Modules 18 & 19: Information Processing& Forgetting and Memory
advertisement

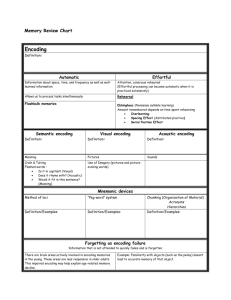
Psychology Mr. Plouffe Korea International School Modules 18 & 19: Information Processing& Forgetting and Memory Construction Pages 262-271 Name: __________ Block:____ Read pp. 262 to 271. Answer the following questions. 1. Provide examples of how the most seemingly mundane task involves memory. 2. Ralph Haber (1970) showed us that despite our feelings of feebleness when we compare our memories to someone with a photographic one, we are still very impressive. What evidence from Haber’s study supports this conclusion? 3. What is a flashbulb memory? Can you remember where you were exactly when you learned about the 9/11 attack on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon? 4. Explain each one of these steps: a. Encoding: b. Storage: c. Retrieval: 5. Encoding. Explain what the following terms mean: a. Automatic processing: b. Effortful processing i. Rehearsal ii. The next-in-line effect 6. Suggest why attempting to read new material just before bed may lead to that material not being remembered. 7. Can we really learn a language while we sleep? (p. 266) 8. Why is a spaced-out learning schedule bound to create memories which last longer than cramming? 9. Define the following and provide an example of how each helps us encode; therefore remember better: a. Encoding meaning b. Encoding imagery c. Mentally organizing information i. Chunking Psychology Mr. Plouffe ii. Hierarchies Korea International School