Cell Organelles: Structure & Function - Biology Presentation
advertisement

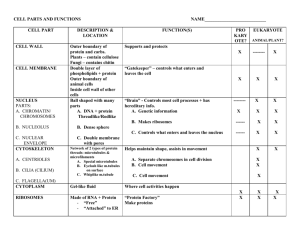
Structure Largest organelle Spherical Dark patches=chromatin Surrounded by nuclear envelope Composed of 2 fluid filled membranes Has nuclear poreallows large molecules through Nucleolus inside Function Contains genetic material Chromatin consists of DNA and proteins Contains instructions for making proteins When cells divide, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes Nucleolus makes RNA and ribosomes. Structure: Consists of flattened membrane-bound sacs cisternae which are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. RER- Ribosomes Smooth ER- no Ribosomes Function: Smooth ER- Involved in synthesising, storing and transporting lipids. RER- Transports proteins made on attached ribosomes (large surface area) Golgi Apparatus Structure: Stack of membrane-bound, flattened sacs Function: Receives proteins from the ER Modifies them e.g. adds sugar (Post office) to make glycoproteins Packages proteins into vesicles to be transported inside cell or to the outside Produces secretory enzymes (like those secreted by pancreas) Mitochondria Structure: 2 membranes separated by a fluid filled space Inner membrane is folded to form cristae – provides large surface area for the attachment of enzymes involved in respiration. Central part is the matrix. Contains protein, traces of DNA and lipids. DNA allows mitochondria to produce its own proteins. Enzymes found in the matrix. Lots of mitochondria are found in active cells (like muscle) which require plentiful supply of ATP. Function Site where ATP is produced during respiration Chloroplasts Structure: 2 membranes separated by fluid filled space Inner membrane is continuous with a network of thylakoids A stack of thylakoids is called a granum Chlorophyll molecules are present on these membranes. Function: Site of photosynthesis Light energy is used to derive carbohydrate molecules from carbon dioxide. Function: Contain digestive enzymes which break down materials (such as in white blood cells – phagocytosis) Release enzymes to the outside of the cell (exocytosis) to destroy materials around the outside of the cell Structure: Spherical sacs surrounded by a single membrane Break down old cells after they have died (autolysis) and digest worn out organelles Specialised lysosome (acrosome) in head of sperm cells helps it penetrate the egg Organelles NOT surrounded by membranes Ribosomes Centrioles Ribosome Structure No membrane Very small organelles in the cytoplasm and bound to rough ER Consist of 2 subunits – large sub-unit and small sub-unit Function: Site of protein synthesis which acts as an assembly line to use mRNA to assemble proteins. Centrioles Structure No membrane Small protein tubes of microtubules. Function: Form fibres in cell division known as spindles which separate chromosomes.