* What gives the skies of urban areas this smoggy brown color
advertisement
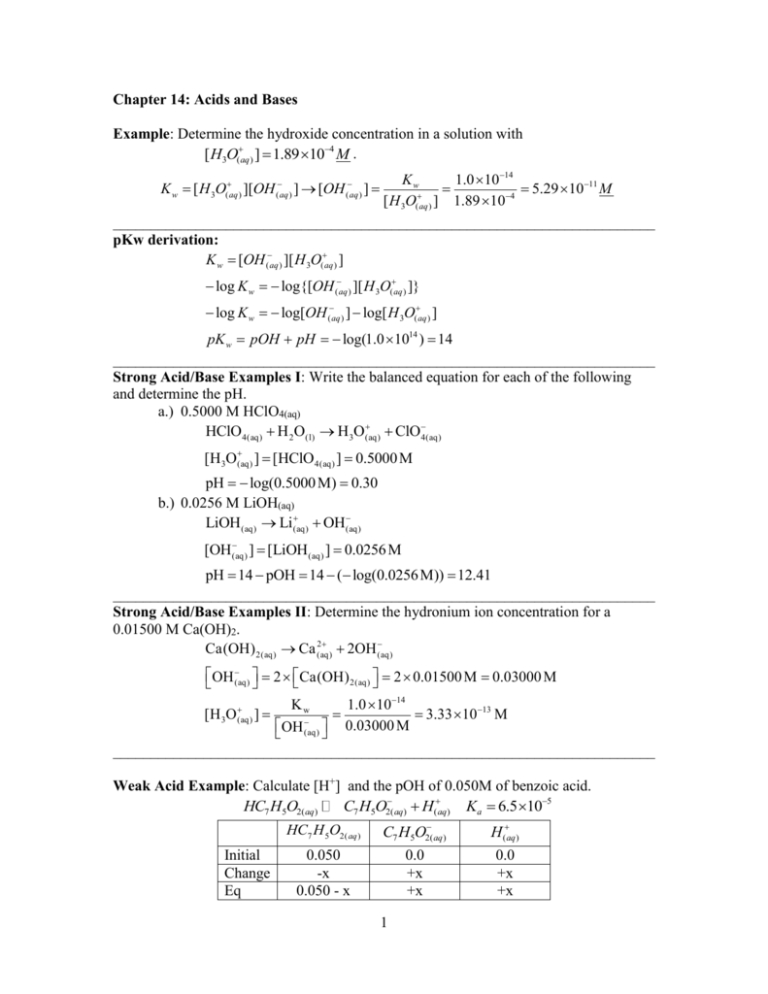
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases
Example: Determine the hydroxide concentration in a solution with
[ H3O(aq ) ] 1.89 104 M .
Kw
1.0 1014
5.29 1011 M
[ H 3O(aq ) ] 1.89 104
________________________________________________________________________
pKw derivation:
K w [OH (aq ) ][ H 3O(aq ) ]
K w [ H 3O(aq ) ][OH (aq ) ] [OH (aq ) ]
log K w log{[OH (aq ) ][ H 3O(aq ) ]}
log K w log[OH (aq ) ] log[ H 3O(aq ) ]
pK w pOH pH log(1.0 1014 ) 14
________________________________________________________________________
Strong Acid/Base Examples I: Write the balanced equation for each of the following
and determine the pH.
a.) 0.5000 M HClO4(aq)
HClO4(aq) H 2O(l) H3O(aq)
ClO4(aq)
[H3O(aq)
] [HClO 4(aq) ] 0.5000 M
pH log(0.5000 M) 0.30
b.) 0.0256 M LiOH(aq)
LiOH(aq) Li(aq)
OH(aq)
[OH (aq)
] [LiOH (aq) ] 0.0256 M
pH 14 pOH 14 ( log(0.0256 M)) 12.41
________________________________________________________________________
Strong Acid/Base Examples II: Determine the hydronium ion concentration for a
0.01500 M Ca(OH)2.
2
Ca(OH) 2(aq) Ca (aq)
2OH (aq)
OH (aq)
2 Ca(OH) 2(aq) 2 0.01500 M 0.03000 M
Kw
1.0 1014
[H 3O (aq)
]
3.33 10 13 M
OH (aq) 0.03000 M
________________________________________________________________________
Weak Acid Example: Calculate [H+] and the pOH of 0.050M of benzoic acid.
