1_1.3_thermal Decomposition Of Carbonates And - science
advertisement

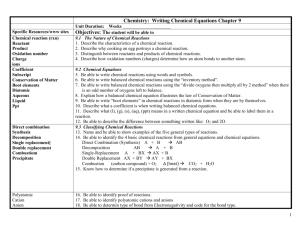
Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Key words; balanced chemical equation GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson I can: • Most metal carbonates will undergo thermal decomposition. Metal carbonates all decompose on heating in a similarly. • Atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction. Atoms and symbols are used to represent and explain what is happening to the substances in chemical reactions. • Conservation of mass occurs in a chemical reaction. No atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction so the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants and we can write balanced equations showing the atoms involved. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide What are we learning about today? HINT: acdeehiimmnotolports GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Recap THERMAL DECOMPOSITION occurs when heat is used to breakdown substances. Interpersonal: THINK FOR 30SECS Write a GENERAL equation for the What do you expect to be thermal decomposition When LIMESTONE decomposes CARBON produced when potassiumthen carbonate of OXIDE is produced. DIOXIDE and CALCIUM is decomposed? metal oxides Intrapersonal: CHAT with your partner LIMEWATER TURNS MILKY when a person blows through a straw into the solution. This is the lab test for CARBON DIOXIDE. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Task: Use your knowledge OVERVIEW: You and your partner will study a metal carbonate by • Describing its appearance • Plan the thermal decomposition investigation • Complete the thermal decomposition investigation • Explain your findings to another table group (red-yellow, green-blue) GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide The decomposition of metal carbonates Aim To plan an experiment to compare how different metal carbonates decompose when heated. Equipment • 2 x Test tubes and Delivery tubing • Retort stand and clamp • Bunsen burner and heat proof mat • Spatula, Metal carbonate and Limewater Method (Your plan should include the following: • A diagram of the apparatus. • A step-by-step account of how you would do the experiment. • A description of the following: – - How you are going to tell when the carbonates have decomposed.? How you will compare how quickly they decompose? How can you time exactly when the limewater goes milky? Is it possible to make this consistent? – controlling variables How can you make this experiment safe?) GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide The decomposition of metal carbonates Results Draw out a table using the headings below and write down the observations for each metal carbonate • Name of carbonate • Observations Conclusions • What patterns can you detect from your results? • Was your test fair? • Were your results accurate? Reliable? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Peer Learning Join another pair from another table and spend 10 mins each to teach what has happened in the experiment you have just completed. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson I can: • Most metal carbonates will undergo thermal decomposition. Metal carbonates all decompose on heating in a similarly. • Atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction. Atoms and symbols are used to represent and explain what is happening to the substances in chemical reactions. • Conservation of mass occurs in a chemical reaction. No atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction so the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants and we can write balanced equations showing the atoms involved. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Chemical Reactions Complete the following equations; Calcium Carbonate magnesium oxide + carbon dioxide CuO + CO2 ZnCO3 GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide For each of the chemical reactions above; Use the MASS NUMBER of each element to write balanced chemical equations GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Practice these equations in FULL – you choose the level of difficulty; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Thermal decomposition of magnesium carbonate Calcium added to hydrochloric acid Zinc metal added to sulphuric acid Calcium oxide is added to water to form a single compound Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate Zinc metal added to hydrochloric acid Calcium is added to water Magnesium metal is burnt Hydrogen gas is added to chlorine gas Calcium is added to oxygen gas Magnesium metal is added to hydrochloric acid GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Key words; ionic, covalent, bonding GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson I can: •Compounds can be formed by ionic and covalent bonding. •Ionic bonding involves the giving or taking of electrons. •Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons. •All bonding takes place to stabilise elements. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide MASS NUMBER PROTON NUMBER (ATOMIC) How many neutrons are there? •The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus •The proton (atomic) number is the number of protons in the nucleus. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide What about electrons? •The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus •The proton (atomic) number is the number of protons in the nucleus. The number of electrons equals the number of protons GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Electron Configuration tells us how the electrons are arranged around the nucleus in energy levels (shells). •The first energy level (shell) can contain a maximum of 2 electrons •The next energy levels (shell) can contain a maximum of 8 electrons •2,8,8,8 etc… GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide •Have a go at drawing out carbon in a dot and cross diagram… Mass number > Proton number > What is the electron configuration? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide RULES Proton number = Protons in the nucleus Mass number = Protons + Neutrons in the nucleus Number of Protons = Number of Electrons Electron configuration = 2,8,8,8 GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Draw dot and cross diagrams for: •Sodium •Potassium •Fluorine •Chlorine GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Plenary How many protons and neutrons in the nucleus? How many electrons? What is the electron configuration? How many electrons in the outer shell? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide •Ionic bonding occurs between metal elements and nonmetal elements •The outer electrons are not shared but they are donated or gained. (Given away or received) Why do elements want to share, donate or gain electrons? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Task Two Na Would it be easier to lose 1 or gain 7 electrons to have a full outer shell? Cl GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide - + Na Cl What compound is formed? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide What do you think will happen here? Mg S GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide What is the name of this compound? 2- 2+ Mg S GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Have a go!!!! Draw out the following simple Ionic compounds: a) Potassium chloride – KCl b) Lithium fluoride -LiF c) Sodium iodide – NaI Start by drawing a dot and cross diagram. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Can you name the compounds? Which are ionic compounds? 1. MgO Magnesium Oxide 2. NaCl Sodium Chloride 3. CO Carbon Monoxide 4. FeS Iron (II) Sulphide 5. FeSO4 Iron (II) Sulphate 6. LiOH Lithium Hydroxide GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide The covalent bond When non-metal atoms react together, they need to gain electrons to fill their outer shell and become stable. H incomplete outer shells H They can only do this if they share electrons with each other. The atoms share electrons so there H H is a strong force that joins the atoms together. This is called a covalent bond. both atoms have a full outer shell GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Task Two H H 1) Draw dot and cross diagrams for the following simple covalent compounds a) Chlorine gas (Cl2) b) Methane (CH4) c) Ammonia (NH3) GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Cl C H O H H H H Cl Cl GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; Be able to write balanced equations for reactions of quicklime with water & slaked lime with carbon dioxide Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson I can: •Compounds can be formed by ionic and covalent bonding. •Ionic bonding involves the giving or taking of electrons. •Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons. •All bonding takes place to stabilise elements. GCSE Core Chemistry