Acids & Bases
advertisement

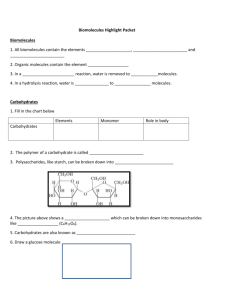
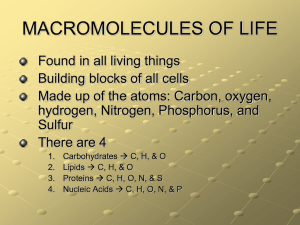
Answers on a separate sheet: Wednesday 1. What kind of molecule is water? 2. Draw a water molecule (include the elements and charges). 3. List 2 properties of water with an example. Organic Molecules Contain carbon (usually bonded to another carbon) Small organic molecules (monomers) join together to form large organic molecules (polymers) There are 4 classes of organic polymers (macromolecules): carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids Polymers are created by dehydration synthesis (the removal of water) Polymers are broken down by hydrolysis (the addition of water) Carbohydrates Molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen Store large amounts of energy that can be used quickly 1. Simple Carbohydrates (sugars) Monosaccharides are made of only one sugar monomer (ex. Glucose) Disaccharides are made of two sugar monomers (ex. Sucrose) Carbohydrates 2. Complex Carbohydrates (polysaccharides) Starch - used as energy storage in plants Glycogen - used as energy storage in animals Carbohydrates Cellulose (a.k.a. fiber) – structural molecule in plants; cannot be digested by animals Chitin - structural molecule in fungi and arthropods Proteins composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are made of long chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds Proteins Structural Proteins collagen (found in cartilage & tendons) keratin (found in hair & nails) actin & myosin (found in muscles) Proteins Functional Proteins hemoglobin (carries oxygen in red blood cells) antibodies(fight foreign invaders in the immune system) enzymes (biological catalysts) Enzymes speed up reactions by reducing activation energy (EA) are VERY specific are NOT used up during a reaction their shape determines their function Enzymes 2 How Enzymes Work 1. enzymes have a pocket on their surface called an active site 2. the molecule(s) that fits 1 into the active site is/are called the substrate(s) 3. the reaction takes place at the active site 4. the products of the reaction are released 3 4 Right Now 1. Turn in Enzyme Lab 2.Take out review/warm up answer sheet Answer on your paper: Thursday 1. List the 4 elements that make up 96% of living things. 2. What are small organic subunits called? Large ones? 3. Why do we eat carbohydrates? Give an example of a monosaccharide and a polysaccharide. 4. List 2 proteins and their function. What Affects Enzyme Activity? 1. Temperature p.7 decrease in temp. will decrease reaction rate enzyme will lose shape (denature) after being exposed to extremely high heat 2. pH extreme pH can decrease reaction rate or denature the enzyme 3. Concentration increased substrate or enzyme concentration will increase reaction rate p. 2 The water molecule separates into two different ions: H2O H+ + OH(H+)hydrogen ions and (OH-) hydroxide ions Strong acid the pH scale measures the amount of H+ Acids (pH 0 – 6.9) Taste sour Feel like water Bases (pH 7.1 – 14) Taste bitter Feel slippery Strong base Right Now 1. Turn in Buffer Lab 2. Vocabulary QUIZ p. 8 Lipids Are insoluble in water Contain many C-H bonds and very little oxygen Examples: Steroids Cholesterol, chlorophyll, sex hormones Lipids Phospholipids Make up cell membranes Fats Composed of a glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains Function in energy storage, insulation, and cushioning 2 Types of Fats 1. Saturated fats Are solids at room temperature Ex. butter, lard 2. Unsaturated fats Are liquids at room temperature Ex. oils Answer on same sheet: Monday 1. If something has a pH of 2 is it an acid or base? Would it be strong or weak? 2. What is the name of the substance that fits into the active site of an enzyme? p.9 Nucleic Acids Store information in the form of a code Are composed of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Made of long chains of nucleotides Examples: 1.DNA – contains instructions 2.RNA – synthesizes proteins Answers on separate sheet: Tuesday 1. What is the mass number if an atom has 6 protons and 6 neutrons? 2. What charge would a sodium atom have with 11 protons and 10 electrons? 3. What is the solvent in an aqueous solution?