Encoding - Wheelerswiki

AP PSYCH DMA
Please write down the questions and answer them.
1.
2.
Explain why the hippocampus is important for memory.
Give three examples of mnemonic devices.
Your graded FRQs are in the out-box
TODAY’S AGENDA
DMA
Review FRQ info
Memory
Flashbulb, feats, encoding, forgetting, etc…
Homework:
• Chapter 9 test – Monday, Sept. 12 th
• Chapter 9 notes due – Monday, Sept. 12 th
• DMAs due Friday
• Chapter 9 review session – Friday, Sept. 9 th at 7:00 AM
FRQ ISSUES
Write your answer in the order of the question!
Example: the question asks you about spacing effect, semantic encoding and rehearsal…
1 st paragraph – spacing effect
2 nd paragraph – semantic encoding
3 rd paragraph – rehearsal
FRQ ISSUES
Be specific!
If you are applying rehearsal…
Bad answer – “I would use rehearsal to help learn vocabulary words”
Good answer – “I could use the technique of rehearsal while studying details such as names and definitions. By using repetition, I will be able to better encode the information and attach meaning to it. Some examples of this include using flashcards and quizzing myself over and over again.”
FRQ GRADING
On the chapter test…
1 FRQ
1/3 of your test grade
Will be one of the practice FRQs
Practice FRQs
Receive list at beginning of chapter
Each question/answer is worth 10 points.
Answer must be a complete draft (not missing any parts of the question)
Answer must use the TDA method
Answer must demonstrate all the FRQ techniques discussed in class.
MEMORY
Long-Term Memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system
A SIMPLIFIED MEMORY MODEL
External events
Sensory input
Attention to important or novel information
Sensory memory
Encoding
Short-term memory
Encoding
Retrieving
Long-term memory
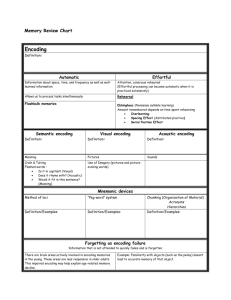
ENCODING: GETTING INFORMATION IN
Encoding
Effortful Automatic
ENCODING
Automatic Processing unconscious encoding of incidental information
space
time frequency well-learned information
word meanings we can learn automatic processing
ENCODING
Effortful Processing
requires attention and conscious effort
Rehearsal
conscious repetition of information
to maintain it in consciousness
to encode it for storage
ENCODING
Ebbinghaus used nonsense syllables
TUV ZOF GEK WAV the more times practiced on Day 1, the fewer repetitions to relearn on Day 2
Spacing Effect
distributed practice yields better long- term retention than massed practice
How can you use this info to your benefit?
MEMORY – RELAXATION & RECALL
How it works….
Wheeler will turn off the lights, get comfortable, take a few deep breaths & close your eyes.
Wheeler will read a list of words to you
Just listen – don’t write anything down.
WRITE EVERYTHING THAT YOU REMEMBER
FROM THE LIST DOWN…
ENCODING: SERIAL POSITION EFFECT
Percentage of words recalled
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Position of word in list
Serial Position Effecttendency to recall best the last items in a list
WHAT DO WE ENCODE?
Semantic Encoding
encoding of meaning including meaning of words
Acoustic Encoding
encoding of sound
especially sound of words
Visual Encoding
encoding of picture images
ENCODING
PLEASE TURN TO A NEIGHBOR AND DISCUSS
HOW THIS ENCODING INFORMATION CAN
MAKE YOU STUDY MORE EFFICIENTLY.
ENCODING
Imagery
mental pictures
a powerful aid to effortful processing, especially when combined with semantic encoding
Mnemonics
memory aids
especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
MEMORY DEMONSTRATION
Steps
Listen to the list of letters (don’t write anything down!)
When the list is done – write down as many of the letters (in the correct order) as you can.
ENCODING
Chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units
like horizontal organization--1776149218121941 often occurs automatically use of acronyms
HOMES-H uron, O ntario, M ichigan, E rie, S uperior
ARITHMETIC-A R at I n T om’s H ouse M ight E at T om’s
I ce C ream
ENCODING: CHUNKING
Organized information is more easily recalled
ENCODING
Hierarchies
complex information broken down into broad concepts and further subdivided into categories and subcategories
Encoding
(automatic or effortful)
Meaning
(semantic
Encoding)
Imagery
(visual
Encoding)
Chunks
Organization
Hierarchies
STORAGE:RETAINING INFORMATION
Iconic Memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli a photographic or picture image memory lasting no more that a few tenths of a second
Echoic Memory
momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
STORAGE:LONG-TERM MEMORY
Amnesia --the loss of memory
Explicit Memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and declare also called declarative memory hippocampus --neural center in limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage
Implicit Memory
retention independent of conscious recollection also called procedural memory
MEMORY LOSS
Clive Wearing
Worst case of memory loss known.
STUDY GROUPS
Reconnect with your group…
1.
Discuss when and where you are going to meet to study for Monday’s test.
2.
Huddle-up the desks and begin reviewing
Chapter 9.