Federalists and Anti
advertisement

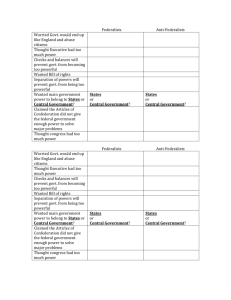
Federalists and Anti-Federalists In what ways did the Constitution seek to erect barriers against “mobocracy?” “Mobocracy”- the rule/domination by the masses • federal judges were appointed for life • the president was to be indirectly elected by the Electoral College • senators were to be chosen indirectly by state legislatures What democratic elements existed in the Constitution? • It was based on two main principles of republicanism– government was based on the consent of the governed – Limited government Ratification • Ratification- approval • Ratify- to approve • Ratification of the Constitution required the approval of 9 states • Special ratifying conventions (meetings) were held in each state • Federalists supported ratification • Anti-Federalists opposed it The Great Debate in the States • Special elections held for members of ratifying conventions – Candidates—federalist or antifederalist—were elected based on whether they were for or were against Constitution • Four small states quickly accepted Constitution • Pennsylvania was first large state to ratify • Massachusetts presented challenges, including demand for bill of rights Federalists • Wanted a strong federal government (thus the Constitution) • Generally lived along the seaboard • Generally wealthier, more educated, and better organized than the Anti-Federalists. • Led by James Madison, Alexander Hamilton and John Jay – Wrote The Federalist Papers In Federalist No.10 and Federalist No. 51, Madison argued that a strong national government and the Constitution’s system of checks and balances would strengthen liberty. In Federalist No. 78, Hamilton wrote of the importance of a judicial branch to protect liberty. A copy of The Federalist signed by George Washington Anti-Federalists • Sam Adams, Patrick Henry, John Hancock, Richard Henry Lee • Generally states’ rights proponents, backcountry people, small farmers • Generally the poorest classes • Feared that a strong federal government would take away their liberties • Believed a bill of rights was necessary Federalists Anti-Federalists • Competing interests in a large republic would ensure that no one group would be able to ignore the rights of everyone else. • A strong gov’t is needed for protection from foreign nations • A strong gov’t is needed to pay the nation’s debts and provide a stable currency • Republican gov’t works better in smaller areas • Government should be close to the people • Citizens rights should be listed • Vague wording might lead to an abuse of power Why do the Federalists win? • They had a very effective and well-organized campaign • George Washington and Ben Franklin (most respected men in America) supported the Constitution • The Federalist Papers were very persuasive • The promise to add a bill of rights swayed some Anti-Federalists Map 9-4 p174 • June 1788 the Constitution was officially adopted Table 9-3 p175 Congress convened in New York’s Federal Hall on March 4, 1789 to: • Elect a first president (George Washington) and vice president (John Adams). • Add a Bill of Rights. The last two states, Rhode Island and North Carolina, now reconsidered earlier rejections and ratified as well, bringing the total to 13 states. • He used Virginia’s Bill of Rights as a model. James Madison was assigned to create a Bill of Rights. • Madison avoided any statements about equality that might offend the slave states. • Ten amendments guaranteed individual freedoms. • To prevent future abuse or limitations on freedom, any unmentioned rights were retained by the people. The Bill of Rights The Bill of Rights