Polar Covalent Bonds
advertisement

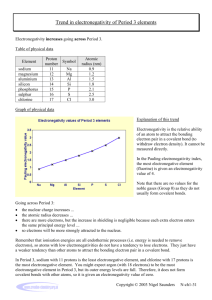
Polarity What are the similarities and differences between polar and nonpolar molecules? CH 8.4 Polarity When one atom is more electronegative than another atom. The “stronger” atom can pull the shared electrons closer, making it slightly negative. This leaves the other atom slightly positive. EX: H2O (covalent bond) Results in Hydrogen Bonds in water Helps water form “skin” called surface tension. Very important for Biology and life Electronegativity pg 177 Ionic Bonding ● ● ● ● ● Pull so strong that electrons given and taken one atom wants the electrons more, pulls harder Uneven distribution of electrons Due to a large difference in electronegativity eg NaCl Na Cl Na Cl Like dissolves in Like Polar/charged substances dissolve in polar liquids Table salt (NaCl) dissolves in water as Na+ and Cl- Nonpolar Covalent Bonding ● ● ● ● electrons shared both atoms want electrons the same amount no difference in electronegativity eg Cl2 Why do we care? •Like Dissolves Like = only materials with positive and negative parts will dissolve in water •Nonpolar molecules will NOT dissolve in water (oil and water for example) Alkanes are nonpolar Even though Carbon is slightly more electronegative than Hydrogen… There is no (-) or (+) end/pole pg 238 Bond Types Difference in Electronegativity Type of Bond Example 0-0.4 Nonpolar covalent H--H 0.4-1.0 Moderately polar covalent H--Cl 1-2 Very polar covalent H--F 2+ Ionic NaCl Review: Due Wednesday: p238-244 #30-37 p706-707 #18-25 p711 #26-29