Origins of Sociology
advertisement

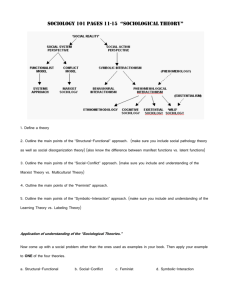
Origins of Sociology Basic Timeline of Sciences First intellectual ideas focused on religious philosophy Religious leaders = only literate citizens Greeks developed secular schools to train intellectuals (2500BP) Philosophy focused - Forerunner to university study Greeks recorded history Religious beliefs often = absolute. Church and science in conflict During Renaissance Humanism …set of ideas and that looked to humanity for answers flourished Natural and Social Sciences Examples of Natural Sciences Examples of Social Sciences Biology Psychology Astronomy History Physics Cultural Geography Geology Anthropology Chemistry Political Science Zoology Economics Oceanography Sociology Sociology Emerges In 18th and 19th century Europe Rise of factory-based, industrial economy Explosive growth of cities = social problems New ideas about democracy, political rights, and individualism Combination of other social sciences Auguste Comte (1798–1857) French social thinker who coined the term “sociology” (1838) Relied on statistical analysis (positive sociology) Sociology as a discipline, viewed as radical and a threat to power structure Sociological Approaches, Perspectives or Paradigms Theory Statement of how and why specific facts are related Theoretical approach Basic image of society that guides thinking and research Determines questions and study Goal of study Sociology has 3 Major Theoretical Approaches Structural- Functionalism Conflict Theory Symbolic Interactionism Structural-Functionalism Basic View: Society is a complex system, parts work together to promote solidarity and stability ( Macro) Individuals are naturally cooperative and accept the social system as is. Too rapid change=broken social ties (dysfunction….a disorder in society) Key elements: Social structure Social function Manifest functions Latent functions Criticisms: Social-Conflict Approach •Basic View : Sees society as arena of inequality that generates conflict and change (Macro) •Conflict is necessary for equality and change Factors such as race, sex, class, and age are linked to social inequality. Dominant group vs. disadvantaged group Society structured in ways to benefit a few at the expense of the majority. gender conflict race conflict Social Conflict Approach Social-conflict approach used to understand society and to bring about societal change that would reduce inequality Criticisms: Symbolic-Interaction Approach Basic View: Focuses on social interactions in specific situations Micro approach Views society as the product of everyday interactions of individuals Key elements: Society is shared, dynamic constructed reality developed through interaction. Sports: Playing the Theory Game Structural-functional: Recreation and help social relationship building. Social-conflict: Social inequality exists in sports. Gender-conflict: Gender equality is not evident, especially in earnings and prestige. Race-conflict: Racial conflict still exists. Symbolic-interaction: Understanding varies by each player