Fungi - Explore Biology
advertisement

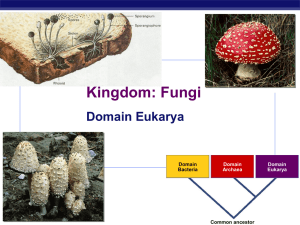
Kingdom: Fungi Eukaryotes Domain Bacteria AP Biology Domain Archaebacteria Domain Eukaryotes 2007-2008 Common ancestor General characteristics Classification criteria eukaryotes heterotrophs must feed off of others mostly multicellular except one-celled yeasts AP Biology cell wall Structure Cells long thread-like cells multiple nuclei cell wall made from chitin just like crab shells chitin cell wall septum pore nuclei AP Biology How do Fungi get their Nutrition? fungal cells Heterotrophs secrete digestive enzymes absorb digested material into cell predators plant cell membrane paralyzing prey parasites feeding on living creatures decomposer breakdown dead remains AP Biology Cool… Fungi live IN their food! Chocolate cake, anyone? plant cell wall plant cell Ecological Roles Decomposers recycle nutrients Symbiotic Relationships lichen fungi + algae pioneer species in ecosystems makes soil from bare rock mycorrhizae fungi + plants AP Biology enables plants to absorb more water Mycorrhizae Critical role in plant growth extends water absorption of roots without mycorrhizae Endomycorrhiza AP Biology Ectomycorrhiza with mycorrhizae Reproduction Asexual budding in yeast Sexual gills on mushroom mushroom spores spread by wind spores on gills AP Biology fungus growing in soil Fairy Rings AP Biology Importance of fungi to humans Food production bread beer, wine Medicine production antibiotics penicillin AP Biology Any Questions?? AP Biology 2007-2008 Zygomycete (Bread Mold) Life Cycle spores mating strain hypha sporangium MEIOSIS (2n) diploid AP Biology (n) haploid FUSION of gametangia mating strain