Special Tests For the Lower Leg and Ankle
advertisement

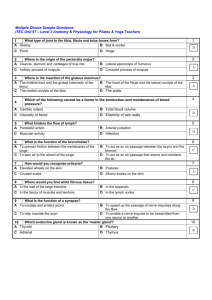
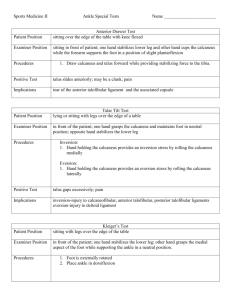
Mike Boisselle Geared Towards Athletic Training Students Special Tests Specific procedures applied to determine the presence of pathomechanics Unique to each structure, joint, or body part Bilateral Comparison Keep In Mind While Performing Special Tests Anatomy Isolate Stabilize Bilateral comparison Patient position Positive signs Medical Emergencies Homan’s Sign •Patient is in supine position, in knee extension •Dorsiflex patient and squeeze gastroc •Positive sign-pain •Pain indicating thrombophlebitis Anterior Drawer Test Patient seated legs over table Stabilize distal tibia and fibula Apply anterior force to calcaneus Positive test: pain and/or laxity Indicating anterior talofibular ligament sprain Talar Tilt (Inversion) Patient sitting with legs over table Stabilize distal tibia, and grasp talus Tilt the talus into adduction Pain and/or laxity indicates calcaneofibular ligament damage Talar Tilt (Eversion) Patient sitting with legs over table Stabilize distal tibia, and grasp calcaneus Tilt the calcaneus into abduction Pain and/or laxity indicates deltoid ligament damage Thompson Test Patient prone on table with heels off edge Examiner squeezes muscle belly of gastrocnemius-soleus complex Normal response is slight plantar flexion Absence of plantar flexion indicates Achilles tendon rupture Tap or Percussion Test Patient sitting with feet over tables edge Passively dorsiflex patient Apply a firm tap to patients heel Pain is indicative of possible fracture Feiss Line Patient seated legs over table Draw a dot on medial malleolus, and first MTP joint Draw a line connecting dots Observe the navicular tubercle Weight bearing and non weight bearing Feiss Line (continued) Non weight bearing navicular drop Indicates congenital pes planus Weight bearing navicular drop Indicates functional pes planus Interdigital Neuroma Test Patient seated with legs over table Squeeze the metatarsal heads together 3 minutes Pain, tingling, numbness in the foot, toe or ankle Positive test indicating interdigital neuroma Compression Test Patient sitting feet just over edge Compress the tibia and fibula Start away from pain, work towards Pain may indicate fracture That cannot be right… Kleiger’s Test Patient sitting at edge of table Stabilize distal tibia and fibula Grasp calcaneus Dorsiflex and externally rotate Pain or laxity indicates syndesmosis sprain Tinel’s Sign Patient sits with feet at edge of table Tap posterior tibial nerve on medial side Positive test- radiating pain and tingling Indicative of tarsal tunnel syndrome