2-3 Human Information Processing
advertisement
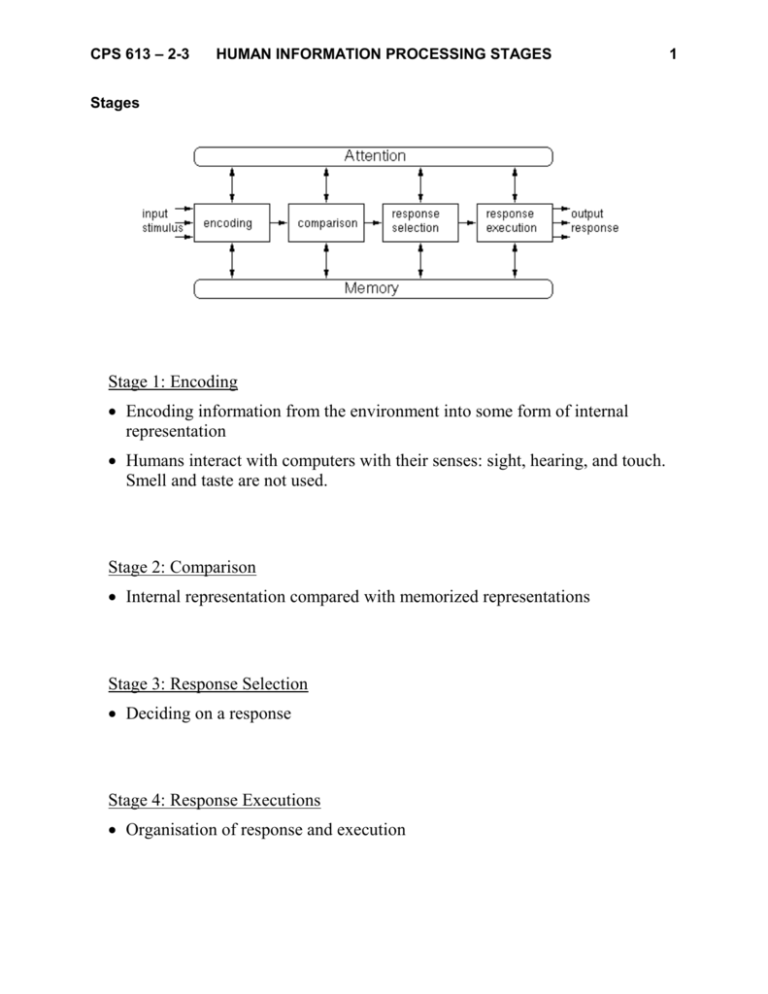
CPS 613 – 2-3 HUMAN INFORMATION PROCESSING STAGES Stages Stage 1: Encoding Encoding information from the environment into some form of internal representation Humans interact with computers with their senses: sight, hearing, and touch. Smell and taste are not used. Stage 2: Comparison Internal representation compared with memorized representations Stage 3: Response Selection Deciding on a response Stage 4: Response Executions Organisation of response and execution 1 CPS 613 – 2-3 HUMAN INFORMATION PROCESSING STAGES 2 Goal: make user effective. Effectiveness Effectiveness = Speed + Correctness/Accuracy Both are a function of age, fitness, skill, fatigue of the user, which cannot be controlled. U.I. can be controlled though. Speed: time broken down into: reaction time (1) + thinking time (2-3) + movement time (4) Reaction time is a function of sense through which stimulus is received: - auditory signals perceived faster than visual signals, faster than pain signals. - More than one sense faster. Movement time function of distance of object: closer = easier to get to Accuracy: (4) Hitting correct target Not necessarily inversely related to speed Function of size of object: bigger = easier to “hit” Fitt’s Law T is the average time taken to complete the movement. a and b are model parameters. D is the distance from the starting point to the center of the target. W is the width of the target measured along the axis of motion. W can also be thought of as the allowed error tolerance in the final position, since the final point of the motion must fall within ±W⁄2 of the target's center.











