Lecture 9 Functional Groups
advertisement

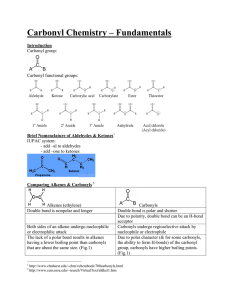
Ch 10.5 Functional Groups Definition Functional Groups • Have specific name/formula/structure • Carry out specific Rx • Have specific characteristics a) If they contain O, S, N: makes molecule polar, higher MP/BP, soluble in water, liquid/solid at RT b) If they contain C and H only: makes molecule non-polar, low MP/BP, soluble in organic solvents, gases at RT Alk-anes, enes, ynes • Hydrocarbons with single, double, triple bonds • C-C or C=C or C=C • Caution: add enough Hydrogen to fill remaining covalent bonds • CH3-CH3 or CH2=CH2 or CH=CH Aromatic HC • Molecules containing Benzene rings • substituent called Phenyl Alcohols • Contain hydroxyl group • - OH • Example: Ethanol Ethers • Oxygen bridge in a carbon skeleton • C-O-C • Example: Diethyl ether Aldehyde • Contain Carbonyl group: O double bonded to Carbon C=O • located at the end of Carbon skeleton Example: Propanal Ketone • Carbonyl at a center Carbon Example: Propanone Amine • Contains Nitrogen • Three different types of amines • Primary – NH2 attached to 1 C and two H • Secondary C-NH-C attached to two C and one H • Tertiary C-N-C attached to three C, no H! C • Raises pH of a solution Carboxylic Acids • Carboxyl =Alcohol and Carbonyl group at the same carbon • Lowers pH of solution! • Example: Ethanoic Acid Ester Carboxylic Acid in the center of a molecule Ethyl ethanoate Amide • Like Carboxyl group, OH replaced by NH2 • Ethanamide Thiol • Thiol group • -SH • Ethane thiol