Hemispheres, Sensory and Motor Cortexes, Split Brain and Plasticity
advertisement

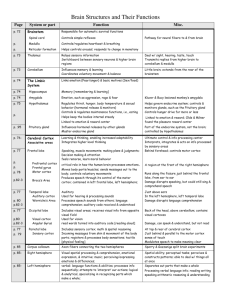
HEMISPHERES, SENSORY AND MOTOR CORTEXES, SPLIT BRAIN, PLASTICITY, ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 2 Motor Cortex Motor Cortex – An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements Sends messages from brain to body Right Motor Cortex controls movement of left side of the body Page 77 Motor Cortex Motor Strip Dominance For each of the following answer left, right, or both. 1.With which hand do you write? 2.With which hand do you throw a ball? 3.Which hand do you use to hold scissors? 4. When holding a baseball bat, which hand is on top? 5.Which hand deals out playing cards? Motor Strip Dominance 6.When you cross your arms, which arm is usually on top? 7.When you cross your leg, which leg is usually on top? 8. When putting on a pair of pants, which leg goes into the pants first? 9. When putting on a jacket or sweater, which arm goes into the sleeve first? 10.Which hand is on top when you clap? High number of right answers means that you are left strip dominant. Sensory Cortex Sensory Cortex – An area at the front of the parietal lobe that registers and processes body sensations. Receives messages from the body to the brain Right Sensory Cortex receives sensory information from the left side of the body Parts of the sensory cortex receive senses from various body parts – the more sensitive, the more cortex area devoted to it. Sensory Cortex Phantom Limb Phantom Limb – feeling sensations or movements coming from a limb that has been amputated. Ex. when touching the face of someone whose fingers have been amputated, the person also reports a sensation in their nonexistent fingers. WHY? Sensations may come from a body image stored in the brain Re: p. 83 2nd paragraph Line 9 Phantom Limb Video (till last1:00) Brain Plasticity Plasticity – the brains capacity for modification Neural tissue can reorganize as a response to damage Ex. Morgan Madson and Volleyball Ex. Child has a right hemispherectomy, now the functions of the left brain have made new connections to perform tasks the right brain use to perform. Picture on p. 83 - Brain Plasticity - the story of Jody Girl Living With Half Her Brain Children have more plasticity than adults Hemispheres of the Brain Contralateral Control – left hemisphere controls right side of the body, and the right hemisphere controls the left side of the body. 2 Students complete CD ROM Activity while class completes Hemispheric Dominance Inventory Hemispheres of the Brain Left Hemisphere Receives sensory messages and controls motor functions of the right half of the body Research indicates the left hemisphere is more active during logic and sequential tasks and language Hemispheres of the Brain The cerebral cortex can be divided into two hemispheres Corpus Callosum – Nerves that connect the two hemispheres. Split Brain Split brain – condition in which the corpus collosum is severed. Purpose is to reduce seizures in patients with uncontrollable epilepsy Roger Sperry – architect in split brain surgery. (Began by splitting the brains of cats and monkeys and found no serious effects) Split brain patients have “two separate minds” – in textbook, pg. 85 – Severed Corpus Callosum (ctshad) Stop at phone..left does not see it…right does..cannot say it but can write it with left hand. Psychquest demo on splitbrain CD ROM Activity with word flashing Association Areas Association Areas- Any area of the cerebral cortex that does not control muscle movements or receive sensory information – Rather, these areas involve higher mental functions (learning, remembering, speaking, and thinking) Association Areas Association Areas Aphasia – impaired use of language. RE: bottom of p80 Broca’s Area – speech production Damage to this area may disable muscle movements needed for speech Broca's aphasia - Sarah Scott - teenage stroke MNEMONIC :BROKEN CD PLAYER NO LONGER PRODUCES SOUND Wernicke’s Area – language comprehension Damage to this area may disable one’s ability to understand language Wernicke's and Broca's Aphasia Endocrine System Endocrine System – The body’s “slow” communication system. This system is made up of numerous glands that secrete various chemicals, called hormones, throughout the body. These hormones affect organs, muscles and other glands in the body The Endocrine System: How it Works Endocrine System (:35) Endocrine System Hypothalamus – control center of the endocrine system. (specifically controls the adrenal glands) Types of Glands Pituitary Glands (aka “master gland”)– a pea sized structure located at the base of the brain. The pituitary glands regulate and control other glands. Releases growth hormone. Adrenal Glands – produce adrenaline (also called epinephrine), regulates the heart rate and blood pressure. Helps trigger the fight or flight response. Endocrine System Pancreas – regulates levels of sugar in the blood by secreting insulin Thyroid – located in the neck, this gland regulates metabolism Ovaries – produce female sex hormones – estrogen Testes – produce male sex hormones – testosterone Neuroscience review Psychology Rap VIDEO- Crash course The chemical brainm (last 3 mins.) PDF File: Recent Brain Discoveries If Time, Brain worksheet