Unit 9 Lesson Plans- Stoichiometry 2014
advertisement

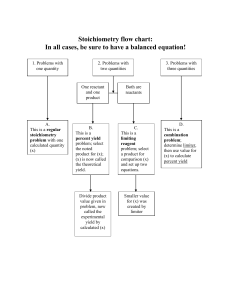
Unit 9 Lesson Plans- Stoichiometry 2015-2016 CP Lesson 97 98 99 100 101 102 Objective Notes- Stoichiometry - What is Stoichiometry? - How can looking at an equation tell you about moles and mass of the compounds? - How can mole ratios be determined from a balanced equation? - What is a mole to mole conversion? How can the mole to mole be determined? Notes- Stoichiometry Conversions - How are mole to mass problems done? How are they different from a mole to mole conversion? - How are mass to mass problems done? How many steps are mass to mass conversions? - What units must be shown for these types of problems? What conversion factor must be used for these conversions? Go over Stoichiometry WS - Stoichiometry Practice (WS#2) - What are the three types of stoichiometry? - What is the difference between a mole to mole, a mole to mass and a mass to mass? - How can students logically determine which conversion is necessary in the problem and can logic help them determine the conversion factor? - How many places are necessary in the final answer? Go over Stoichiometry WS #3 Stoichiometry Quiz - How can mole ratios be determined for a balanced chemical equation? - Can the three types of stoichiometry problems be distinguished and calculated? - Can a stoichiometry problem be solved without first writing a balanced chemical equation? - What is a hydrocarbon combustion reaction? Lab #16 Stoichiometry Lab - What happens when aluminum foil is added to copper (II) chloride? - What is the balanced chemical equation for this single replacement reaction? - What happens to the temperature of the reaction as the reaction proceeds? - How can the theoretical yield of the products be calculated from the starting masses? A- S’more Activity - What is stoichiometry and can it be applied to calculate how many S’mores can be made from a set amount of materials? - What is a limiting reactant? Can students practice the concept of a limiting reactant is by making S’mores? Homework (due dates) - Stoichiometry WS (#1-4) Per 2- 3/28 - Stoichiometry WS (#5-8) Per 2- in class - Stoichiometry WS #3 Per 2- in class - Stoichiometry Quiz Per 2- 3/31 - Finish Lab #16 Per 2- 4/4 - S’more Activity Per 2- 4/6 103 104 105 106 Notes- Limiting Reactant - What are the steps needed to calculate the limiting reactant? - Once the limiting reactant is found what other calculations can be done? - How can the left over excess reactant be calculated? - How can excess used during a reaction be determined? - Why is the balanced equation so important during limiting reactant problems? Limit Practice - How can a limiting reactant be calculated? Where do the comparison numbers come from when finding which reactant is limiting? - Why do students start with the limiting reactant for every other type of calculation dealing with a limiting problem? Notes- Percent Yield - How is percent yield calculated and how is it different from percent error? - How can the theoretical be calculated from a basic stoichiometry and then be plugged into a percent yield problem? Stoichiometry Review - What are the three types of stoichiometry and how can they be calculated? - What is a limiting reactant and how can it be calculated? - How can the theoretical yield of a product be calculated once the limiting is determined? Stoichiometry Test - How can the type of stoichiometry problem be determined? - How can percent yield be calculated? - How can a limiting reactant problem be determined without the problem specifically saying find the limiting reactant? - How can a mole ratio be determined? - How can an equation be interpreted in terms of moles and mass? Limiting Reactant WS Per 2- 4/7 - Percent Yield WS Per 2- in class Study Stoichiometry Test Per 2- 4/8