The South and West Transformed 1865
advertisement

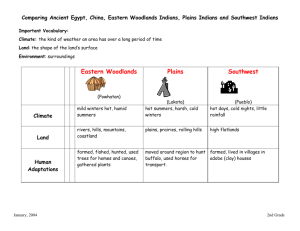
Chapter 6 The South Remained largely agricultural and poor after the Civil War Farming became more diversified; grain, tobacco, and fruit crops (small farms replaced large plantations) To combat economic isolation, southerners lobbied the federal government for more rail building Sustained economic development requires resources, labor, and capital investment. (industry is a three legged stool. Public education was limited in the South, there were few technical and engineering schools Cash Crop – products grown not for there use but sold for cash Cotton remained a staple crop after the Civil War and during the war many European textile factories found other sources (depressed prices) Farmers’ Alliance – farmers in Texas in the 1870 began to organize as a group for lower prices for supplies (lobbied for lower transport cost and loan rates) Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth amendments gave many gains that were stifled by the courts. Voting, Education, businesses, purchasing power, farmer groups (Federal Laws) Ku Klux Klan used terror and violence Civil Rights Act of 1875 – congress guaranteed black patrons the right to ride trains and use public facilities Supreme Court ruled that these were local issues The federal government forced Native Americans west past the Mississippi to lands they were to have FOREVER during the 1840’s. Westward expansion would soon dissolved this promise “Great American Desert” Native Americans had many diverse cultures influenced by geography • • • • Pacific North west – fish and forests South hunter-gatherers South West – arid lands Pueblo people Plains – buffalo (Natives saw themselves as part of nature) President Jackson moved the Cherokees off their land in Georgia and onto the Great Plains (Whites were discouraged form contact with the Native Americans) Gold and Silver Reservations – specific areas set aside by the government for Indians’ use Sand Creek Massacre – 1884 incident in which Colorado militia killed a camp of Cheyenne and Arapaho Indians (video) Expansion west by whites time again broke promises made by the federal government, the United States Peace Commission concluded that lasting peace would only come when the Indians settled on farms and “became whites.” Red River War – U.S. failed to fulfill the “Treaty of Medicine Lodge,” and keep white buffalo hunters off Indian land Sitting Bull – famed fighter, trained holy man, first ever chief of the seven bands Battle of the Little Big Horn – led by Crazy Horse, Custer and all of his men were killed Chief Joseph – led a group of refugees to Canada 1,300 miles Wounded Knee – sealed the Indians demise after being weakened more than 100 men women and children were killed Assimilated – to be absorbed into the main culture of a society Dawes General Allotment Act – replaced the reservation system with an allotment system. Each family was given 160-acre farmstead