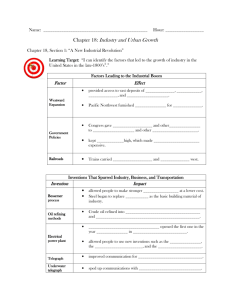
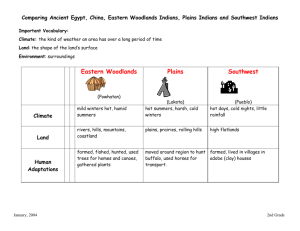
USII * 2a
advertisement

The American Civil War (1861-1865) • 1860 » Lincoln wins presidential election – 7 Southern states declare secession • 1861 » Confederate forces fire on Fort Sumter, in South Carolina (April 12th) • 1862 » Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation • 1863 » Lee’s defeated in Gettysburg • 1864 » Grant fights battles of attrition against Lee • 1865 (April 7th)» Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse Reconstruction • The period of Reconstruction took place in the southern United States from the end of the Civil War in 1865 until 1877. • United States 1861 13th Amendment • Bans slavery in the U.S. and any of its territories • Adopted on December 6, 1865, officially abolished and continues to prohibit slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. The 14th Amendment • Grants citizenship to all persons born in the U.S. and guarantees them equal protection under the law • Passed in 1868 to guarantee due process and equality before the law for all citizens, including newly-freed slaves. – Due Process - A legal concept where a person is ensured all legal rights when he/she is being deprived of life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness for a given reason The 15th Amendment • Ensures all citizens the right to vote regardless of race or color or previous condition of servitude. (1869) • No mention of women in this Amendment, women would gain the right to vote with the passage of the 19th Amendment in 1919. Civil Rights Act of 1866 • A piece of United States legislation that gave further rights to the former enslaved African Americans after the end of the American Civil War. • Authorized the use of federal troops for its enforcement • Legislation = Laws – As citizens they could make and enforce contracts, sue and be sued, give evidence in court, and inherit, purchase, lease, sell, hold, and convey real estate and personal property. Reconstruction • The Reconstruction policies were harsh and created problems in the South. • Reconstruction attempted to give meaning to the freedom that former enslaved African Americans had achieved. Fundamental Issues • Role former Confederates might play in the US government. • Role freed slaves would play in American society. • Infrastructure of the South, where most of the war had been fought, also had to be rebuilt. Policies and Problems • Southern military • Northern soldiers leaders could not hold supervised the South office • Freedman’s Bureau, • African Americans could established to aid hold office former enslaved African Americans in the South • African Americans gained equal rights as a • Southerners resented result of the passing of northern the Civil Rights Act of “carpetbaggers,” who 1866, which authorized took advantage of the federal troops for its South during enforcement Reconstruction Reconstruction Plans • Lincoln: – Reconstruction plan called for reconciliation • Reconciliation - restoration to harmony; renewal of friendship. – Preservation of the Union was more important than punishing the South Reconstruction Plans (cont’d) • Lee: – Urged Southerners to reconcile at the end of the war and reunite as Americans when some wanted to continue to fight – Became president of Washington College which is now known as Washington and Lee college Reconstruction Plans (cont’d) • Douglass: – Fought for adoption of constitutional amendments that guaranteed voting rights – Powerful voice for human rights and civil liberties for all Reconstruction ended with the Election of 1876 • Federal troops removed • Rights that African Americans had gained were lost through Black Codes – Black Codes - laws that placed severe restrictions on freed slaves such as prohibiting their right to vote, forbidding them to sit on juries, limiting their right to testify against white men, carrying weapons in public places and working in certain occupations. Racial Segregation • Based upon race • Directed primarily against African Americans, but other groups also were kept segregated. “Jim Crow” Laws • “Jim Crow” Laws were passed to discriminate against African Americans. “Jim Crow” Laws • Made discrimination practices legal in many communities and states throughout the South • Were characterized by unequal opportunities in housing, work, education, and government. Plessey vs. Ferguson • The case produced the ruling by the Supreme Court that racial segregation was legal and constitutional if there was “separate but equal” facilities for Black and White. • It rested on the question whether the state of Louisiana's law requiring separate railcar facilities for Whites and Blacks were against the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Amendments of the Constitution. African American Response • Booker T. Washington – Believed equality could be achieved through vocational education; accepted social separation – Founded Tuskegee Institute • W.E.B. Du Bois – Believed in full political, civil, and social rights for African Americans. USII – 2b: • Advances in transportation linked resources, products and markets. Advancements in the transportation of resources: • Moving natural resources (e.g. copper and lead) to Eastern Factories Advancements in the transportation of resources: • Moving iron ore deposits to sites of steel mills (e.g., Pittsburgh) Advancements in the transportation of resources: • Transporting finished products to National Markets • National Market – means you can now sell goods all over the country USII – 2a • During the 19th Century, people’s perceptions and use of the Great Plains changed. • Technological advances allowed people to live in more challenging environments Physical Features and Climate of the Great Plains: • Flatlands that rise gradually from east to west. Physical Features and Climate of the Great Plains: • Land eroded by wind and water. Physical Features and Climate of the Great Plains: • Low rainfall Physical Features and Climate of the Great Plains: • Frequent dust storms Physical Features and Climate of the Great Plains: • Because of new technologies, people saw the Great Plains not as a “treeless wasteland” but as a vast area to be settled. Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Barbed wire Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Steel Plows Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Dry Farming Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Sod Houses Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Beef Cattle Raising Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Wheat Farming Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Windmills Inventions and adaptations on the Great Plains: • Railroads USII – 4a • New opportunities and technological advances led to westward migration following the Civil War. • Population changes, growth of cities, and new inventions produced problems in urban areas • Inventions had both positive and negative effects on society Reasons for Westward Expansion: • Opportunities for Land Ownership – Homestead Act Reasons for Westward Expansion: • Technological advances, including the transcontinental railroad Reasons for Westward Expansion: • Possibility of wealth created by the discovery of gold and silver Reasons for Westward Expansion: • Adventure Reasons for Westward Expansion: • A new beginning for former slaves Westward Expansions Impact on American Indians • American Indians opposed western expansion and thus were involved in several battles. – Battle of Little big Horn – Sitting Bull – Geronimo - Apache Leader who escaped capture several times… Westward Expansions Impact on American Indians • Forced relocation from traditional lands to Reservations • Chief Joseph of the Nez Perce, “from where the sun now stands…” Westward Expansions Impact on American Indians • Reduced population through disease and warfare. – Battle of Wounded Knee Westward Expansions Impact on American Indians • Lifestyle changes and assimilation attempts – Reduction of Buffalo population Westward Expansions Impact on American Indians • The expansion reduced their homelands through treaties that were broken. Reasons for Increased Immigration: • Hope for better opportunities Reasons for Increased Immigration: • Religious Freedom Reasons for Increased Immigration: • Escape from oppressive governments Reasons for Increased Immigration: • Adventure Reasons why cities developed: • Specialized industries including: – Steel in Pittsburgh, PA – Meat packing in Chicago, IL – Textile in New England – Automobile in Detroit, MI “Captains of Industry” 1. John D. Rockefeller • Oil 2. Andrew Carnegie • Steel 3. Henry Ford • Automobile 4. Cornelius Vanderbilt • Shipping and Railroads Reasons why cities developed: • Immigration from other countries Reasons why cities developed: • Movement of Americans from rural to Urban areas for job opportunities Inventors that contributed to great change and industrial growth • Thomas Edison Lighting and mechanical uses of electricity • Alexander Graham Bell - Telephone service Rapid industrialization and urbanization led to overcrowded immigrant neighborhoods and tenements. • Some of the efforts to solve immigration problems: – Settlement houses, such as the Hull House founded by Jane Adams – Political machines that gained power by attending to the needs of new Immigrants(e.g., jobs, housing) Some of the challenges faced by cities during this time period • Tenements and Ghettos • Political Corruption (political machines) From Agriculture to Industry Between the Civil War and WWI, the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation Postwar Changes in Farm and City Life • Mechanization (e.g., the reaper) had reduced farm labor needs and increased production Postwar Changes in Farm and City Life • Industrial development in cities created increased labor needs Postwar Changes in Farm and City Life • Industrialization provided access to consumer goods (e.g., mail order catalog) Factors resulting in growth of industry: • Access to raw materials and energy Factors resulting in growth of industry • Availability of a workforce Factors resulting in growth of industry • Inventions Factors resulting in growth of industry • Financial resources (money) Reasons for the rise and prosperity of big business • National Markets created by transportation advances Reasons for the rise and prosperity of big business • Lower – cost production Reasons for the rise and prosperity of big business • Advertising Reasons for the rise and prosperity of big business • Captains of Industry Examples of big business: • Railroads – Cornelius Vanderbilt Examples of big business: • Oil – John D. Rockefeller Examples of big business: • Steel – Andrew Carnegie Examples of big business: • Shipping and Railroads List the products for some “Captains of Industry”: John D. Rockefeller • Oil Andrew Carnegie • Steel Henry Ford • Automobile Cornelius Vanderbilt • Shipping and Railroads Negative Effects of Industrialization: • Child labor Negative Effects of Industrialization: • Low wages and long hours Negative Effects of Industrialization: • Unsafe working conditions Rise of organized labor: • Formation of unions – Growth of the American Federation of Labor Rise of organized labor: • Strikes – Aftermath of Homestead Strike Progressive Movement Workplace Reforms: • Improved safety conditions Progressive Movement Workplace Reforms: • Reduced Work Hours Progressive Movement Workplace Reforms: • Placed Restrictions on child labor Women’s Suffrage • Suffrage is the right to vote • Increased educational opportunities Women’s Suffrage • Attained Voting Rights – Women gained the right to vote with the passage of the 19th amendment to the Constitution of the United States of America – Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton worked for women’s suffrage Temperance Movement • Composed of groups opposed to the making and consuming of alcohol Temperance Movement • Supported the 18th Amendment prohibiting the manufacture, sale, and transport of alcohol.