Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups Presentation
advertisement

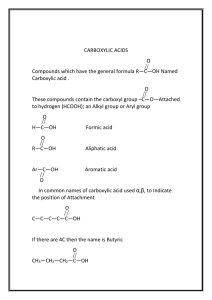
Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups Origin of organic compounds • Naturally occurring organic compounds are found in plants, animals, and fossil fuels • All of these have a plant origin • All of these rely on the “fixing” of C from CO2 • Synthetic organic compounds are derived from fossil fuels or plant material Introduction • • • • Most current research focuses on Organic Originally from “organic” meaning life Not just chemistry of life, chemistry of carbon Exceptions: – oxides of carbon (CO2, CO) – carbonates,bicarbonates(NaHCO3,CaCO3) – cyanides (NaCN, etc) One C with no H, or with metal • Carbon can form four bonds… C C C C C Carbon forms four bonds • Carbon can form four bonds, and forms strong covalent bonds with other elements • This can be represented in many ways … H O C C H Cl C CH C Cl H CH2 H3C Cl C C H3C CH3 CH CH CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH2 Functional groups • Functional groups are parts of molecules that result in characteristic features • About 100 functional groups exist, we will focus on about 10 • Useful to group the infinite number of possible organic compounds • E.g. the simplest group is hydrocarbons • Made up of only C and H • Not really a functional “group” • Further divided into: • Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Aromatics Hydrocarbons Alkanes C H H H H H C C C C C H H H H H H Alkynes C Alkenes C H H C H H H C C C C C H H H H H Aromatics C H H C C C H H H C C C H H H H H H H C C C C H C C H H Functional groups • Read 1012 - 1014 • You will need to memorize family name and associated general structure (use study H2N notes: includes ether group) C CH • Handout Molecular model kits • Build this structure: O H2C CH2 • Assignment: in groups build each of the “Examples” in table 24.1 • Each member must have the exact same molecule (thus you must agree on structure) • Show me the structure(s) after building each Hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl • There are other names that describe patterns of atoms that are parts of functional groups. • “Hydroxyl” refers to –OH • “Carbonyl” refers to C=O • “Carboxyl” refers to COOH Q: which functional groups contain a hydroxyl group? A carbonyl group? A carboxyl group? Hydroxyl: alcohols, carboxylic acids. Carbonyl: aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, amides, esters. Carboxyl: carboxylic acids Note that properties such as boiling and melting point change due to functional groups For more lessons, visit www.chalkbored.com