Sociological Approaches
advertisement

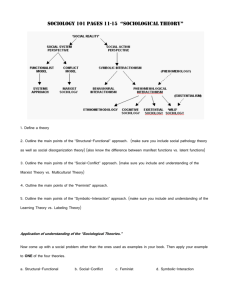
SOCIOLOGICAL APPROACHES WHAT IS SOCIOLOGY? “...The systematic study of human society ” Systematic Scientific discipline that focuses attention on patterns of behavior Human society Group behavior is primary focus; how groups influence individuals and vice versa STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONAL System whose parts work together Consequences serve as function of society Manifest Latent Dysfunctions MANIFEST Intended consequences Students learn content as a results of a teacher’s careful lesson planning LATENT Unintended consequences Students learn socialization skills through group work portion of the assignment. DYSFUNCTION Manifest : anticipated negative disruptions Ex: groups will be off task Latent: unanticipated negative disruption Ex: class doesn’t finish assignment in allotted time. WHO’S WHO IN THE STRUCTURAL-FUNCTIONAL PARADIGM Auguste Comte Emile Durkheim Helped establish sociology as a discipline Herbert Spencer Importance of social integration during times of rapid change Compared society to the human body Robert K. Merton Manifest functions are recognized and intended consequences. Latent functions are unrecognized and unintended consequences. Social dysfunctions are undesirable consequences. SOCIAL CONFLICT Society is structured in ways to benefit a few at the expense of the majority. Society is structured around inequality. That conflict generates change. Ex: underperforming students are targeted for special programs. WHO’S WHO IN THE SOCIAL-CONFLICT PARADIGM Karl Marx The importance of social class in inequality and social conflict W.E.B. Du Bois Race as the major problem facing the United States in the 20th century FEMINISM & GENDER CONFLICT APPROACH A point of view that focuses on inequality and conflict between women and men Closely linked to feminism, the advocacy of social equality for women and men Women important to the development of sociology: Harriet Martineau and Jane Addams RACE CONFLICT APPROACH • A point of view that focuses on inequality and conflict between people of different racial and ethnic categories • People of color important to the development of sociology: Ida Wells Barnett and W.E.B. Du Bois SYMBOLIC INTERACTION Society is the product of interactions. These are subjective, as each person has their own views, experiences, memories, thoughts and expectations. Ex: school is the interaction of teachers and students and the relationship they build. WHO’S WHO IN THE SYMBOLIC-INTERACTION PARADIGM Max Weber George Herbert Mead Understanding a setting from the people in it How we build personalities from social experience Erving Goffman Dramaturgical analysis CRITICAL EVALUATION OF EACH APPROACH Structural-Functional Social-Conflict Too broad, ignores inequalities of social class, race & gender, focuses on stability at the expense of conflict Too broad, ignores how shared values and mutual interdependence unify society, pursues political goals Symbolic-Interaction Ignores larger social structures, effects of culture, factors such as class, gender & race (too much emphasis on microlevel)