Transforming the West
advertisement

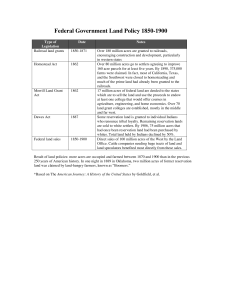
Transforming the West 1860-1900 Native Americans and the West Plains Indians – many tribes that live on the Great Plains Diversity: Some were settled farmers Others used horses to hunt buffalo Similar culture: Life revolves around extended families, cooperation, consensus Religious and harvest celebrations Native Americans and the West Threats to their way of life: Miners and settlers start moving to the plains in the 1850s Exhausted the grassland that buffalo needed Railroads hire people to kill buffalo 9 million killed! Ruins the Native way of life Native Americans and the West Conflicts with the military: After the Civil War, military troops sent West to protect new settlers Misunderstandings brutality Sand Creek – Gold rush brings 100,000 settlers, who take all the Indians’ resources Natives are starving, government won’t fulfill its treaties Leave their reservations to hunt buffalo, steal livestock Military massacres a peaceful band of Indians at Sand Creek Native Americans and the West New government policies: Government sets up new reservations, ‘persuades’ Natives to move there Fort Laramie Treaty – Sioux agree to move to South Dakota for $ and provisions Treaties are deceptive, unfair But still lots of skirmishes in the Plains Government stops signing treaties and just makes executive orders Native Americans and the West Custer’s Last Stand Sioux who refuse to sign the Fort Laramie Treaty and move - led by Sitting Bull Colonel Custer is sent to drive them out of the Black Hills to the reservation Custer is outnumbered, reckless Troops are wiped out Now people want to crush the Indian rebellion Native Americans and the West “Saving” the Indians: Some Americans are outraged at the government’s actions Helen Hunt Jackson - A Century of Dishonor Want to ‘save’ them Create schools, make them give up their customs Backfires Break up reservations and tribes, make them citizens and independent farmers Dawes Severalty Act – gives individual Indians 160 acres, taught to farm Outcome – speculators buy up all the best Indian land Leaves Native Americans worse off Native Americans and the West The End of Resistance: Sioux are starving in the 1880s Turn to a prophet – Wovoka – who sees the apocalypse coming Tells Indians to return to traditional ways The Ghost Dance Military is afraid of this movement Sitting Bull is killed Massacre at Wounded Knee Settling the West The Railroads Pacific Railroad Act 1862 Transcontinental railroad is built Chinese, Irish workers build it Benefits of the railroads: Can fight Indians more easily Railroad companies sell their land Settlers from the East, immigrants Encourage them to grow cash crops – wheat, corn, cotton Homesteads Homestead Act of 1862 160 free acres if you farm the land for 5 years 400,000 people move But railroads, speculators take the best land In dry plains, you need more than 160 acres to survive Timber Culture Act – 160 more acres if you plant trees Desert Land Act – 640 acres if you irrigate it Difficult psychological adjustment New Farms, New Markets Improvements in farming: Cash crop farming: New strains of wheat and corn Steel plows, better planters, other tools Barbed wire Increased demand for crops Dangerous – if you only sell one crop, you are dependent on the railroads, the market Unpredictable weather New States & Societies New states: Kansas, Nevada, Nebraska, Colorado, etc. Socially conservative, but allow women to vote Mormonism spreads: Communities in conflict with non-Mormons Mormons try to be independent, but… U.S. v. Reynolds Government forces them to integrate into society Mexican Americans in the Southwest Discrimination, exclusion Most are left in poverty Exploiting the Land Mining Gold discovered throughout the West Comstock Lode in Nevada Starts with individuals trying to get rich Need expensive equipment, huge investments to mine it Boom-and-bust towns Environmental costs Cowboys and the cattle frontier Open-range cattle boom – 1860s and 70s Ranchers can make fortunes raising cattle in Texas, driving them north to ship to the east Cities grow where the railroads are Early periods of violence Not as violent as movies like to show Cowboys don’t see the $$ Short-lived Railroads end long-range Cattle prices decline Barbed wire drives The Oklahoma Land Rush, 1889 Settlers are pushing for land in Indian Territory (now called Oklahoma) Government People rush in to claim homesteads Curtis Act makes 2 million acres available – 1898 – dissolves the Indian territory The myth of land Americans want it! But later they will pay… The Myth of the West The ‘Myth’ of the West The Turner Thesis Frederick Jackson Turner’s lecture Says that the frontier is closed Idealized view of the West Popular culture spreads this image – the ‘frontier’ is a place of adventure, romance, escape Wild West Shows Writers The National Parks Movement People are awed by the beauty of the West Some call for saving the land Regulation of water, public lands Doesn’t happen Yellowstone National Park – 1872 – to preserve it from settlement the conservation movement – led by John Muir and the Sierra Club Starts