Stoichiometry - Magoffin County Schools
advertisement

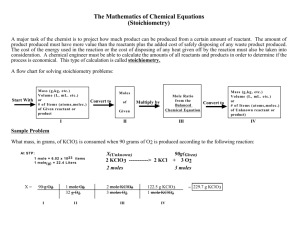
Bell Ringer • How many moles of Sodium Sulfite, Na2SO3, are contained in 235.5 grams? • FW of Na2SO3 = 126.06 g/mole • 235.5 g Na2SO3 • X 1 mole Na2SO3 = 235.5 moles Na2SO3 126.06 g Na2SO3 126.06 • = 1.86815802 moles Na2SO3 = 1.868 moles Na2SO3 Mass Problems (Stoichiometry) Mass Relationships within Chemical Reaction Learning Target • I CAN solve a mass-mass relationship problem (stoichiometry) using dimensional analysis. What is Stoichiometry? • Simply put, STOICHIOMETRY is the study of the RELATIONSHIP between REACTANTS and PRODUCTS in a chemical reaction. – In other words, if there is X AMOUNT OF REACTANTS, what MASS OF PRODUCT can be produced? • Recall that a CHEMICAL EQUATION represents what occurs on the SUBMICROSCOPIC LEVEL in a chemical reaction. • An EQUATION is the chemist’s “RECIPE” so to speak. • In STOICHIOMETRY, the chemist studies the AMOUNT of REACTANTS/PRODUCTS REQUIRED/PRODUCED in a CHEMICAL REACTION. • Generally, a STOICHIOMETRIC CALCULATION has THREE PARTS: • 1. CONVERT the STARTING QUANTITY of substance [REACTANTS OR PRODUCTS] to MOLES: – A. If the reactant/product is an ELEMENT, find the ATOMIC MASS on the periodic table; remember the unit is g/mole. – B. If the reactant/product is a COMPOUND, calculate the FORMULA WEIGHT of the compound, also in g/mole.( Formula Weight Calculator ) • 2. Establish the MOLE RATIO from the BALANCED EQUATION: • The mole ratio is the RATIO OF THE COEFFICIENTS of the two substances in question. – Example 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O – What is the MOLE RATIO between Hydrogen and Water? – 2 mol H2 : 2 mol H2O • 3. Convert MOLES OF FINAL SUBSTANCE [REACTANTS/PRODUCTS] to GRAMS of FINAL SUBSTANCE. – You will need to calculate the FORMULA WEIGHT OF THE FINAL SUBSTANCE. • 4. Round the FINAL ANSWER to SIGNIFICANT FIGURES. EXAMPLE PROBLEM • Table Salt, Sodium Chloride, is formed by the reaction of Chlorine gas with Sodium metal according to the equation: • 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl • How many grams of Sodium Chloride could be formed from 45.0 grams of Sodium? Steps • 1. If necessary, BALANCE THE EQUATION. • 2. LABEL the amount(s) GIVEN and the amount(s) to BE FOUND. • 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl 45.0 g ?g • 3. Set up a DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS: • Starting Amount • • Mole Ratio (coeffiecients from the equation) 1 Mole FW Final Product of Top Line ______________________ =_____ = _____ Product of FW 1 Mole X Bottom Line Start • • FINAL ANSWER Grams Moles MoleGrams • IF SET UP CORRECTLY ALL UNIT CANCEL EXCEPT THE LAST ONE! • 4 Begin with the AMOUNT GIVEN and work toward the AMOUNT PRODUCED. • 45.0 g Na 1 mole Na 2 mol NaCl 58.44 g = • X 22.989 g Na 2 mol Na 1 mol NaCl • 5. MULTIPLY all values ACROSS THE TOP, then all values ACROSS THE BOTTOM, then DIVIDE the TOP by BOTTOM. • • = 5,259.60 g = 114.39 g = 114 g NaCl 45.978 Practice Problem • If Calcium Hydroxide reacts with Hydrogen Chloride according to the following equation, how many grams of Calcium Chloride would be formed if 75.0 grams of Calcium Hydroxide are used in the reaction? • Ca(OH)2 + 2 HCl CaCl2 + 2 H2O