BUS 173 Lecture 11

BUS 173 Lecture
11
Simple Moving Averages
•
Simple Average
•
Advantage?
•
Disadvantage?
•
Regression
•
Advantage?
•
Disadvantage?
•
Deviation
•
MAD/MAPE
•
MSE
Covered in Last Class
•
Conditions
•
Stable time series (No significant trends)
•
Good for short-range forecasts
•
Two forms
•
Simple Moving Averages (SMA)
• 3 period
•
4 period
•
5 period
Smoothing methods
𝑀𝑜𝑣𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 =
(𝑚𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑛 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑠) 𝑛
3 period M.A =
(𝑚𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 3 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑠)
3
(𝑚𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 4 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑠)
4 period M.A =
4
(𝑚𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 5 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑠)
5 period M.A =
5
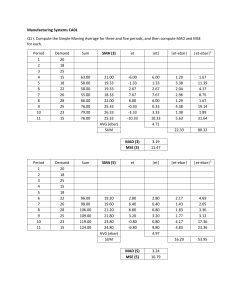
Find out the 3, 4, 5 MA’s for the next example
Simple Moving Averages
Example 1 (Lecture 10 Ex)
Months Demand (in thousand)
December ‘12
January ’13
February ’13
March ’13
April ’13
May ’13
June ’13
July ’13
August ’13
September ’13
October ’13
November ’13
December ’13
January ’14
February ’14
March ‘14
23
28
31
34
37
33
24
20
17
16
20
25
29
31
30
26
•
Which MA is the best possible forecast in this situation?
•
How do we find out the effectiveness of the forecasts
•
MAPE
•
MSE
Assessing the Forecast
Week
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Sales (1000s of gallons)
17
21
19
23
18
16
20
18
22
10
Example 2 – Gasoline
12
Sales
20
15
22
25
20
15
10
5
0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 Graph for Example 2 10 11 12
Example 1
MAPE =?
MSE = ?
Use of SMA
Example 2
MAPE =?
MSE = ?
End of Lecture
Thank You