Lecture: Physical Geography of Russia and the Republics
advertisement

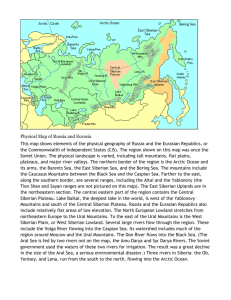
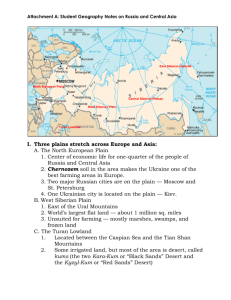
Russia and the Republics PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY Landforms and Resources Russia and the Republics take up a huge land area Russia is the largest country in the world 3 times the land area of the US Spreads across the continents of Asia and Europe West of the Ural Mountains = Europe East of the Ural Mountains = Asia Crosses 11 timezones Nearly 1/6th of the earth’s land surface Divided into the Northern European Plain, the West Siberian Plain, the Central Siberian Plateau, and the Russia Far East Former Soviet Republics (15) – all part of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) 1922 – 1991 Armenia; Azerbaijan; Belarus; Estonia; Georgia; Kazakhstan; Kyrgyzstan; Latvia; Lithuania; Moldova; Russia; Tajikistan; Turkmenistan; Ukraine; Uzbekistan Northern European Plain Stretches for 1000 miles from western border of Russia to the Ural Mountains Because of the fertile soil in the region, this is a major agricultural area 75% of the region’s 290 million people live in this plain 3 of the area’s largest cities are in this region: Moscow, Russia’s capital; St. Petersburg, and Kiev, the capital of the Ukraine Label Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova (page 338) West Siberian Plain The Ural Mountains separate the Northern European and West Siberian plains Some geographers say the Ural Mountains separate Europe and Asia Others consider Europe and Asia to be one continent called Eurasia Central Siberian Plateau and the Far East An area of high plateaus, mountains, and uplands The Russian Far East contains volcanic ranges, peninsulas and islands Lena River Kamchatka Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky a city in the Russian Kamchatka Peninsula Kamchatka Salmon Kuril Island Southern Landforms The Caucasus Mountains run between the Black and Caspian Seas and form the border between Russia and Transcaucasia Transcaucasia: a region that contains Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia Central Asia: the region that includes the republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan Transcaucasia and Central Asia Label Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan (page 338) Label countries of Central Asia (p 338) Rivers and Lakes Major rivers in the region include the Lena, the Yenisey, and the Volga The Volga is the longest river on the European continent and carries about 60% of Russia’s river traffic Lakes Major lakes in the region include the Aral and Caspian Seas Both are saltwater lakes The Caspian Sea is the largest inland sea in the world The Aral Sea has lost 87% of its water volume since the 1960’s Major irrigation projects have diverted water away from the rivers that feed the Aral Pesticides and fertilizers in runoff were carried by rivers and streams into the Aral Sea Killed all the native fish As water evaporated, windstorms blew chemicals onto nearby populations causing an increase in disease Label Caspian and Aral Seas Camels grazing near fishing ships abandoned after the Aral Sea dried up Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the deepest lake in the world At its deepest, it is more than a mile deep It holds 20% of the world’s freshwater Thousands of species of plants and animals live in the lake Lake Baikal, the deepest lake in the world Regional Resources Russia and the Republics have a wealth of natural resources but have struggled with how to manage them Challenge: how to transport resources over vast distances, rugged terrain, and harsh climates The area has huge reserves of coal, iron ore, and other metals It is a leading producer of oil and natural gas Russia holds 1/5th of the world’s timber One of the world’s largest producers of hydroelectric power Resource Management Many of the region’s resources are located in Siberia The part of Russia that lies on the continent of Asia Businesses find it difficult to attract workers to this area Distance decay: long distances between places make communication and transportation difficult Political and economic change in recent years has made managing resources difficult Climate and Vegetation The region is so vast that there is a wide range of climates Areas in a Siberian town of Oymyakon have reported temperatures of -95 degrees In areas of Transcaucasia, the climate is pleasant and used to be a vacation spot before ethnic conflict made travelling dangerous http://www.msn.com/en-us/news/world/10000-year-old-extinct-lion-cubsdiscovered-in-near-perfect-condition-in-siberian-permafrost/ar-BBmu4NI Transporting cargo on frozen Lake Baikal