Nutrition ppt essentialnutrients2012
advertisement

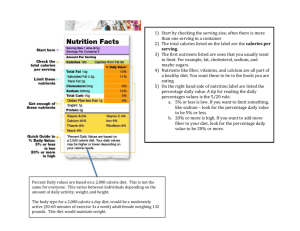
NUTRITION: ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS 8th Grade Health 1. What does “diet” really mean? 2. What are essential nutrients? 3. How can I tell what nutrients are in the food I eat? 4. How does eating the correct amounts of food affect my long-term health? Unit Goals Students will… Understand that good nutrition on a daily basis is essential to promote health and ability to work and play Define the roles of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins found in food and how they are used by the body Understand that a healthy diet is based on eating correct daily amounts of foods recommended in the food pyramid Determine portion sizes when planning meals, and reading food labels to determine nutrient value Let’s find out what you already know! 1. 2. 3. 4. Determine price of the product per serving size Provide the recipe for replication of the product Provide the serving size and the nutritional values within that serving Provide the manufacturer’s name and address Serving sizes on a food label must be stated in clear, common terms, such as: 1. Inches, feet and meters 2. Cup, teaspoon and piece 3. Gallon, ton and yard 4. Handful, mouthful and thumb The 3 nutrients that provide the body with energy are: 1.Calories, vitamins and minerals 2.Fats, vitamins and minerals 3.Calories, fats and vitamins 4.Fats, carbohydrates and proteins 1. Calorie 2. Fat 3. Protein 4. Carbohydrate Today I will read the student introduction to nutrition and learn vocabulary words and basic nutrition information that will help me make healthy choices. Student Intro & Study Guide Put your name, date, and class period on your paper Read the “Student Introduction” to Nutrition (2.4 & 2.5) Complete the study guide as you read When you are finished, get out a book to read or work on other homework quietly Day 2: Review + Food Labels Review student intro and study guide Discuss the evolution of the food pyramid and proportionality Food label activity Learning Target Today I will learn about the food pyramid and how to read a food label so that I can make informed, healthy choices. Food provides your body with energy and stamina to live your life to the fullest! Food provides your body with nutrients! Process of Satisfying Hunger You feel satisfied You Need Energy You eat to get rid of hunger You feel hungry NUTRIENTS Nutrient- substances in foods that provide energy, helps the body grow, and maintain necessary functions To receive all of the nutrients food can provide, a person should eat a variety of foods from the food pyramid each day. Essential Question #1 What does “diet” mean? A diet is the regular course of eating and drinking adopted by a person. It is the food a person eats every day! A healthy diet is made up of the correct daily amounts of food from the food groups in the food pyramid. The food pyramid puts foods into groups needed for a healthy diet. Messages from the Food Pyramid Activity Proportionality Moderation Variety Personalization Gradual Improvement History of USDA’s Food Guidance Food for Young Children 1992 1916 1940s 1970s 2005 1950s-1960s http://www.mypyramid.gov/ Message: Variety In the Dietary Guidelines: Consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods and beverages within and among the basic food groups. In MyPyramid graphic: Color bands represent that all food groups are needed each day for health. Food Groups are Color Coded In the Dietary Guidelines: Adopt a balanced eating pattern. ◦ Sufficient amount of fruits and vegetables, ◦ 3 or more ounce equivalents of whole-grain products per day ◦ 3 cup equivalents per day of fat-free or low-fat milk or milk products. In MyPyramid graphic: Differing widths of the color bands suggest about how much food should be eaten from each group. The new and improved pyramid illustrated in a plate. http://www.choosemyplate.gov/ What are the recommended daily amounts? Dependent upon 3 factors: Food Measurements 1. Age Cup = volume Milk, fruits, veggies 2. Gender 3. Activity Level Ounces = weight Grains, meats, beans Portion Size The amount of a specific food an individual eats. How have portion sizes changed? http://hp2010.nhlbihin.net/portion/ Portion Distortion! Portion Size & Food