Animalia
advertisement

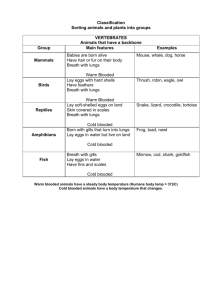
multicellular, eukaryotic, no cell wall, heterotrophs, capable of movement, reproduce sexually, body symmetry (radial or bilateral) 9 Phyla- 8 invertebrate and 1 vertebrate Porifera- two cell layers, collar cells w/flagella, filter feeders, ex. sponges Cnidarians- Stinging cells, radial symmetry, simple nervous system only stimulus and response, central cavity only one body opening, ex. jellyfish, coral, hydra, sea anemone Plathyhelmenthes: flat worms, only one body opening, three cell layers,ex. Tapeworm, Fluke, Planarian, Marine worms Nematode: round worms, first with two body openings, 3 cell layers, many parasitic, Heartworm, Roundworm, Vinegar Eel Annelid: segmented worms, two body openings, 3 cell layers, beginning of circulatory system, and digestive system (crop), ex. Earthworm and Leech Plathyhelmenthes Annelid Nematode soft body, more complex body systems developing, eyes and nervous system, levels of communication beyond stimulus and response 3 classes Gastropod (snails and slugs), Cephalopod (squid octopus cuttlefish and chambered nautilus), Bivalve (oyster, clam, mussel, scallop) Bivalves Gastropods Cephalopods jointed legs, exoskeleton, body segments (head, thorax, and abdomen), metamorphosis (complete or incomplete) 4 classes: Insect -6 legs (ant, grasshopper, beetle, bee, wasp) Arachnid -8 legs (spider, tick, horseshoe crab), Crustacean -10 legs (shrimp, lobster, barnacles, crayfish) Myrapods -many legs, centipede and millipedes Characteristics: spiny skin, complex regeneration capacity, found only in marine environments, radial symmetry, Examples: Sea urchin, Sand dollar, Starfish, Sea cucumber Chordate notachord, complex body systems, sexual reproduction (internal or external fertilization) 5 classes: Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Fish, moist skin covered in scales, gills to breathe, 2 chambered heart, cold blooded, 3 types: 1. bony ex Trout, Salmon, Bass, Catfish, Grouper, Tarpon. 2. jawless, ex. Lamprey and tunicates 3. cartilaginous ex. Sharks and Rays Amphibian, cold blooded, 3 chambered heart, born in water, develop lungs, smooth moist skin, ex. salamander, newts, frogs, and toads (only dry skin) Reptile, dry leathery skin with scales, cold blooded, 3 chambered heart, amniote/terrestrial eggs, ex. Lizards, snakes, turtles, alligator, crocodile Bird, warm blooded, 4 chambered heart, hollow bones, body with feathers Mammal, warm blooded, 4 chambered heart, milk producers, body with hair/fur Placental (live birth), Marsupial (pouch) ex. Kangaroo, and Monotremes (egg) ex Platypus Innate: 1. 2. 3. Instincts- complex pattern of innate behaviors, reflexes, fight or flight, courtships, species recognition (language, song, flashes of pattern/light) Territory- physical space needed for breeding, feeding, and shelter, organisms can expend a lot of energy defending territory some will fight to the death. Migration- instinctive seasonal movement, response to a changing environment, includes hibernation (cold) and estivation (dry and hot) Learned: Habituation- animal repeats a successful behavior, and does not repeat an unsuccessful behavior, birds learn which moths are poisonous by color and avoid eating them after becoming ill or getting a bad taste. Deer return to the same grazing field when successful. Imprinting – salmon and turtles return to same stream or beach to lay eggs in which they hatched, the environment left an imprint or memory Mechanical- physical structures Chemical- stinging sensations, poisons, bad taste, paralysis Camouflage- color or pattern that blend into environment ◦ Disruptive- ex zebra ◦ Cryptic- ex chameleon and squid ◦ Countershading- ex Fish have light belly and dark back