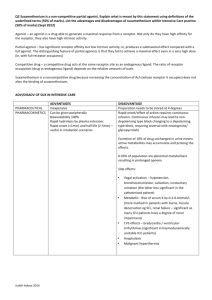
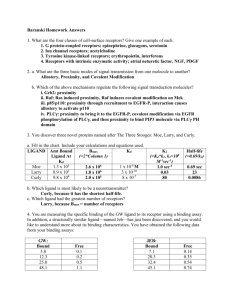
Drugs that do act on receptors
advertisement

Receptors and Drug Action Receptors: •Specific areas of cell membranes (proteins, glycoproteins)* •When bound to ligand, positive or negative biological responce Ligand cellmembrane with receptor Biological responce Extracellular fluid Cell membrane Few ex. of free receptors in cytoplasma Cytoplasma Organelles Cell Nucleus Drugs that do act on receptors: Drugs that do not act on receptors: Acetylcholin (Neurotransmittor) Antacida: CaCO3 + HCl ca. 5Å Acetylcholin Agonists Diuretica (osmotic) O Pilocarpine Carbacholin N O Me N O Akylating agents (cancer) O H H2N O N O O Cl Cl Cl Cl N Nu N Acetylcholin Antagonists N Nu Atropin N Psoralenes N O O O N O NH2 R O O R' O N HN h N N OH O HN Cyclopentolat O N R O O O R' O O O NH2 N OH O Agonist: Binds to (have affinity for) receptor Binding leads to biolog. responce (Agonists have intrinsic activity / efficacy) Antagonist: Affinity for receptor No intrinsic activity N H Binding of ligand to receptor •Covalent bond •Ionic bond •Hydrogen bond •Hydrophobic interaction Covalent bond strong; 50-150 kcal/mol, Normally irreversible bonding ex. Acetylcholine esterase inhibitors Acetylkolin-esteras e N O O Kolin Acyltransferas e Acetylkolin (AcCh) Synapse Nerve cell Effector celle reseptor Nerve potensial AcCh AcCh AcCh AcCh (exess) Ch-acetyltransferase Ch AcCh-esterase Ch N Kolin (Ch) OH Reversible inhibitors O AcCh OH O N O O k3(AcCh) OH O OH N HO O OH Inhibitor Me2N O O R O k3(inhibitor) NMe2 OH O Me2N HO OH R More difficult to cleave Reversible inhibitor (drugs): k3 (inhib) < k3(AcCh) Neostigmin Pyridostigmin N Myastenia gravis (weak muscles, reduced sensitivity to Acetylcholine) O O O N N O N Irreversible Inhibitors Not drugs, nerve gasses, insecticides etc. Gen structur mustard gasses L R2 P O R1 N O L: Leaving group R1: alkoksy R2: alkyl, alkoksy, amino N P F O P O O O O O O Sarin Tabun OH O Aging OH R2 P O OR O P R1 O not tox. Act as mustard gasses Pralidoxim OH HO N L R1 N Me Pralidoxim motgift OH OR O P R1 O N N Me O Malaoxon P O R1 OH only insects O P O O S O O Malation OR L O O S P O S P OR O Ionic bond 5-10 kcal/mol, Reversible bonding Hydrogen bond 2-5 kcal/mol, Reversible bonding Hydrophobic interaction 0.5-1 kcal/mol, Reversible bonding Acetylcholin O O O O H N O O N H Anion cavity N Lipophilic area H H-bind acceptor HO O OH The occupancy theory: The more receptors sites occupied by ligand, the stronger responce The rate theory: The more ligand-receptor interact / unit time, the stronger responce The induced-fit theory: Agonist Receptor Conformation A No ligand bound + Agonist Responce Conformation B + Antagonist Antagonist ConformationA or Inactive conformation C The macromolecular pertubation theory: (induced fit + rate theory) Responce The activation -agregation theory: Always dynamic equilibr. Agonist Responce + Agonist Responce Conformation B (Active) Antagonist + Antagonist Responce Inv. Agonist Responce B (opposite of responce A) Responce A + Inverse agonist Dose-Responce Relationships [A] - equil. towards AB A-B A + B L-R L + R [L] - equil. towards LR ?? L L-R R locked in membrane (do not move freely) L dissolved in extracellular fluid R Reaction on solid - liquid interface Biological responce % biolog. effect % biolog. effect 100 100 50 50 EC50 EC50 [Agonist ligand] log [Agonist ligand] biolog. effect X Y Efficacy (how high activity is possible) Efficacy X = Efficacy Y (both can give 100% responce) Z Efficacy X> Efficacy Z (Z cam only give ca 30% responce) EC50 X and Y Potency (how easily is a given responce reached (ex EC50) EC50 Z Potency X > Potency Y Potency X = Potency Z Potency Z > Potenzy Y log [Agonist ligand] Types