File
advertisement

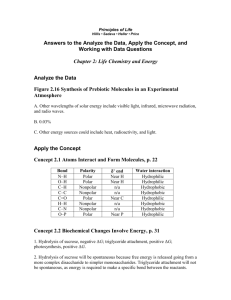
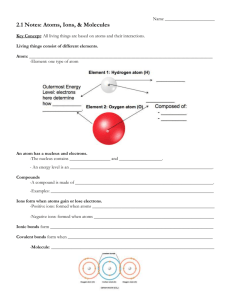
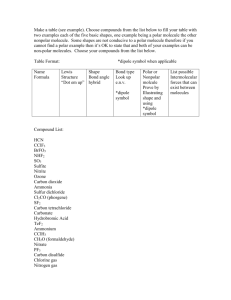
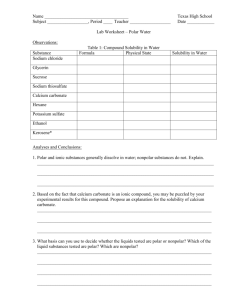
SAPONIFICATION Polymers SAPONIFICATION The making of soap from a fat or oil and a caustic material such as lye or sodium hydroxide SOAP MOLECULES HAVE BOTH A POLAR HEAD & A NONPOLAR TAIL POLARITY OF SOAP MOLECULES POLAR HEADS – WATER- LOVING – HYDROPHILIC – COMPOSED OF CHARGED OR PARTIALLY CHARGED PARTS NONPOLAR TAILS – WATER-FEARING – HYDROPHOBIC – COMPOSED OF A LONG UNCHARGED HYDROCARBON CHAIN “LIKES DISSOLVE LIKES” WATER IS A POLAR SOLVENT. IT WILL DISSOLVE POLAR SOLUTES TO MAKE A HOMOGENEOUS SOLUTION. PARTIALLY NEGATIVE OXYGEN PARTIALLY POSITIVE HYDROGENS (polar molecules are called dipoles) “LIKES DISSOLVE LIKES” HEXANE IS A NONPOLAR SOLVENT. IT WILL DISSOLVE NONPOLAR SOLUTES TO MAKE A HOMOGENEOUS SOLUTION. NONPOLAR HEXANE UNCHARGED HYDROCARBON CHAINS POLAR AND NONPOLAR ARE IMMISCIBLE POLAR VINEGAR WILL NOT MIX WITH NONPOLAR OIL. THE MIXTURE REMAINS HETEROGENEOUS. SURFACTANT ACTION SOAP MOLECULES ARE SURFACTANTS, SURFACE SEEKING. IN A BEAKER OF POLAR WATER, SOAP MOLECULES SEEK THE SURFACE. Polar heads of soap molecules face toward polar water and nonpolar tails stick out. water surface SURFACTANT ACTION SOAP MOLECULES ARE SURFACTANTS, SURFACE SEEKING. IN A BEAKER OF NONPOLAR HEXANE, SOAP MOLECULES SEEK THE SURFACE. Nonpolar tails of soap molecules face toward nonpolar hexane and polar heads stick out. hexane surface HOW DOES SOAP CLEAN? CONSIDER THE ENVIRONMENT: AQUEOUS POLAR MEDIUM NONPOLAR DIRT OR OIL UNIQUE QUALITY OF SOAP MOLECULES = GREASE OR DIRT THE SOAP MOLECULES CAN SURROUND NONPOLAR DIRT OR GREASE WITH THE POLAR HEADS POINTING OUT TOWARD THE POLAR AQUEOUS MEDIUM AND THE NONPOLAR TAILS STICKING INTO THE DIRT OR GREASE. THE RESULTING STRUCTURE IS CALLED A MICELLE. MICELLE FORMATION This is a micelle. The interior green portion of the cluster is composed of hydrophobic nonpolar parts and the exterior is composed of hydrophilic polar parts. CLEANING ACTION OF SOAP In cleaning, the nonpolar ends of soap molecules attach to nonpolar grease or dirt, letting water seep in underneath. The grease or dirt is pried loose and surrounded by soap molecules with the polar ends facing out. The micelles are then carried off by a flood of polar water. Classzone has a 30 second clip of micelle formation. micelle formation SAPONIFICATION: THE CHEMICAL REACTION ` OIL AND LYE SOAP AND GLYCEROL THIS IS THE OVERALL REACTION!!!!!! THE ASSESSMENT IS ON: • THE EQUIPMENT AND PROCESSES USED IN THE LABORATORY • HOW SOAP CLEANS CLOTHES, HAIR, SKIN AND DISHES • THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF SOAP MOLECULES • THE BOOK MATERIAL, PPT NOTES AND EDMODO VIDEOS DISCUSSION QUESTIONS • Soap was expected as the product in this reaction. Explain how the properties of the lab product are consistent with commercial soap. • Describe the differences in the bubbles of the three soaps. Which soap bubbled the least and how would this be beneficial to its function? • Describe the differences in the pH of the three soaps. Which soap had the pH farthest away from neutral (7)? Would you use this soap to wash your hair and face? Explain. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS • Describe the results of adding calcium, magnesium and iron ions to the soap solutions. The same phenomenon occurs when hard water and well water are used to wash hair, skin and clothes. In fact, the shower and tub also suffer. Explain. • What are several reasons for error in this lab? Explain how each of these reasons impacts the results in this lab.