Macromolecules ppt
advertisement
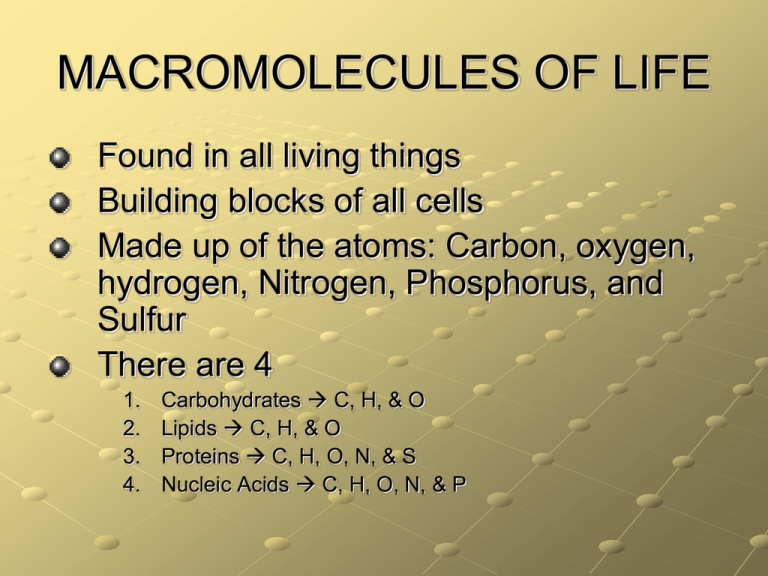
MACROMOLECULES OF LIFE Found in all living things Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur There are 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrates C, H, & O Lipids C, H, & O Proteins C, H, O, N, & S Nucleic Acids C, H, O, N, & P Carbohydrates Basic units: sugars Provide energy and structural support Fiber is a carbohydrate that prevents constipation Foods: breads, cereals, vegetables, fruits, & seeds Extra glucose is converted into glycogen in the liver Glucose Test for Simple Carbohydrates Benedict’s solution • Benedict's solution is a chemical indicator for simple sugars such as glucose: C6H12O6. • Aqua blue: negative test; yellow/green/brick red, etc.: positive test Test for Complex Carbohydrates Test for Complex Carbohydrates Iodine Solution • Iodine solution Æ color change = blue to black Lipids/Fats Basic units: fatty acids Functions: provides energy & structure, cushions the body, and prevents heat loss Found in butter, margarine, candy made of fatty acid molecules that consist of two distinct regions: a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain a hydrophilic head Test for lipids Test for Fats (lipids) Sudan IV • If lipids are present the Sudan IV will stain them reddish‐orange (positive test). Also used is the paper bag method. If the bag shows a grease spot then there are fats present. Saturated Fats contain single carbon-to-carbon bonds has lots of hydrogen solid at room temperature (beef, pork, chicken, dairy) found in animal products Reduce Intake! can clog blood vessels Unsaturated Fats contain double or triple carbon-to-carbon bonds & fewer hydrogen atoms Liquid at room temperature (oils, nuts, & seeds) found in plant products Better Intake! Molecular structures of Fats Saturated Fat Unsaturated Fat DNA Structure discovery James Watson and Francis Crick with DNA Model in 1953. Nucleic Acids Atoms: C, H, O, N, P Basic units: nucleotides composed of Sugar Phosphate group Base: cytosine, guanine, adenime, thymine, uracil There are two types: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Function: DNA directs & controls all activities of all cells in an organism – RNA helps DNA – DeoxyriboNucleic Acid DNA is the hereditary material passed on from parents to offspring Structure: doublestranded Phosphate group Sugar deoxyribose Bases Cytosine – Guanine Adenine – Thymine RNA RNA helps the DNA RiboNucleic Acid Structure: singlestranded Basic units: nucleotides Phosphate group Sugar ribose Bases Cytosine – Guanine Adenine – Uracil Nitrogenous Bases Proteins Atoms: C, H, O, N, S Basic units: amino acids (20) Provide energy & structure, repairs body tissues Some are called hormones, enzymes, neurotransmitters, etc. Foods high in protein: meat, eggs, poultry, milk & milk products, nuts, dried beans, peas, & lentils Proteins Primary Structure The very basic strand of amino acids Secondary Structure The hydrogen-bond interaction among strands of amino acids giving alpha helices and beta-sheets shapes . Proteins Tertiary Structure Quaternary Structure Interaction between alpha helices and beta-sheets. These protein domains for small globular proteins. Small globular proteins form protein aggregates. A famous example is hemoglobin. Protein Structures Protein Structures (Cont’d) Enzymes Are proteins Speed up chemical reactions without being consumed or using energy Enzymes Amylase - breaks down sugar Proteases - break down proteins Lipases - break down lipids Catalase - breaks down hydrogen peroxide Enzyme Action Models Models Enzyme Action Models lock and key model substrate & the enzyme fit together perfectly induced-fit model Enzyme changes shape slightly to accommodate the substrate Factors that affect enzyme action: 1. Temperature – 37oC best for human enzymes 2. pH – different for each enzyme a. b. c. 7 for amylase in the mouth 2 for pepsin in the stomach 8 for trypsin in the intestines 3. Concentration of enzyme and substrate 4. Coenzymes – helpers such as minerals and vitamins Macromolecules parts of the cell Membrane





