File - Fendy Lormine E
advertisement

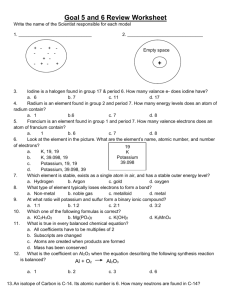
Fendy Lormine Chemistry 1 6-13-13 Chemists didn’t know that Potassium and sodium were different until the 18th century. That’s because they didn’t realize that vegetable alkali from potassium came from deposit earth, whereas mineral alkali from sodium came from wood ashes. Potassium was the first metal isolated by electrolysis. Potassium is never found free in nature, but is obtained by electrolysis of the chloride or hydroxide. Oranges contains lots of potassium, they are good for the body. Potassium is an element from the periodic table discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1807 in England. The atomic symbol for Potassium is (K). It’s Atomic number is 19. It’s color silver white. It’s Atomic Name is Potassium. It’s an Alkali metal so it is classified in the metal group. Potassium only has two stable Isotopes, K-39 and K-41, K-40 is a radioisotope of Potassium. K-40 is often also regarded as a stable isotope K-40 and K-41, are used to study the impact of potassium on the growth of plants and of the human cardiovascular system. Other temporary Isotopes of Potassium are K-42 and K-43 39K (93.6%), 40K (0.01%), and 41K (6.7%). Potassium is part of group one because it’s an alkali metal and it’s one of the most energetic elements in the periodic table. Atomic Mass: 39.0983 amu Melting Point: 63.65 °C (336.8 K, 146.57 °F) Boiling Point: 774.0 °C (1047.15 K, 1425.2 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 19 Number of Neutrons: 20 Period in the periodic table: 4 Atomic Radius of potassium is 235 Pm The electron configuration for potassium is: K 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 Ionization is any process by which a neutral atom or molecule gains or loses electrons when combined with a another atom. Potassium is most likely to form a positively charged ion with an energy of 1+, because it looses an electron. The first ionization energy of potassium is 418.8 kJ mol-1 Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. Or the ability of an atom to attract another in a chemical bound. The electronegativity of potassium according to Pauling is,0.8. http://www.webelements.com/potassium/history.html http://www.webelements.com/potassium/ http://www.webelements.com/potassium/isotopes.ht ml http://chemistry.about.com/od/elementfacts/a/potassi um.htm http://www.chem.latech.edu/~deddy/Lectnote/Chap7 B.html http://www.webelements.com/potassium/atoms.html http://www.chemguide.co.uk/atoms/bonding/electron eg.html http://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/k.htm http://www.chemicalelements.com/elements/k.html