion with a +2 charge and turn it into Copper Ion with a +1 Charge. This makes the bennedicts solution change colors.