Pons
advertisement

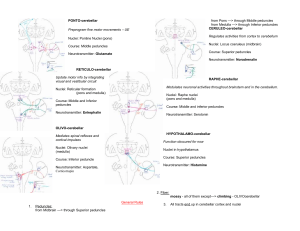
Brain Stem I Basic Neuroscience QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. James H. Baños, Ph.D. Overview Major external features Transverse sections Pathways: The big Four Neurotransmitter nuclei Major Brain Stem Activities Conduit Ascending and descending pathways Integrative functions Complex motor patterns Respiratory and cardiovascular activity Regulation of arousal and level of consciousness Cranial Nerve functions Major External Features Brain Stem Midbrain Pons Medulla Midbrain Cerebral Peduncles Interpeduncular cistern Origin of CN III -- Oculomotor Nerve Corpora Quadrigemina Superior Colliculi Inferior Colliculi Midbrain Corpora quadrigemina CN III Cerebral peduncles Interpeduncular cistern Pons Cerebellar Peduncles Superior (Dives under the colliculi) Middle (Bridge of the pons) Inferior (inferior/medial to middle) Floor of the 4th Ventricle Pons Pons Middle cerebellar peduncle Pons Superior cerebellar peduncles Middle cerebellar peduncle Inferior cerebellar peduncles Pons 4th Ventricle Inflow from aqueduct of Sylvius Sulcus limitans Medulla Pyramids Pyramidal decussation Inferior olive Obex (inferiormost point of the 4th ventricle) Medulla Obex Pyramids Inferior olive Medulla Inferior Olive Pyramids Transverse Sections Transverse Sections But first…a word about orientation… Clinical Anatomical Midbrain Cerebral peduncles Substantia nigra Red nucleus Midbrain Myelin Stained Cerebral peduncles Midbrain Substantia nigra Midbrain Red Nucleus Midbrain Colliculi Midbrain Substantia nigra Midbrain Red nucles Substantia nigra Pons 4th ventricle Pontine nuclei Locus ceruleus Pons Pontine nuclei 4th vent Locus ceruleus Pons are needed to see this picture. TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor QuickTime™ and a Locus ceruleus Pons 4th ventricle Pontine nuclei Locus ceruleus Pons 4th ventricle Sulcus Limitans Middle cerebellar peduncle Pons QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Unc ompressed) decompres sor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Rostral Medulla Pyramids Inferior Olive Rostral Medulla Pyramids Inferior olive Caudal Medulla Sensory nuclei Nucleus Gracilis Nuclues Cuneatus Pyramidal decussation Caudal Medulla Nucleus cuneatus Nucleus gracilis Tectum and Tegmentum Tectum and Tegmentum Tectum Area posterior to the ventricular space Only prominent in the midbrain Superior and inferior colliculi (“tectal plate”) Tectum and Tegmentum Tectal Plate Tectum and Tegmentum Tegmentum Area anterior to the ventricular space (but not everything anterior) This is the embryologically oldest areas of the brainstem Area anterior to the tegmentum “added on” during development Big Four Pathways Remember the Big Four? Corticospinal tract Dorsal Columns Spinothalamic tract Spinocerebellar tracts Big Four Pathways Corticospinal tract Spinothalamic tract Ascending pain/temperature Dorsal columns/Medial lemniscus Descending motor Ascending somatosensory and conscious proprioception Spinocerebellar tracts Ascending unconscious proprioception The Big Four -- Caudal Medulla Lateral Cuneate Nucleus Corticospinal tract Medial Lemniscus Spinothalamic tract Spinocerebellar tracts The Big Four -- Rostral Medulla Corticospinal tract Medial Lemniscus Spinothalamic tract Spinocerebellar tracts The Big Four…err…three -- Pons Corticospinal tract Medial Lemniscus Spinothalamic tract The Big Three -- Midbrain Corticospinal tract Medial Lemniscus Spinothalamic tract Brain Stem Nuclei Brain Stem Nuclei Major neurotransmitter nuclei Reticular formation (not really a “nucleus” but acts like a group of nuclei) Nuclei associated with cranial nerves Raphe Nuclei Ridge of cells along the midline in the center of the brainstem Multiple nuclei Caudal projections to the spinal cord and other parts of the brainstem Rostral projections to multiple cortical areas Raphe Nuclei Major serotonin nuclei Technically part of the reticular formation Complex reciprocal relationships with multiple areas Ascending pathways involved in many neurobehavioral phenomena Mood Sleep Feeding/satiety Descending pathways modulate spinal cord function Pain Locus Ceruleus Major norepinephrine nucleus Dorsal wall of the rostral pons Projects to Spinal cord Brain Stem Cortex are needed to see this picture. TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor QuickTime™ and a Locus Ceruleus Function Arousal Modulation of stress responses Linked to Depression Anxiety Post-traumatic stress disorder Accounts for some of the psychiatric symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease Locus Ceruleus Normal Parkinson’s Disease Substantia Nigra One of a few major dopamine center Projects to the basal gangila Function Modulation of movements Major role in Parkinson’s Disease NOT involved in psychiatric symptoms Substantia Nigra QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Substantia Nigra QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Parkinson’s Disease Normal Nucleus Basalis of Meynert NOT in the brainstem, but important Located in the basal forebrain Major acetylcholine nucleus in the brain Provides tonic stimulation to the hippocampus QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Basal Forebrain Nucleus Basalis of Meynert Major neurotransmitter associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Major medications for Alzheimer’s are cholinesterase inhibitors Coming Up… Reticular formation Cranial nerves and their nuclei