Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
advertisement

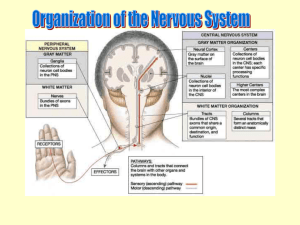
Ch. 13 The Central Nervous System Objectives • Be able to identify the various features of the spinal cord • Be able to identify the major parts of the brain and their functions • Understand how tracts and nuclei are arranged along the brain stem The Spinal Cord • Extends form the foramen magnum to L1 or L2 – About 42 cm long and 1.8 cm thick • Three main functions – Conduction • Conducts information up and down the cord, to and away from the brain and other regions of the trunk – Locomotion • Central pattern generators – Reflexes • Spinal reflexes involuntary response to a stimuli Spinal Cord • Two longitudinal grooves – Anterior median fissure – Posterior median sulcus • 31 pairs of spinal nerves – Segments • Divided into 4 regions – Cervical, thoracic, lumber, and sacral – Terminates at medullary cone • Cauda equina anatomyatlases.org Spinal Meninges • Fibrous connective tissue sheets • Three layers – Dura mater – Arachnoid mater • Subarachnoid space – Below medullary cone, lumbar cistern • CSF – Pia mater • Denticulate ligaments daviddarling.info Cross Sectional Anatomy d.umn.edu Spinal Tracts • Ascending tracts – Carry sensory information up • Descending tracts – Carry motor output down • Decussation – Contralateral – Ipsilateral • Sensory info typically carried by three neurons • Motor info carried by two neurons withealth.net Overview of the Brain • Control center of the body – Composed of an abundance of neurons • Divided into three major regions – Cerebrum • Divided into left and right hemispheres by longitudinal fissure – Gyri, sulci, – Communicate via the corpus callosum – Cerebellum • Posterior and inferior to the cerebrum • Second largest part of the brain – Brain stem • What remain of the brain if the cerebrum and cerebellum are removed – Diencephalon, midbrain, pons , and medulla Grey and White Matter • Arranged opposite of the spinal cord arrangement – Cortex composed of grey matter – Deep nuclei as well – Rest of brain is white matter running in tracts Embryonic Development niaaa.nih.gov Embryonic Development Meninges • Dura mater – Composed of two layers • Periosteal layer • Meningeal layer – Dural sinuses » Superior sagittal » Transverse • Arachnoid mater • Pia mater health.allrefer.com Ventricles • Ventricles – four internal chambers of brain – Lateral (2), third, cerebral aqueduct, fourth, central canal – Choroid plexus – mass of blood capillaries that line ventricles • Produce cerebral spinal fluid faculty.irsc.edu Cerebral Spinal Fluid • Clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of the CNS – Contains more Na+ and Cl- than plasma • Reabsorbed by the subarachnoid villi • Three functions – Buoyancy – Protection – Chemical stability Blood Brain Barrier • Brain require significant supply of blood – Oxygen and glucose • Exposure to blood would make it susceptible to harmful agents • Blood-Brain barrier – Tight junctions between endothelial cells of brain capillaries – Permeable to water, glucose, O2, alcohol, anesthetics • Blood-CSF barrier – Tight junctions between ependymal cells of choroid plexus Cerebrum • Divided into cerebral hemispheres – Gyri, sulcus , and fissures – Lobes • Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital • Insula, fifth lobe, deep – Three regions (superficial to deep) • Grey matter cortex • Inner white matter • Deep basal nuclei emc.maricopa.edu Cerebral Cortex • The “boss” – Allows us to feel, move (voluntary), communicate, remember and understand • Grey matter – Cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons – No nerve tracts • Three kinds of functional regions – Motor areas – voluntary movement – Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensations – Association areas – integrate different info for purposeful action Motor Areas • Primary motor cortex – Precentral gyrus – Pyramidal cells • Conscious control of precise or skilled voluntary movement • Axons become corticospinal tract in spinal cord – Motor homunculus • Premotor cortex – Controls and coordinates skilled motor activity • Brocas area – Motor speech area – Planed motor activity thebrain.mcgill.ca Sensory Areas • Primary somatosensory cortex – Postcentral gyrus • Sensory information relayed via three-neuron synaptic chain – Sensory homunculus • Somatosensory association area – Integrates different sensory information from PSC and produces an understanding of what is being felt Sensory Areas Association Areas • Prefrontal cortex – Involved with intellect, cognition, recall, judgment, consciousness, reasoning, and personality • Language area – Wernicke’s area • Sounding unfamiliar words • Visceral association area – Cortex of insula – Conscious perception of visceral sensations Cerebral White Matter • Responsible for communication within cerebral areas and between cortex and and lower CNS – Myelinated axons that form tracts • Classified based on direction they run in – Commissural tracts • Enable communication between hemispheres – Corpus callosum – Association tracts • Connect different parts of the same hemisphere – Long, different lobes – Short, different gyri – Projection tracts • Connect cerebrum to lower brain and cord centers • Internal capsule – dense band of tracts between thalamus and basal nuclei • Corona radiata – fanning out of band Basal Nuclei • Deep subcortical nuclei lateral to thalamus • Three nuclei recognized – Caudate, putamen, globus pallidus – Lentiform nucleus • Putamen and globus pallidus – Corpus striatum • Putamen and caudate • Involved with motor control scienceblogs.com The Diencephalon • Consists of three paired structures – Thalamus • Relay to the cerebral cortex • Key role in motor control – Hypothalamus thebrainwiki.com • Major control center of autonomic and endocrine systems • Hormone secretion, autonomic effects, thermoregulation, food and water intake, memory – Epithalamus • Pineal gland The Brain Stem • Three regions: midbrain, pons, and medulla • Midbrain – Cerebral peduncles • Descending corticospinal tract – Cerebral aqueduct – Tectum – posterior to aqueduct • Corpora quadrigemina nuclei orble.com – Superior colliculi – coordinate head and eye movements – Inferior colliculi – auditory relay, reflexive response to sounds – Sustancia nigra – inhibitory motor center • Rich in melanin, precursor to dopamine – Red nucleus – fine motor control • Connects with cerebellum – includes nuclei of oculomotor and trochlear nerves Pons • Bulging brain stem region between midbrain and medulla • Consists of tracts • Nuclei of trigeminal, abducens, and facial nerves • Respiratory centers Medulla • Most inferior part of brain stem • Descending tract – Anterior corticospinal tracts (pyramidal) – Tectospinal tracts – motor control of neck • Ascending tracts – Inferior olivary nuclei • Send proprioceptive info to cerebellum – Gracile and cuneate nuclei • Second order neurons decussate, form medial lemniscus • Cardiac and respiratory centers • Reticular formation – grey matter Cerebellum • Located dorsal to medulla and pons – Connected via cerebellar peduncles • Cerebellar features – – – – hemispheres connected via vermis Gyri called folia Three lobes: anterior, posterior, flocculonodular Arbor vitae – white matter • Functions – Coordinated body movements and maintaining equilibrium