of receptors Superfamily Endogenous ligands General structures 1 Fast neurotransmittors ex. Acetylcholine Ligand gated ion chanels 2 Slow neurotransm. ex. noradrenalin Hormones G-Protein coupled receptors 3 Insuline Growth factors Enzyme coupled receptors Catalytic receptors 4 Steroid hormones Thyreoid hormones Vitamin A, D Cytoplasmic receptors Ligand gated ion chanels Ligand binding sites Ligands Fast neurotransmittors ex. Acetylcholine (nicotinic reseptors) Membrane (Phospholipides) Ion chanel Fastest intracellular responce, ms Binding of ligand - opening of chanel - ion (K+, Na+) in or out of cell - responce Nobel prize chemistry 2003, Roderick MacKinnon “for structural and mechanistic studies of ion channels”. http://nobelprize.org/chemistry/laureates/2003/press.html G-Protein coupled receptors G-protein: Guanine nucleotide binding protein Ligand (Agonist) Extracellular fluid Target Intracellular fluid Conform. change Reseptor GDP G-protein GTP +P GDP GDP O HN N N H 2N N O O O P O P O O O O n HO OH GTP Responce n=1; GDP n=2; GTP GTP Subtypes of G-proteins - Targets (Second messenger systems) Ion chanels: G12 Na+ / H+ exchange Enzyms: Gi Inhib. Adenylyl cyclase Gs Stimul. Adenylyl cyclase Gq Stimul. Phospholipase C One ligand can bind to more than one type of G-prot. coupled reseptors second messenger pathways NH2 NH2 N N Adenylyl cyclase O P O P ATP OH N N N O O O N O P O P O P O O O O O HO N N O O P O O OH c-ATP Activate c-AMP dependent protein kinases (Phosphoryl. of proteins, i.e. enzymes) Various responces (ex. metabolism, cell division) Subtypes of G-proteins - Targets (Second messenger systems) Ion chanels: G12 Na+ / H+ exchange Enzyms: Gi Inhib. Adenylyl cyclase Gs Stimul. Adenylyl cyclase Gq Stimul. Phospholipase C Various processes in cell Various processes in cell second messenger pathways Release Ca2+ Activate protein kinases O R R' O O Phopholipase C O O O O P O OH O HO HO R O O P O OH O O + HO HO O P O O OH O O R' O P P DAG Diacylglycerol IP3 Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate P PIP2 Phosphatidylinositol besphophate Several steps Li (Treatmen manic depression) Enzyme coupled receptors - Catalytic receptors Ligands: Peptide hormones 1) Binding of Ligand 2) Dimerisation of reseptor Tyr kinase -OH domain (Janus kinase) Phosphoryl of Tyr -OH -OH STATS protein O P O P O P O P STATS protein STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 1) Phosphoryl. of STAT 2) Release of STAT in cytoplasma 3) STATto cell nucleus 4) Intitation of transcription Cytoplasmic receptors (not bound to cell membranes) Lipophil. ligand thru cell membrane Cell membrane Cytoplasma Responce Cell nucleus HSP-90 Protein DNA HSP-90 DNA (HSP-90: Heat shock protein) mRNA Receptor subtypes Most receptor classes - several sub-types Each subtypes - differend A(nta)gonists Sub types cholinerge reseptors Det somatiske nerves ystem Det autonome nervesys tem CNS Det sympatiske Det paras ympatis ke nervesystem nervesystem CNS CNS Acetylcholin (Neurotransmittor) ganglion Acetylkolin ca. 5Å Noradrenalin O Synapse O N Reseptor O Effektor celle H Muscarinerge receptors M1: G-Protein coupled receptors Stimulate phopholipase A 4.3 Å HO O O Nicotinerge receptors N Nmuscle: Ligand gated ion chanels 5.9 Å M2: G-Protein coupled receptors Inhib. adenylyl cyclase Incr. Na+/Ca2+ N H H N O H Nneuro: Ligand gated ion chanels Incr. Na+/Ca2+ Spare receptors - Partial agonist Full agonist Full responce Spare receptors Partial agonist Weak responce Full responce Responce = Agonist Absens of full agonist Responce Presence of full agonist = Antagonist Desensitizing Receptor and normal amount of ligand = agonist Overstimulated receptor Sensitizing Receptor and normal amount of ligand = Antagonist Overstimulated receptor