Measurements Food Labels U.S. Food and Drug Administration requires food manufacturers to provide nutritional information on their products. Purpose: provide serving size and nutritional value that is within the serving Serving sizes must be stated in clear, common terms Cup, teaspoon, piece, grams, etc. Percent Daily Value BASED ON A 2,000 calorie diet What is the serving size? How many total servings are there? How many calories per serving? How many calories in the whole box How much protein per serving? How much protein in 2 servings? What is the percent daily value of Iron? In the Dietary Guidelines: Engage in regular physical activity and reduce sedentary activities to promote health, psychological well-being, and a healthy body weight. In MyPyramid graphic: Steps and person on them symbolize that physical activity should be a part of everyday healthy living. Personalization: The name “MyPyramid” suggests an individual approach. The person climbing the steps mentally links each viewer to the image. Gradual Improvement: The slogan “Steps to a Healthier You” suggests that improvement should happen in stages, over time. 1.Carbohydrates* 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 2. Fat* 3. Protein* Nutrients that provide the body with energy: 1.Carbohydrates* 2. Fat* 3. Protein* Essential Nutrient #1 Preferred, quick source of Types of Carbs & Food Sources Simple Carbs: • Fruits & fruit juice • Milk (lactose) • Some vegetables • Table sugar • Sweets and colas Complex Carbs: Potatoes • Breads • Cereals • Grains • How Many Calories Are In EACH GRAM OF CARBS? How do you know how many calories you can get from carbohydrates in a serving? Total carbohydrates = 13g Calories pergram of carb= 4 13 X 4 = 52 calories How does our body use carbs? When food enters your mouth… 1. The body breaks down carbs into simple sugars called glucose 2. The sugars are released into the bloodstream 3. The pancreas releases a hormone called insulin when your blood-sugar level rises 4. Insulin moves sugar from blood into cells to be used for energy http://kidshealth.org/kid/diabetes_basics/what/pre vention.html Essential Nutrient #2 Most concentrated (long, slow) source of energy Helps the body with: nerve conduction vitamin absorption Insulation Organ protection Where do we find fats in our diet? Eggs and Dairy MEATS BUTTER OILS CHEESE NUTS Types of Fat 1.Unsaturated- in plant foods & fish Good for your Examples: olive oil, salmon 2. Saturated- from animal products Too much = risk of disease Examples: meat, cheese, butter 3. Trans-fat- “hydrogenated oil” Too much = risk of disease Examples: margarine, fast food HOW MANY CALORIES PER GRAM OF FAT? How do you know how many calories you can get from fats in a serving? Total fat = 14g Calories per gram of fat= 9 14 X 9 = 126 calories ESSENTIAL NUTRIENT #3 A reserve source of energy when carbs and fats are low Protein builds, maintains, and repairs body tissues like muscle. Meats Eggs Fish Nuts Beans HOW MANY CALORIES PER GRAM OF PROTEIN? How do you know how many calories you can get from protein in a serving? Total protein = 24g Calories per gram of protein= 4 24 X 4 = 96 calories Essential Nutrient # 4 Each one has a special job, but in general, vitamins are organic substances that… boost the immune system support normal growth and development help cells and organs do their jobs Two Categories of Vitamins 1. Fat-Soluble: dissolve in fat and can be stored in the body A, D, E, K 2. Water-Soluble: dissolve in water before your body can use them B, C Food Sources of Vitamins From ORGANIC substances… Vegetables Fruits Meats Grains Dairy Products ESSENTIAL NUTRIENT #5 Like vitamins, minerals help your body work properly. Unlike vitamins, minerals are (found in soil, absorbed/eaten by plants and animals) Vegetables Fruits Meats Grains Common Minerals Calcium Iron Magnesium Phosphorous Potassium Zinc One more Essential Nutrient! Water is important for health, performance and appearance Regulates body temperature Provides a means for nutrients to travel to organs Transports oxygen to cells Removes wastes from the body Moistens skin Helps muscles move Cushions joints Protects organs Where else can you get water besides the water fountain or in bottled water? Fruits and veggies Healthy beverages Most food contains some water