HC7 H5O2( aq)
C7 H5O2( aq) H(aq) Ka 6.5 105
HC7 H 5O2( aq )
Initial
Change
Eq
0.050
-x
0.050 - x
C7 H5O2( aq )
0.0
+x
+x
1
H (aq )
0.0
+x
+x
Ka
[C7 H 5O2( aq ) ][ H (aq ) ]
[ HC7 H 5O2( aq ) ]
x2
6.5 105
0.050 x
x 2 3.25 106 6.5 105 x x 2 6.5 105 x 3.25 106 0
x
6.5 105
6.5 10
5 2
4 1 -3.25 106
2
5
3
6.5 10 3.6110
x 1.77 103 M
2
[ H ] 1.77 103 M
x
14 pH pOH pOH 14 pH 14 log[ H ] 11.25
________________________________________________________________________
Percent Dissocation Example: Determine the percent dissociation of 0.050M of benzoic
acid.
HC7 H5O2( aq)
C7 H5O2( aq) H(aq) Ka 6.5 105
We already found [ H ] 1.77 103 M therefore
[ H ] 1.77 103 M
100% 3.54%
0.050M
HA
It should be small since our Ka is so small
________________________________________________________________________
Polyprotic Acid Example: Calculate the [H+] of 0.050M of sulfuric acid.
H 2 SO4( aq ) H (aq ) HSO4( aq )
K a 1
HSO4( aq )
H (aq ) SO4(2aq )
K a 1.2 102
Initially all 0.050M of the H2SO4 dissociates completely into
0.050M H(aq ) HSO4( aq )
H (aq )
HSO4( aq )
SO4(2aq )
Initial
0.050
0.050
0.0
Change
-x
+x
+x
Eq
0.050 - x
0.050+x
+x
2
[ H ( aq ) ][ SO4( aq ) ] (0.050 x) x
Ka
1.2 102
[ HSO4( aq ) ]
(0.050 x)
0.050 x x 2 6.0 10 4 1.2 10 2 x
x 2 0.062 x 6.0 10 4 0
x
0.062
0.062
2
4 1 -6.0 10 4
2
2
0.062 7.90 10
x 8.51 103 M
2
[H+] = 0.050+0.0085 = 0.059M
x
2
________________________________________________________________________
Weak Base Example: Calculate the pH of 0.050 M NH3.
NH3( aq ) H 2O
OH(aq ) NH 4( aq) Kb 1.8 105
OH(aq )
NH 4( aq )
Initial
0.050
0.0
0.0
Change
-x
+x
+x
Eq
0.050 - x
+x
+x
2
[OH ( aq ) ][ NH 4( aq ) ]
x
Ka
1.8 105
[ NH 3( aq ) ]
0.050 x
NH 3( aq )
x 2 9 107 1.8 105 x x 2 1.8 105 x 9 107 0
x
1.8 105
1.8 10
5 2
4 1 -9 107
2
4
x 9.4 10 M
[OH ] 9.4 104 M
pH 14 log[OH ] 14 3.03 10.97
___________________________________________________________________
Conversion from Kb to Ka Example: Determine the Kb of HCN if Ka = 4.9 x 10-10.
K
11014
K w K a Kb Kb w
2.04 105
K a 4.9 1010
___________________________________________________________________
Salt Classification Example I: Classify the following solutions as basic, acidic, or
neutral.
a.) KBr
b.) NaNO2
c.) NH4Cl
Answer:
a.) neutral
b.) basic
c.) acidic
___________________________________________________________________
Salt Classification Example II: Calculate the Ka for the cation & the Kb for the anion in
an aqueous solution containing NH4CN. Is the solution acidic, basic, or neutral?
NH 4CN NH 4 CN
for NH 4 : NH 4 H 2O
NH 3 H 3O
Ka ?
we will not find this K a in a table BUT we can find the K b of NH 3 to it:
NH 3 H 2O
NH 4 OH
K b 1.8 105 K a
Kw
1014
5.56 1010
K b 1.8 105
for CN we will have to use the K a of HCN to get its K b
CN H 2O
HCN OH
Kb ?
3
CN H 3O
HCN H 2O
K a 4.9 1010 K b
Kw
1014
2.04 105
10
K a 4.9 10
Kb CN K a NH 4 the soln is basic
___________________________________________________________________
Salt Example: Calculate the pH of a 0.25M NaC2H3O2, Ka = 1.76x10-5.
Kb
Kw
11014
5.68 1010
K a 1.76 105
C2 H3O2( aq) H 2O(l )
HC2 H3O( aq) OH(aq)
HC2 H 3O( aq )
OH
C2 H3O2( aq)
Initial
0.250
0.0
0.0
Change
-x
+x
+x
Eq
0.250 - x
+x
+x
2
[ HC2 H 3O( aq ) ][OH ]
x
Kb
5.68 1010
[C2 H 3O2( aq ) ]
0.250 x
because we have a large concentration of acetate and a small Kb we
will try and assume 0.250 >> x
x2
x2
5.68 1010 x 1.19 105 M
0.250 x 0.250
1.19 105
ck :
100% 0.005% 5%
0.250
therefore our assumption is valid and [OH-] = 4.77x10-5M
pH = 14 - pOH
= 14 + log[OH] = 9.08
4






