Lindsey AP TEST: Review Session Names with key words: Names
advertisement
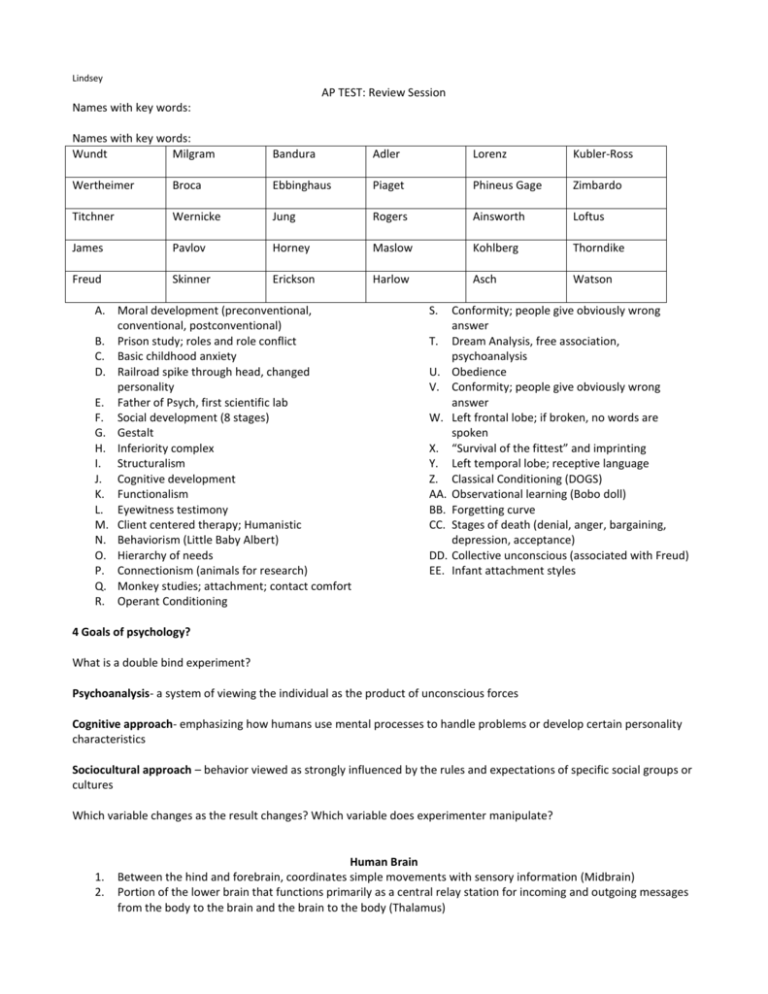
Lindsey AP TEST: Review Session Names with key words: Names with key words: Wundt Milgram Bandura Adler Lorenz Kubler-Ross Wertheimer Broca Ebbinghaus Piaget Phineus Gage Zimbardo Titchner Wernicke Jung Rogers Ainsworth Loftus James Pavlov Horney Maslow Kohlberg Thorndike Freud Skinner Erickson Harlow Asch Watson A. Moral development (preconventional, conventional, postconventional) B. Prison study; roles and role conflict C. Basic childhood anxiety D. Railroad spike through head, changed personality E. Father of Psych, first scientific lab F. Social development (8 stages) G. Gestalt H. Inferiority complex I. Structuralism J. Cognitive development K. Functionalism L. Eyewitness testimony M. Client centered therapy; Humanistic N. Behaviorism (Little Baby Albert) O. Hierarchy of needs P. Connectionism (animals for research) Q. Monkey studies; attachment; contact comfort R. Operant Conditioning S. T. U. V. W. X. Y. Z. AA. BB. CC. DD. EE. Conformity; people give obviously wrong answer Dream Analysis, free association, psychoanalysis Obedience Conformity; people give obviously wrong answer Left frontal lobe; if broken, no words are spoken “Survival of the fittest” and imprinting Left temporal lobe; receptive language Classical Conditioning (DOGS) Observational learning (Bobo doll) Forgetting curve Stages of death (denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance) Collective unconscious (associated with Freud) Infant attachment styles 4 Goals of psychology? What is a double bind experiment? Psychoanalysis- a system of viewing the individual as the product of unconscious forces Cognitive approach- emphasizing how humans use mental processes to handle problems or develop certain personality characteristics Sociocultural approach – behavior viewed as strongly influenced by the rules and expectations of specific social groups or cultures Which variable changes as the result changes? Which variable does experimenter manipulate? 1. 2. Human Brain Between the hind and forebrain, coordinates simple movements with sensory information (Midbrain) Portion of the lower brain that functions primarily as a central relay station for incoming and outgoing messages from the body to the brain and the brain to the body (Thalamus) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Portion of the lower brain that coordinates and organizes bodily movements for balance and accuracy (Cerebellum) Controls blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing (Medulla) Top part of the spinal cord, controls basic biological functions that keep us alive (Hindbrain) Connects the hindbrain with the mid and forebrain (Pons) Controls what we think of as thought and reason (Forebrain) Portion of the lower brain that regulates basic needs (hunger, thirst) and emotions such as pleasure, fear, rage, and sexuality (Hypothalamus) 2 arms surrounding the thalamus, important in how we process & perceive memory and emotion (Amygdala & Hippocampus) (Hippocampus, Forebrain, Hindbrain, Cerebellum, Midbrain, Thalamus, Medulla, Pons, Hypothalamus) What is a neuron? Step 4: In the Brain Trichromatic theory -Theory of color vision that holds that all color perception derives from three different color receptors in the retina Opponent-process theory - Theory of color vision that holds that three sets of color receptors respond in an either/or fashion to determine the color you experience Colorblindness -Partial or total inability to perceive hues. Trichromats -People who have normal color vision Monochromats -People who are totally color blind Dichromats - People who are blind to either red-green or yellow-blue