Forensic Anthropology
Bones of the Leg
Skeletal anatomy of the leg
Comprised of 4 bones
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Patella
Useful for
age/growth
Sex determination
stature determination
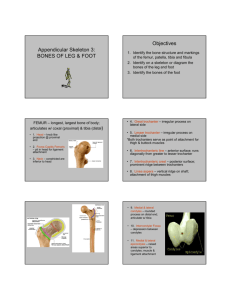
THE FEMUR
Largest, heaviest bone of the body
Ball shaped head
Articulates with innominate, tibia (does NOT
form a straight line with tibia in anatomical
position), patella
Shaft has circular cross section
THE FEMUR – what to know
Proximally
Head
Fovea capitus
Anatomical neck
Greater and lesser
trochanter
Intertrochanteric crest
Linea aspera
Distally
Lateral condyle
Lateral epicondyle
Medial epicondyle
Medial condyle
Intercondylar fossa
Patellar articular surface
THE FEMUR – L from R
Orient
head medially, greater trochanter
Intercondylar
Larger
fossa posterior
condyle is medial
The tibia - description
Second
largest bone in the body
Hinge joint – greatest weight bearing
Articulations:
• Proximal – femur at horizontal platform AND fibula
• Distal – fibula AND talus
• Note there is NO articulation with the patella
Shape
= triangular shaft
• Sharpest angle anterior
• Malleolus at distal end
The tibia – What to know
Proximal end:
Intercondylar eminence
Medial condyle
Lateral condyle
Tibial tuberosity
Fibular facet of tibia
Popliteal line
Interosseous crest
Anterior crest
Distal end:
Fibular notch of tibia
Articular surface for
talus
Medial malleolus
Tibia – Right from left
Orient
plateau superiorly
Make
sure tibial tuberosity is anterior
Medial malleolus is medial
Interosseous
crest points toward fibula
Growth and the humerus
Fusion
ages
♀14-16/ ♂15-18 distal epiphysis
♀13-17/ ♂15-19 proximal epiphysis
Also age related changes in bone density
associated with elderly
The fibula - description
Lateral
to the tibia, most slender long bone
Makes
up the ‘outside’ of the ankle
The fibula
Shaft
– triangular X-section
Flat head at top
Distal end composed largely of lateral malleolus
Articulations
• Proximal – with tibia at fibular facet just below lateral
condyle
• Distal – passes through fibular notch of tibia to
articulate with talus
The fibula – What to know
Proximal End:
Head
Styloid process
Facet for tibia
Interosseous crest
Distal End:
Lateral malleolus
Malleolar facet for
talus
Malleolar fossa
fibula – Right from left
Orient
head superior
Lateral
malleolus is lateral, tip points
posteriorly (when looking at lateral side)
Styloid
process and interosseous crest
Bones of the
hand
Carpal bones
1. scaphoid
2. lunate
3. triquetrum
4. pisiform
5. trapezium
6. trapezoid
7. capitate
8. hamate
Metacarpal bones
9. I
10. II
11. III
12. IV
13. V
Phalanges
proximal 14
middle 15
distal 16
Sorting metatarsals
Longer,
thinner, and more curved than MC
MT1: thickest
MT2: Longest, slight process
Triangular with off-set lateral facet
MT3:
triangular with continuous lateral facet
MT4: base rectangular
MT5: long, lateral process
Bones of the Foot
12. Fifth metatarsal
1. Calcaneus
13. Proximal phalanx of
2. Talus
great toe
3. Navicular
14. Distal phalanx of
4. Medial cuneiform
great toe
5. Intermediate
15. Proximal phalanx of
cuneiform
second toe
6. Lateral cuneiform
16. Middle phalanx of
7. Cuboid
second toe
8. First metatarsal
17. Distal phalanx of
9. Second metatarsal
second toe
10. Third metatarsal
11. Fourth metatarsal
Sorting metacarpals
MC1:
shortest, thickest
MC2:
longest, 2 processes at base
M2 – M5 decrease in size successively
MC3:
1 processes at base
MC4: no processes, facets on both sides
of base
MC5: short, no processes, facet on only
1 side of base
Manual vs pedal phalanges
Manual
phalanges are longer
Flattened in the middle (oval crosssection)
Narrower top to bottom
Pedal
phalanges are ‘slim-waisted’ in the
middle
Circular cross-section
Narrower side to side
Sorting phalanges
Proximal
phalanges: cup-shaped proximal
end (art. w/ MC head)
Medial
phalanges: double-faceted
proximal end
Distal
phalanges: flat, ‘fingernail shaped’
distal end