Planning
advertisement

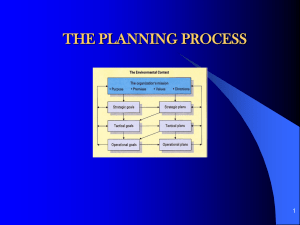
Chapter 4 Planning What Would You Do? Consortium created to compete with Boeing Slow progress, with potential How do you take more business away from Boeing What is your plan? Learning Objectives Planning After discussing this section you should be able to: 1. 2. discuss the costs and benefits of planning. describe how to make a plan that works. Costs and Benefits of Planning The Benefits The Pitfalls of Planning The Benefits Persistence Intensified Effort Direction It Works! Creation of Task Strategies Planning Pitfalls Impede Change & Prevent Adaptation Create a False Sense of Certainty Detachmen t of Planners Blast From The Past Pericles and Planning Leaders must have a vision Planners must be close to events Plans must be flexible How to Make a Plan That Works Maintain Flexibility in Planning Set Goals Develop Commitment to Goals Adapted from Exhibit 4.1 Develop Effective Action Plans Track Progress Toward Goal Achievement Setting Goals Specific Measurable Attainable Realistic Timely Goal Commitment The determination to achieve a goal Increased by: Setting goals through participation Making goals reasonable Making goals public Obtaining top management support Developing Effective Action Plans For accomplishing a goal, these list the: specific steps people resources time period Tracking Progress One method, setting: proximal goals - short-term distal goals - long-term Second method: gather and provide performance feedback make adjustments in: effort direction strategies Maintaining Flexibility Option-based planning keep options open through simultaneous investment invest more in promising options Learning-based planning plans need to be continuously adjusted encourages frequent reassessment and revision of goals Learning Objectives Kinds of Plans After discussing this section you should be able to: 3. 4. discuss how companies can use plans at all management levels, from top to bottom, describe the different kinds of specialpurpose plans that companies use for change, contingencies, and product development. Planning from Top to Bottom Vision Adapted from Exhibit 4.3 Planning from Top to Bottom (cont’d) Vision Top Managers Middle Managers Mission Tactical Plans First-Level Operational Plans Managers Adapted from Exhibit 4.4 Management by Objectives Standing Plans Single-Use Plans Starting at the Top Vision statement of purpose enduring, inspirational, clear, and consistent with company beliefs and values Mission flows from vision more specific goal statements Setting Missions Targeting Common-Enemy vow to defeat a rival Role-Model set a clear, specific target emulate a successful company Internal-Transformation strive to dramatically change the company Bending in the Middle Tactical Plans specify how a company will use resources, budgets, and people to accomplish goals Management by Objectives develop and carry out tactical plans four steps discuss goals participatively select goals jointly develop tactical plans meet to review performance What Really Works? Management by Objectives (MBO) MBO & Production 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 97% Probability of success MBO is based on goals, participation and feedback. Companies that use MBO are 97% more68% likely to outproduce companies that don’t! Finishing at the Bottom Operational plans Single-use plans day-to-day plans cover one-time-only events Standing plans plans for recurring events three kinds policies procedures rules & regulations Budgeting Special-Purpose Plans Planning for Change Planning for Contingencies Planning for Product Development Planning for Change Stretch goals extremely ambitious goals initially employees don’t know how to accomplish Benchmarking identify outstanding practices in other companies adapt them to your company Been There, Done That Steve Kerr on Stretch Goals at GE Stretch goals are more than just demanding more from employees Give employees the tools to succeed Don’t punish failure Planning for Contingencies Scenario Planning Define the scope of the scenario Identify the major stakeholders Identify environmental trends Identify key uncertainties and outcomes of these trends Using steps 1-4, create initial scenarios Check each scenario for consistency and plausibility of facts Create contingency plans from each scenario Planning for Product Development Aggregate product plans Four keys to faster product development cross-functional teams internal and external communication overlapping development phases frequent testing of product prototypes Overlapping Product-Development Phases forBlock a New “Supercomputer Server Diagram Evolution of System Specification Simulation ASIC and Board Design Hardware Mock-ups & Models “Bring-up” Full System Prototype January July Conceptualization Adapted from Figure 4.7 January July Simulation Implementation Ship Date January July What Really Happened? Airbus set specific goals Built planes that were easier and cheaper to maintain, used the same cockpit, and were comfortable for passengers Used options-based planning Positioned itself through innovative new features, functionality, and lower costs.