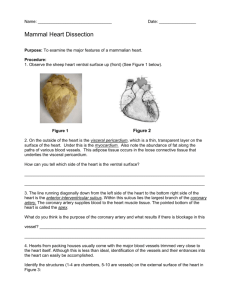
Location and General Features of the Heart
advertisement

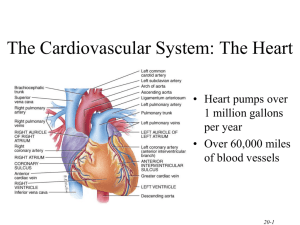
By: Samantha Peterson Laura Soehngen BJ Dean Zach Palesch Four Chambers Left and Right Atrium- upper and receiving chambers Left and Right Ventricles- lower and pumping chambers Atrium means “entrance hall” in Latin Ventricle means “little belly” in Latin http://inspirations786.wordpress.com/2011/11/15/four-chambers-of-heart-islamic-polygamy-of-up-to-four-wives-andmiracle-of-allah/ Layers of Heart Wall Endocardium- smooth thin layer of cells that helps to reduce friction caused by blood that is constantly moving through chambers Pericardium- A sac that fits loosely over the heart Myocardium- muscular wall constantly active and needs a generous supply of oxygen and energy from blood http://paramedicine101.blogspot.com/2009/08/basic-cardiology-part-i.html Inner Anatomy http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/life/human-biology/heart2.htm Outer Anatomy SUPERIOR VENA CAVA AORTA PULMONARY TRUNK RIGHT ATRIUM PULMONARY VEINS LEFT ATRIUM RIGHT VENTRICLE LEFT VENTRICLE http://quizlet.com/2507160/external-heart-anatomy-pics-flash-cards/ Valves of the Heart There are 4 valves of the heart Tricuspid valve: right side, 3 cusps Mitral valve: 2 cusps Pulmonary valve: between Right ventricle and pulmonary artery, opens as Right ventricle contracts and forces blood out to the lungs Aortic valve: between the Left ventricle and the aorta , opens as Left ventricle contracts and forces blood out to the body Heart valves open Cusps forced apart by pressure of blood pumped by ventricle Heart valve closed Pressure causes the cusps to close and seal preventing reverse blood flow Bibliography The Circulatory System by Regina Avraham The Human Body by Steve Parker